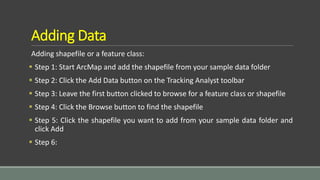
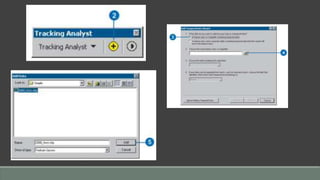
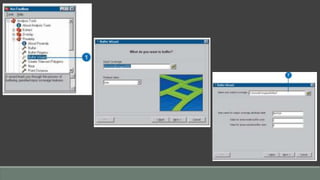
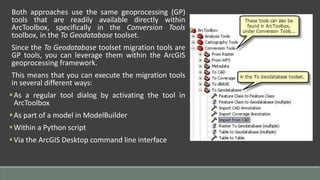
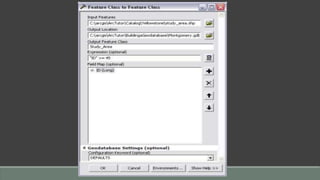
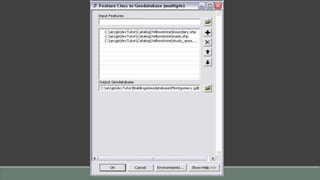
The document provides steps for basic tasks in ArcGIS including adding data, adding symbology, creating buffers, and migrating data between a shapefile and geodatabase. It outlines 7 steps for adding shapefiles or feature classes to a map, 10 steps for applying symbology, and describes how to use buffer tools and wizards to create buffers around selected features at a specified distance. It also explains how to import and export data between a shapefile and geodatabase using geoprocessing tools.