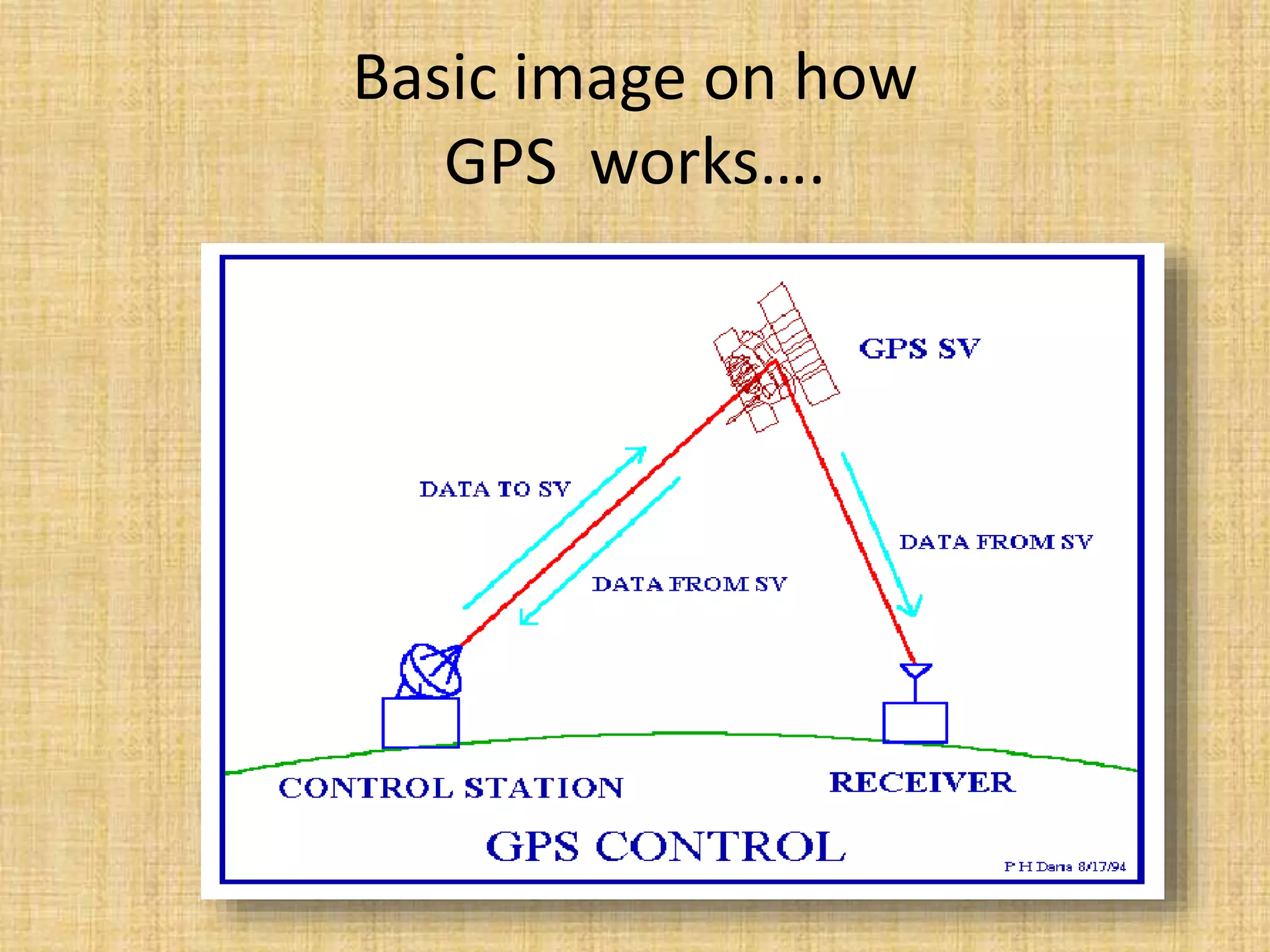
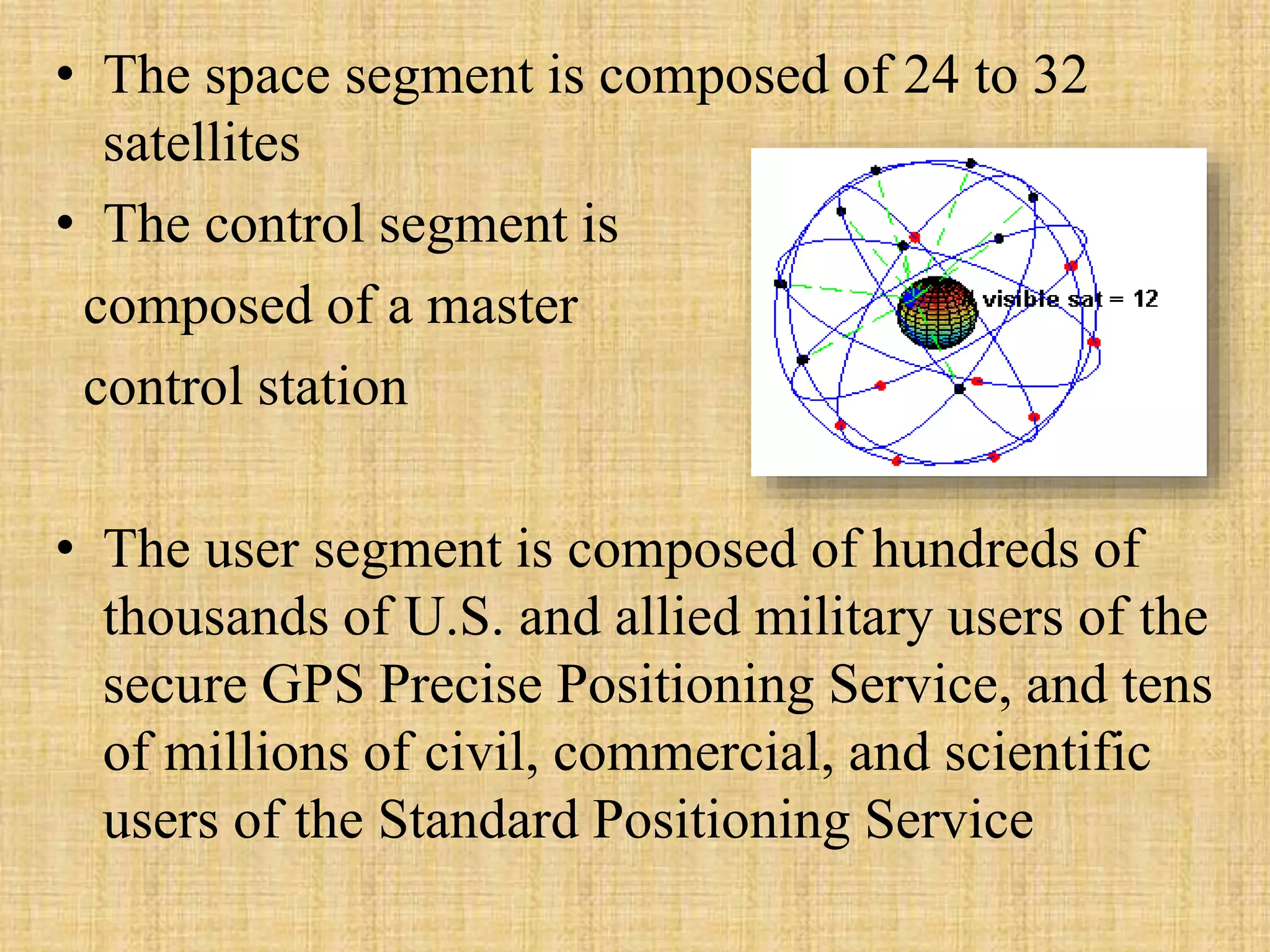
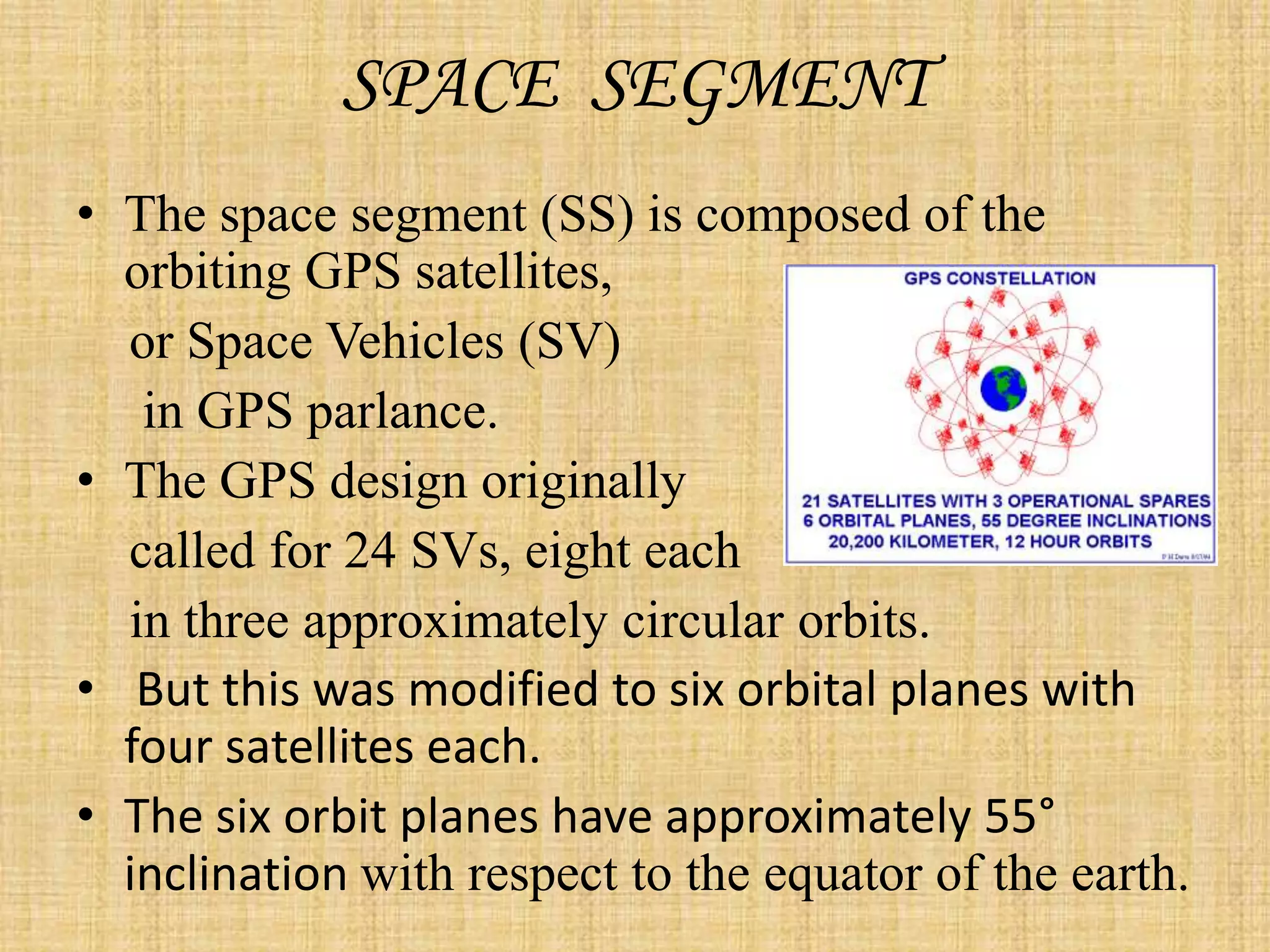
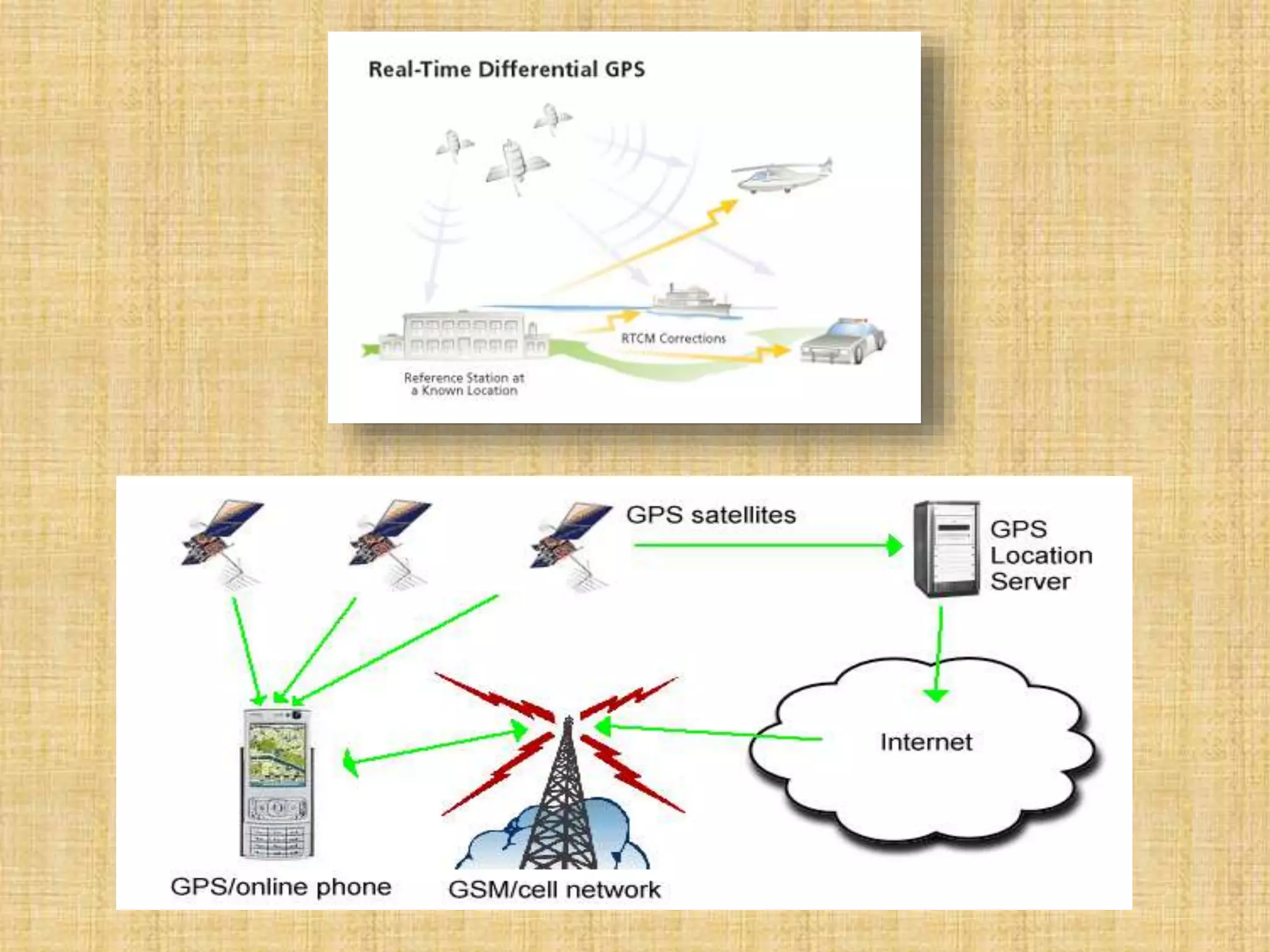
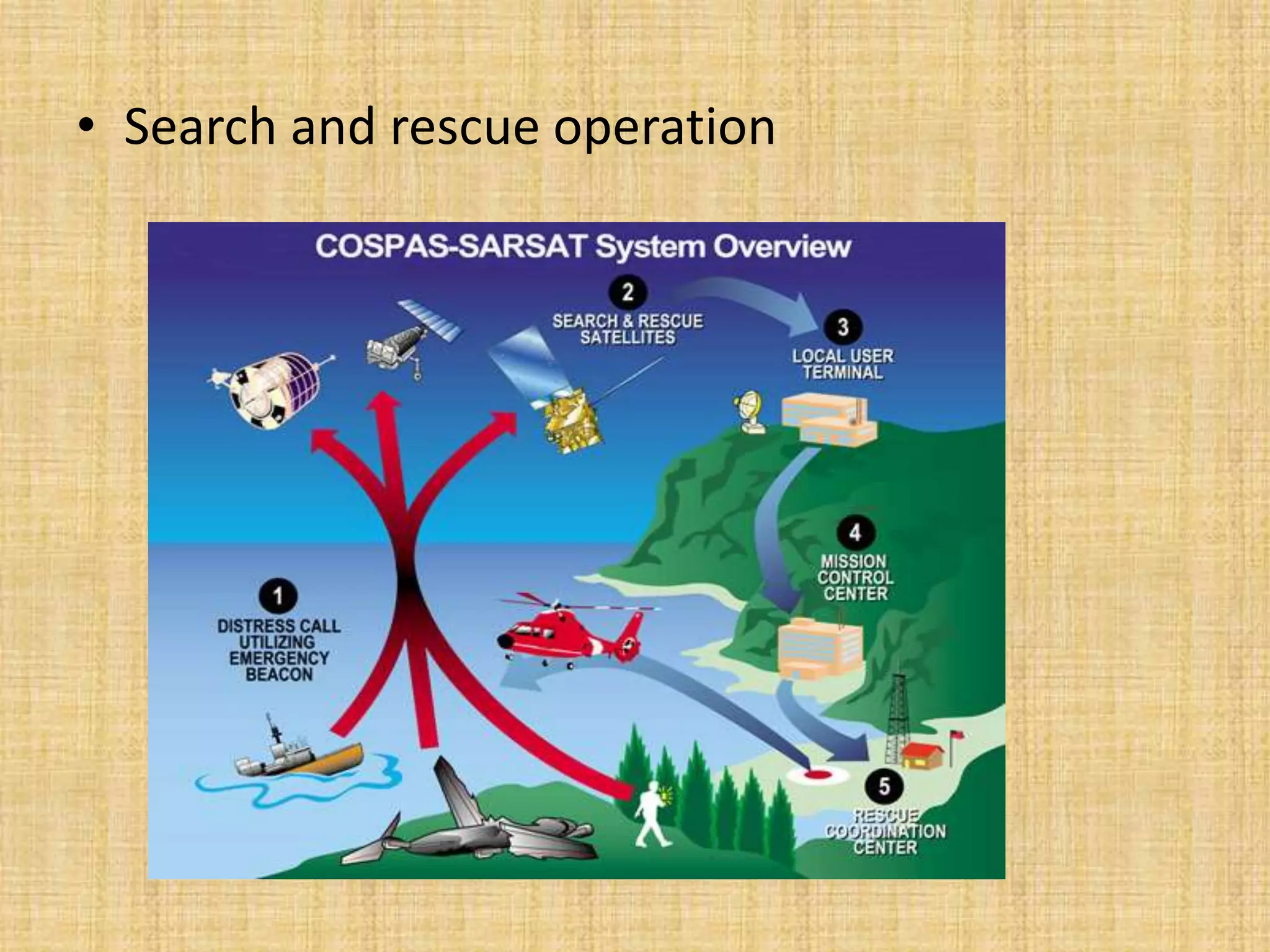
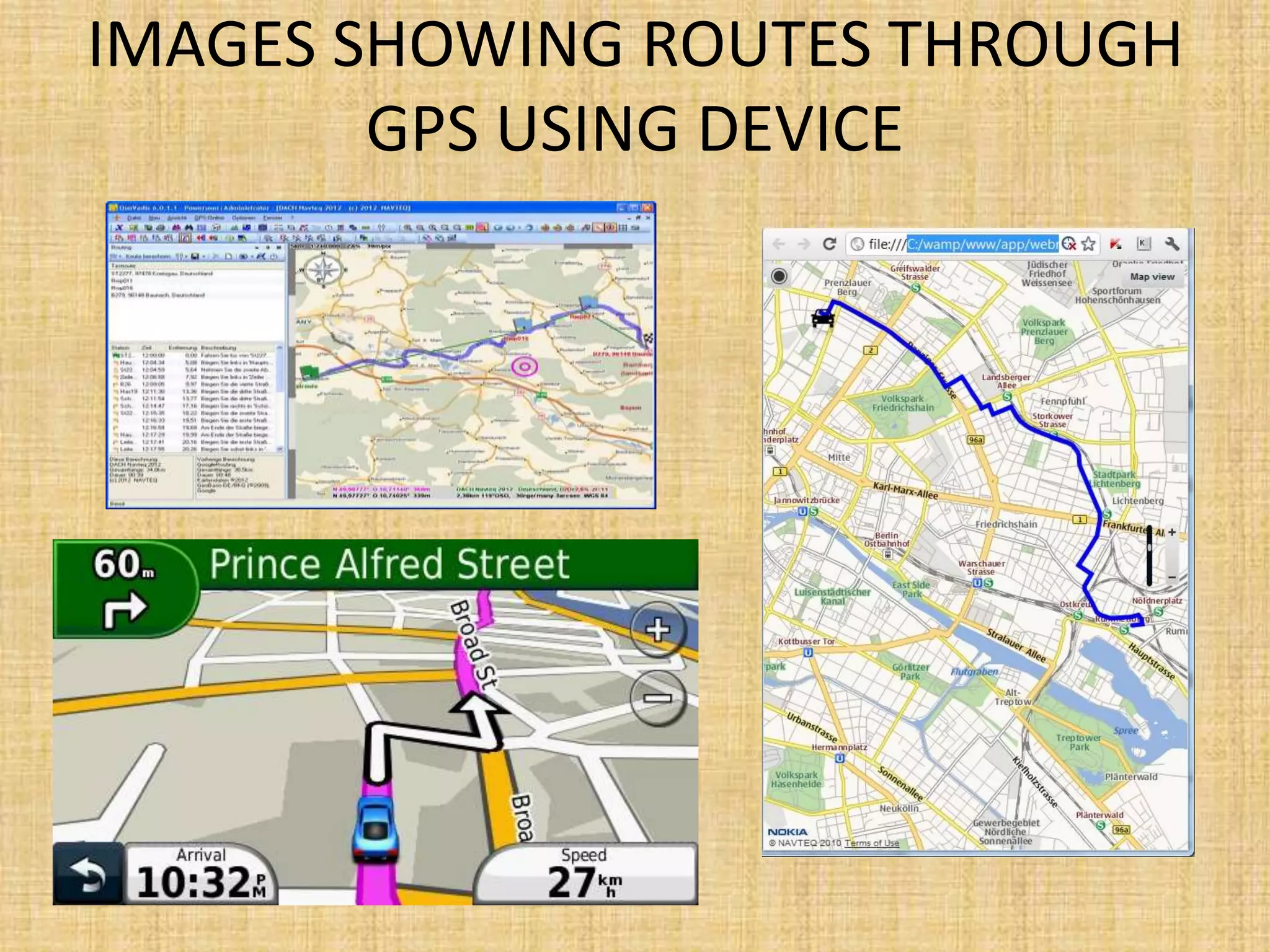
The Global Positioning System (GPS) is a satellite-based navigation system that provides location and time information to users around the world. It was developed by the U.S. Department of Defense in 1973 to overcome limitations of previous navigation systems. GPS consists of three segments - a space segment of 24-32 satellites, a control segment of ground stations that monitor the satellites, and a user segment of GPS receivers. GPS enables a wide range of military and civilian applications including navigation, mapping, timing, and tracking.