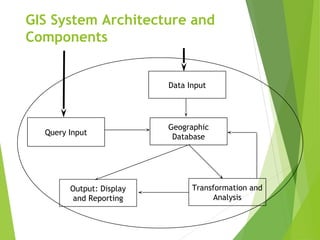
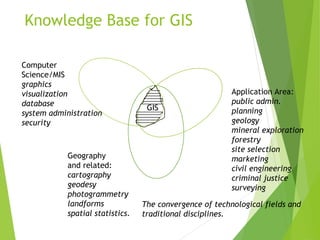
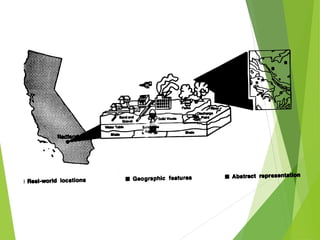
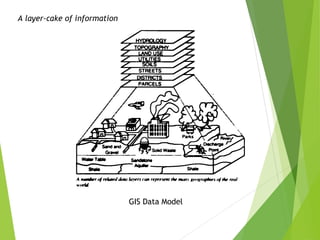
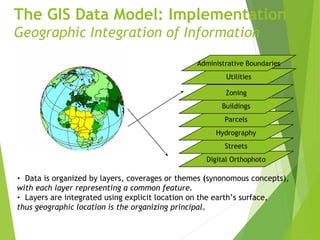
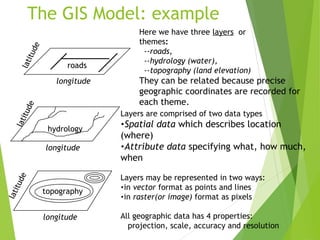
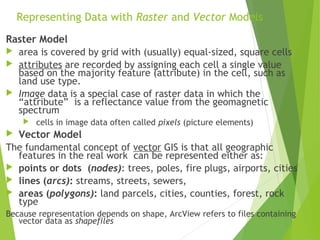
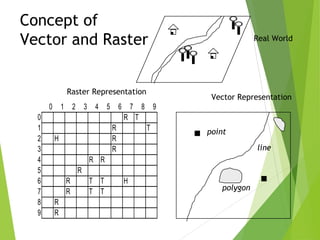
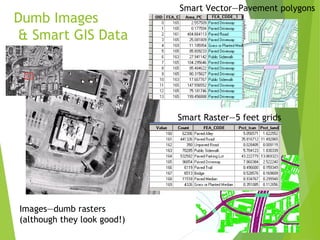
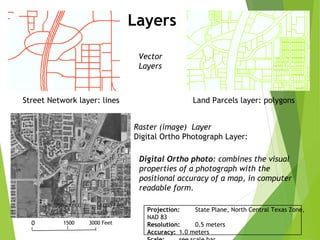
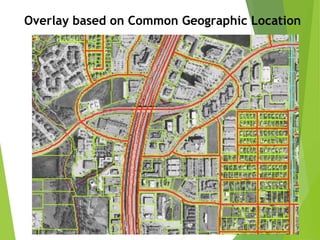
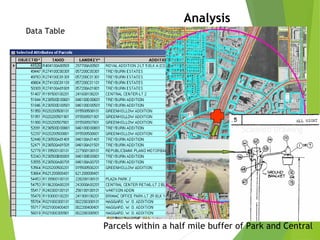
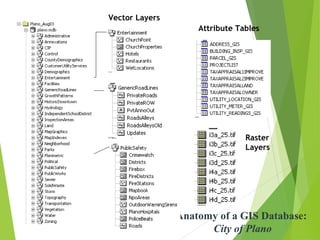
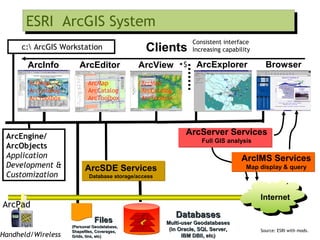
The document outlines the fundamentals of Geographic Information Systems (GIS), emphasizing the various components including geographic data, technologies, and applications in different sectors such as government, business, and science. It discusses GIS system architecture, data models, software solutions, and the importance of geographic information in decision-making. The document also highlights the differences between GIS and related systems, showcasing practical applications in urban planning, public safety, resource management, and more.