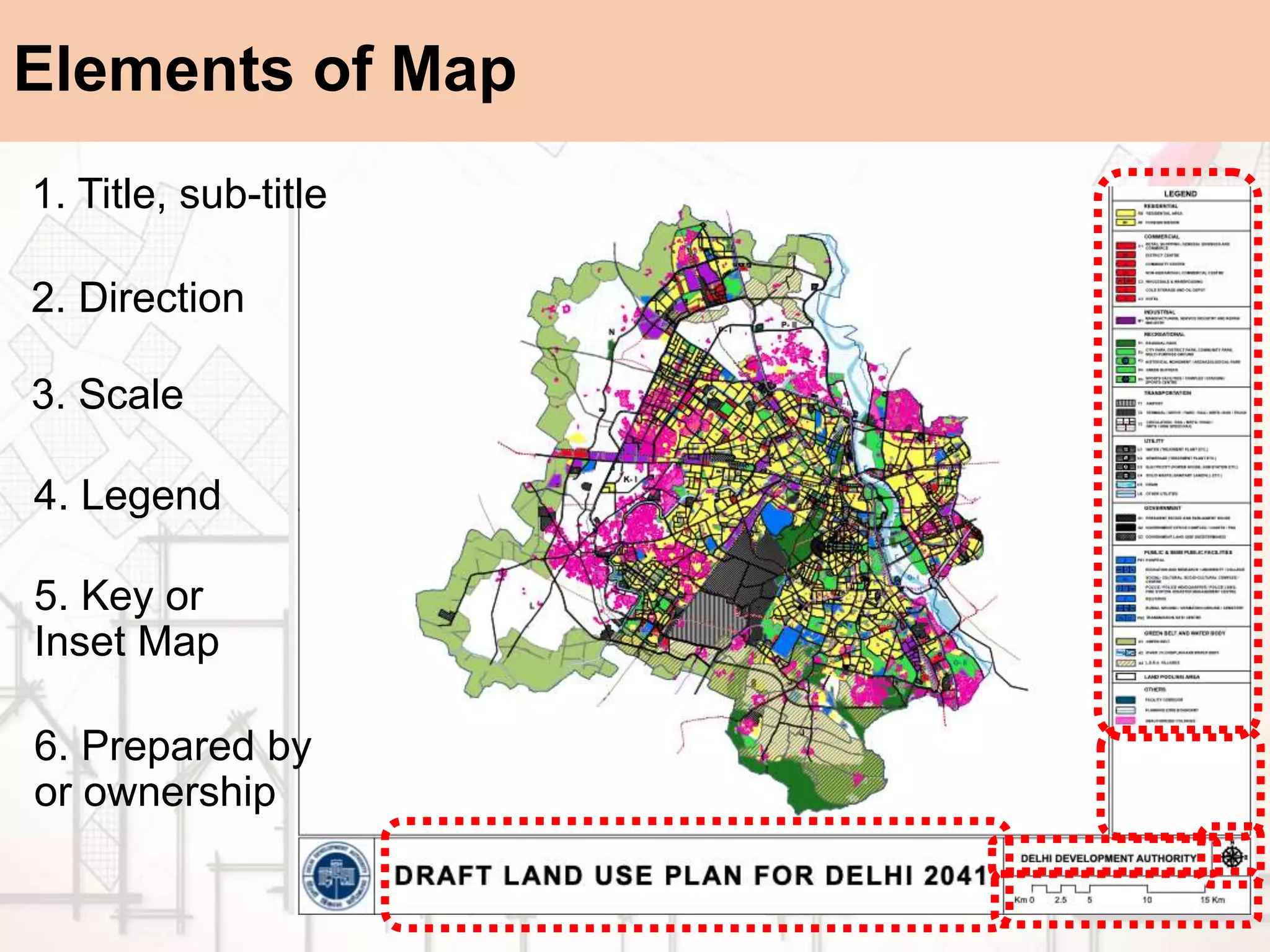
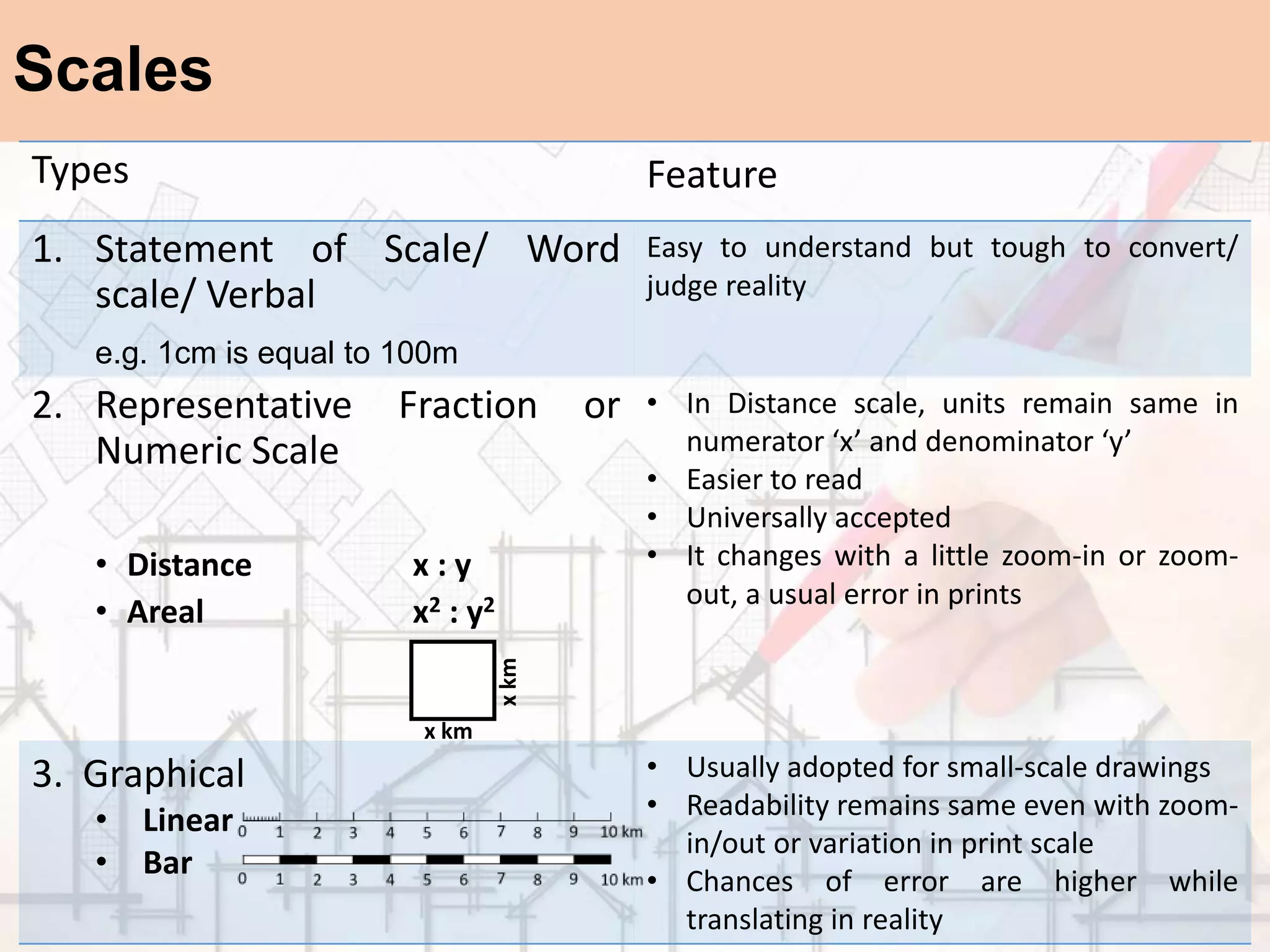
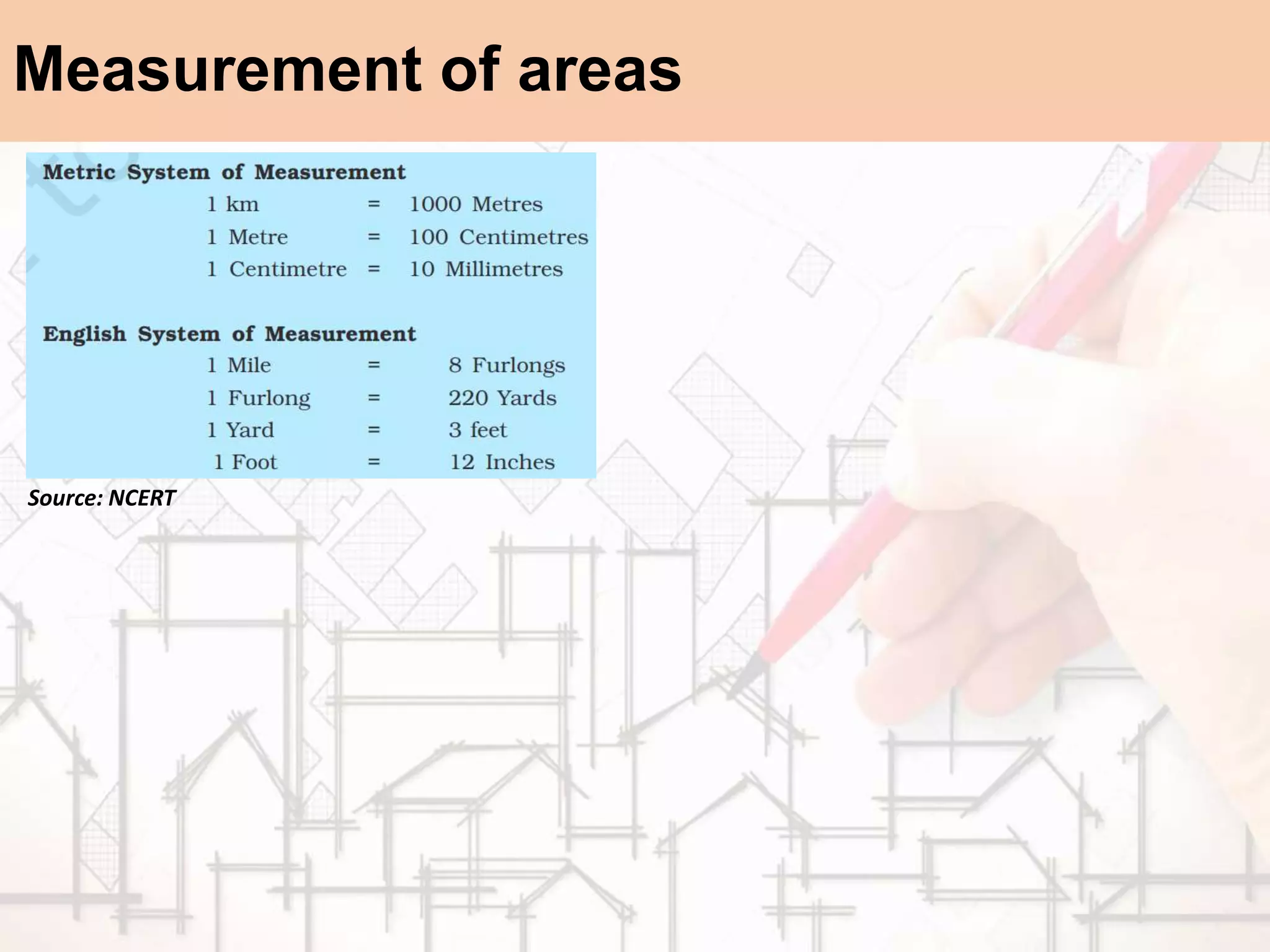
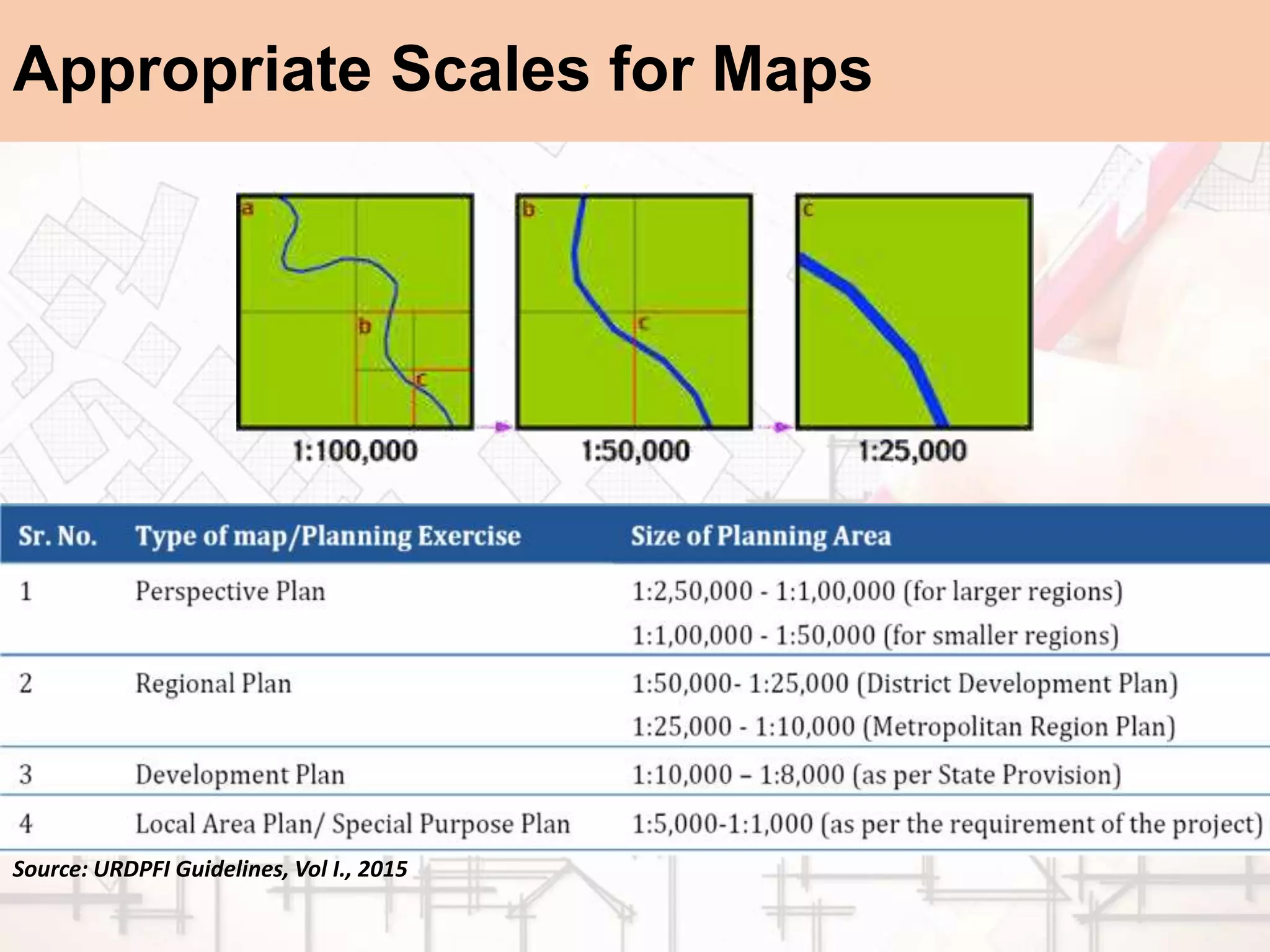
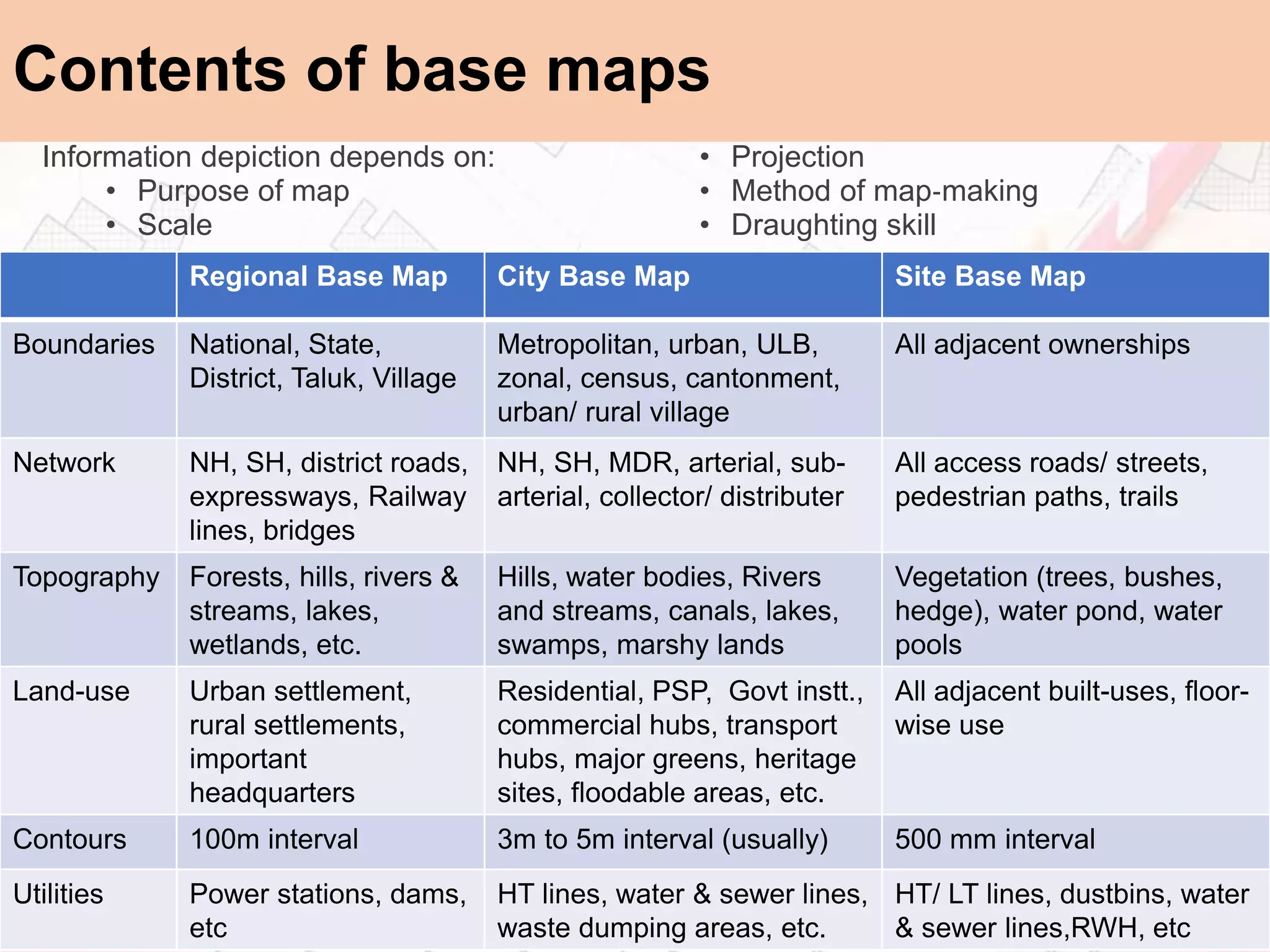
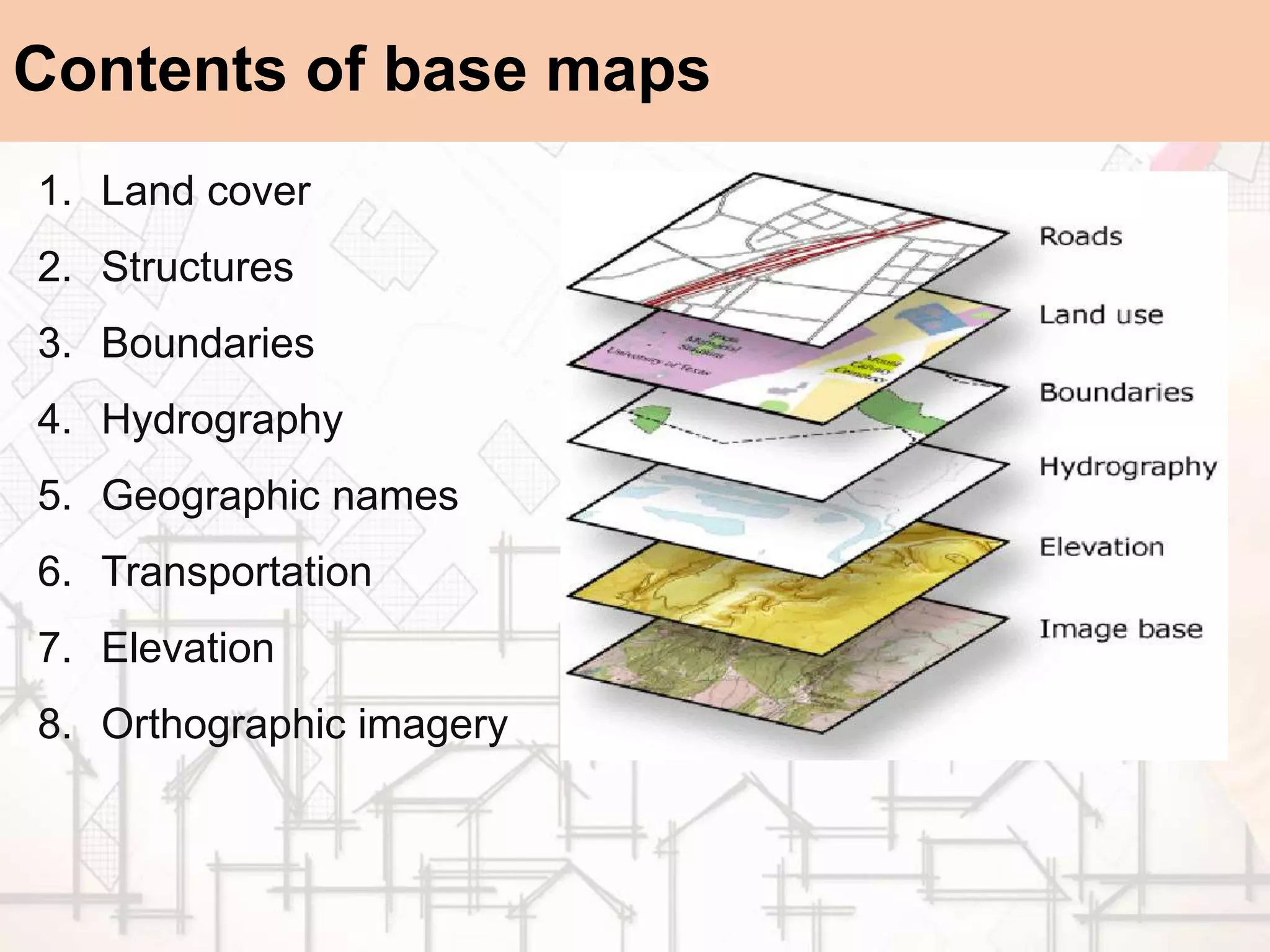
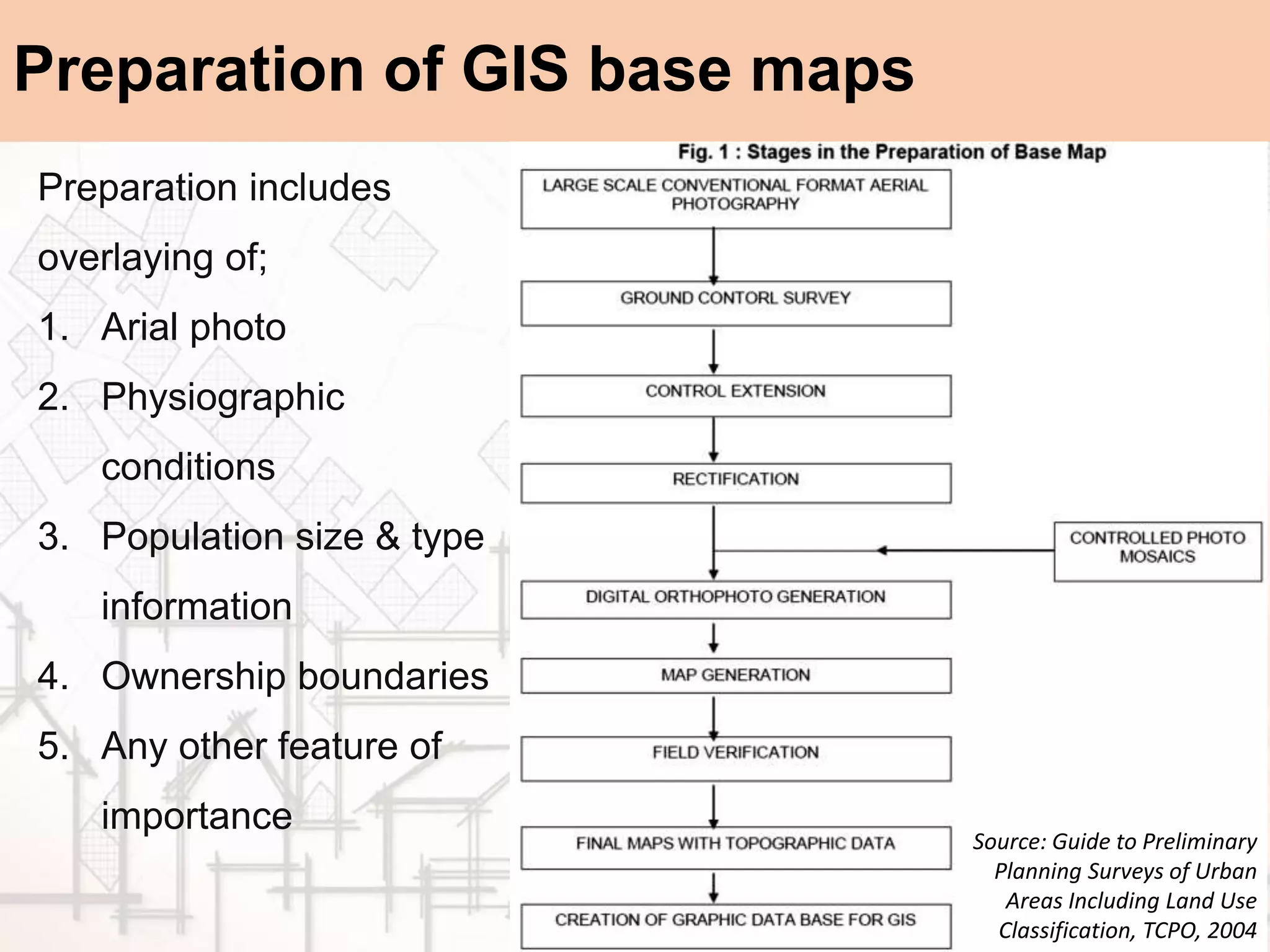
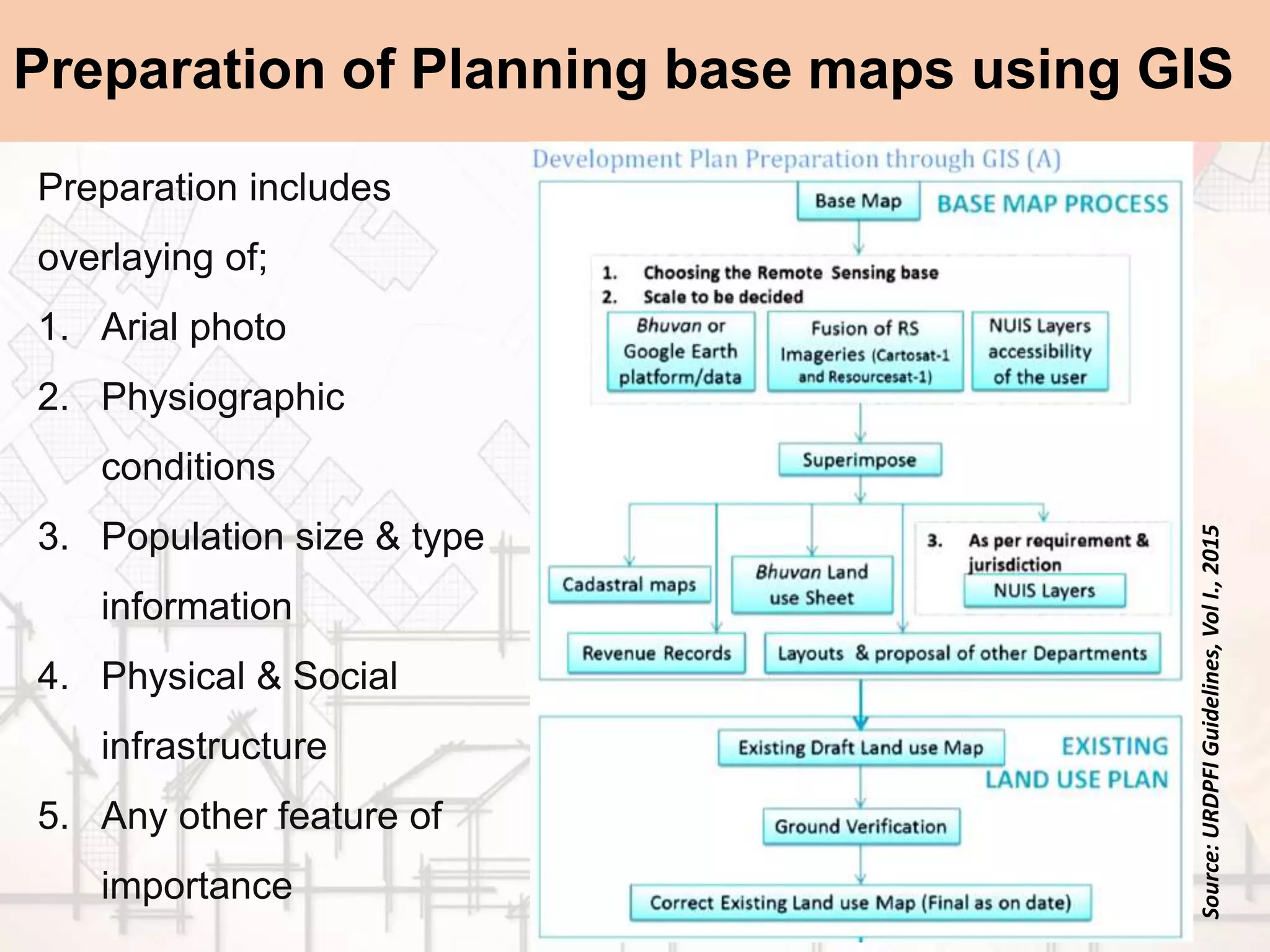
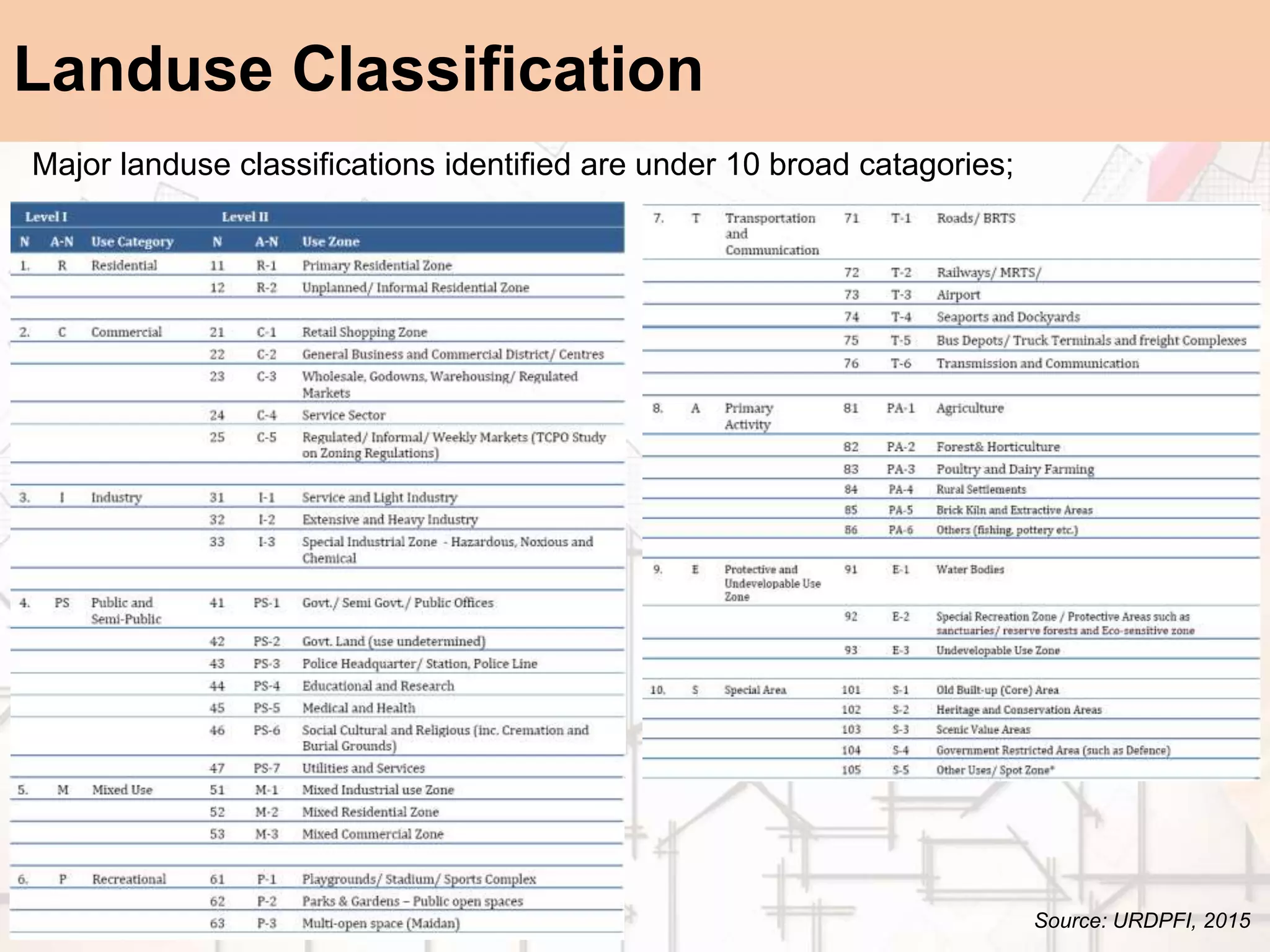
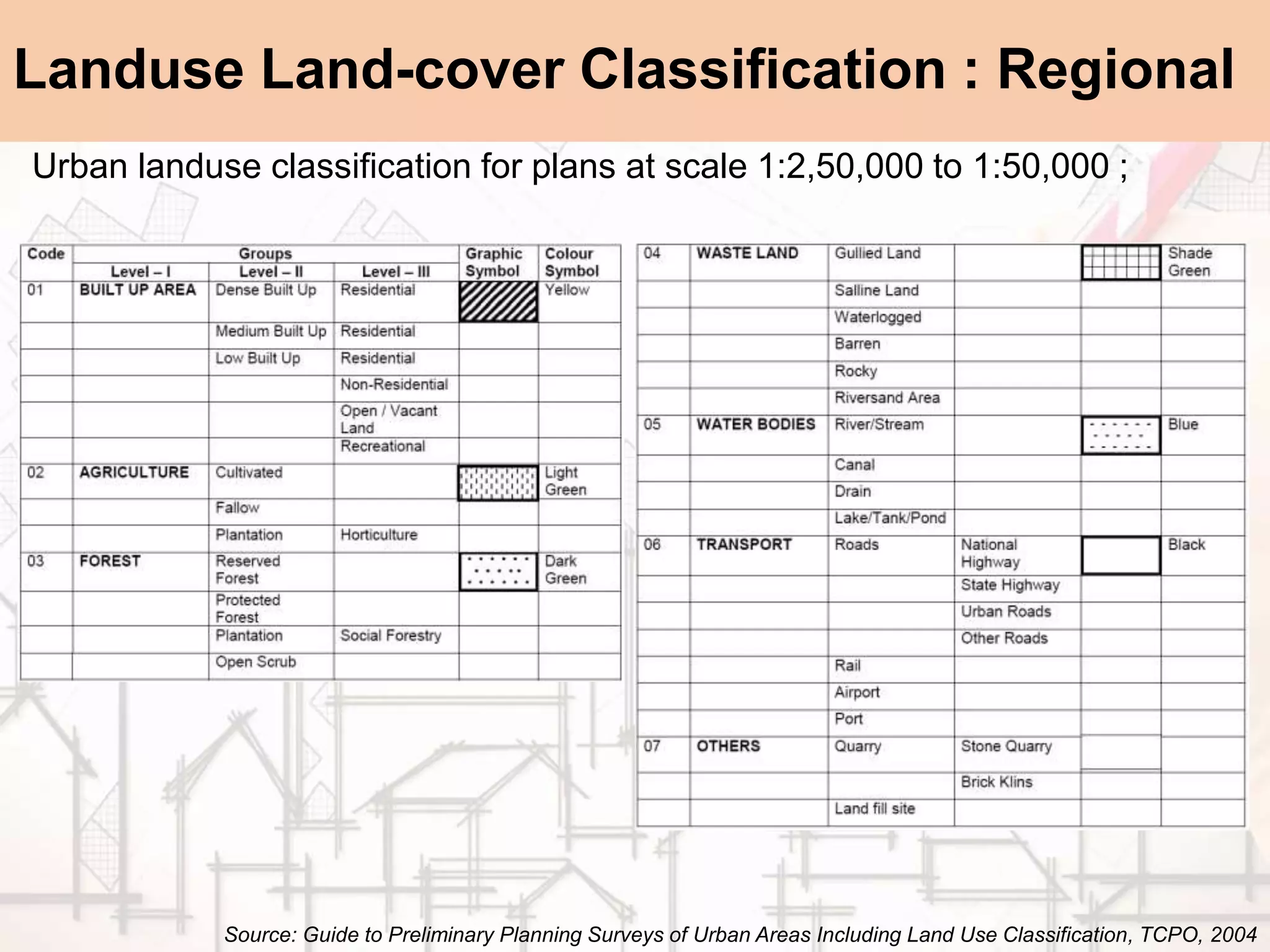
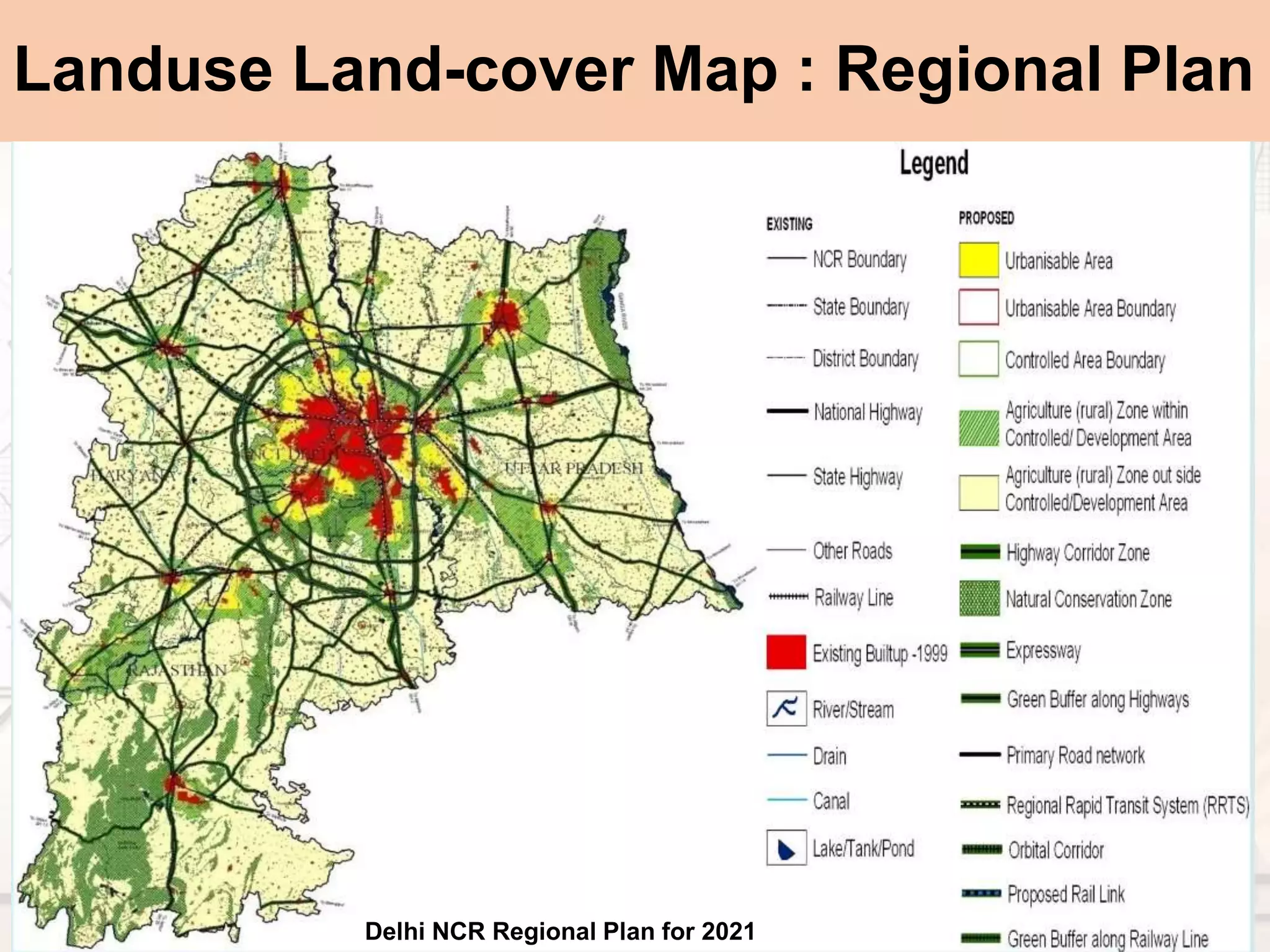
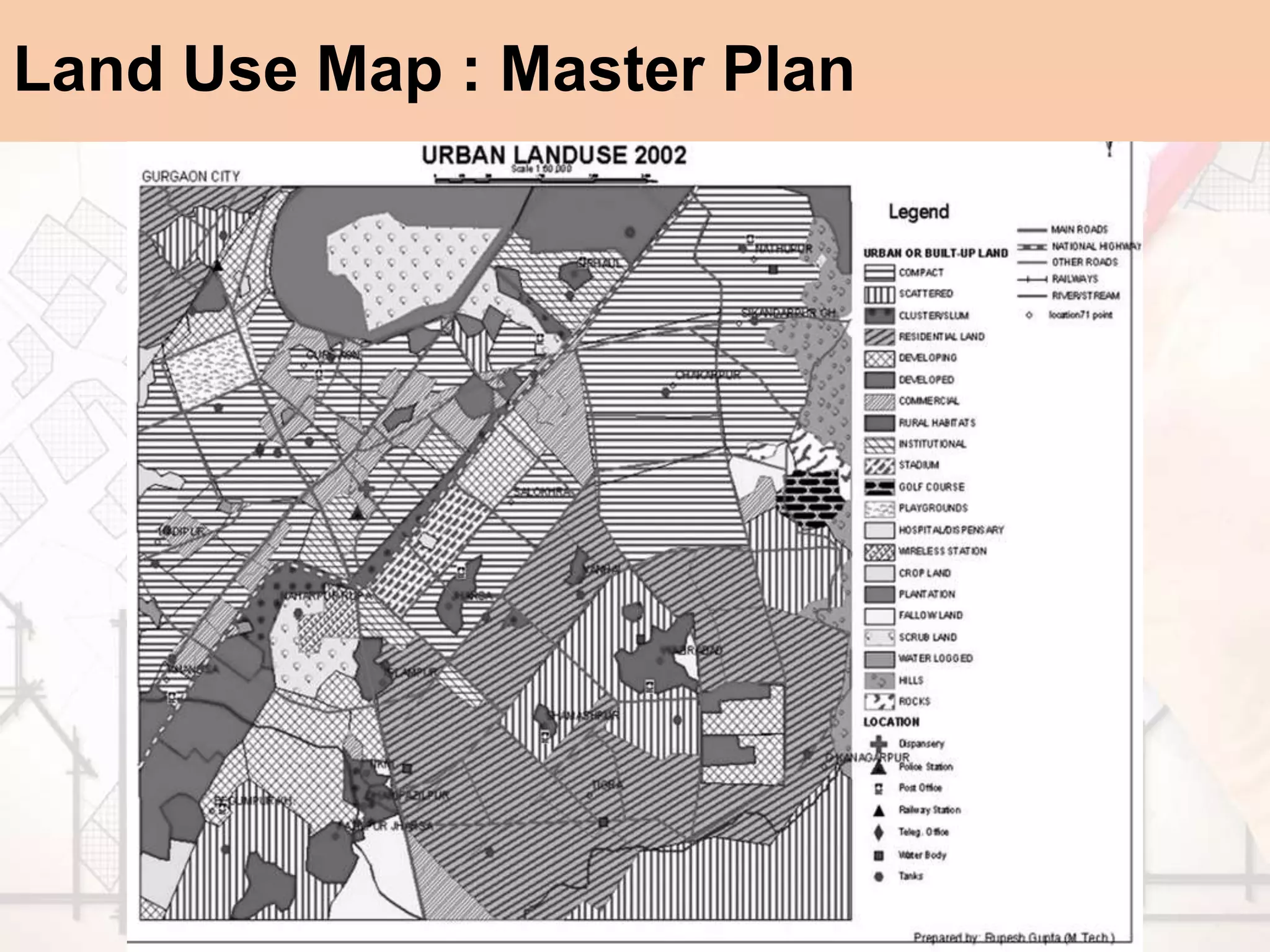
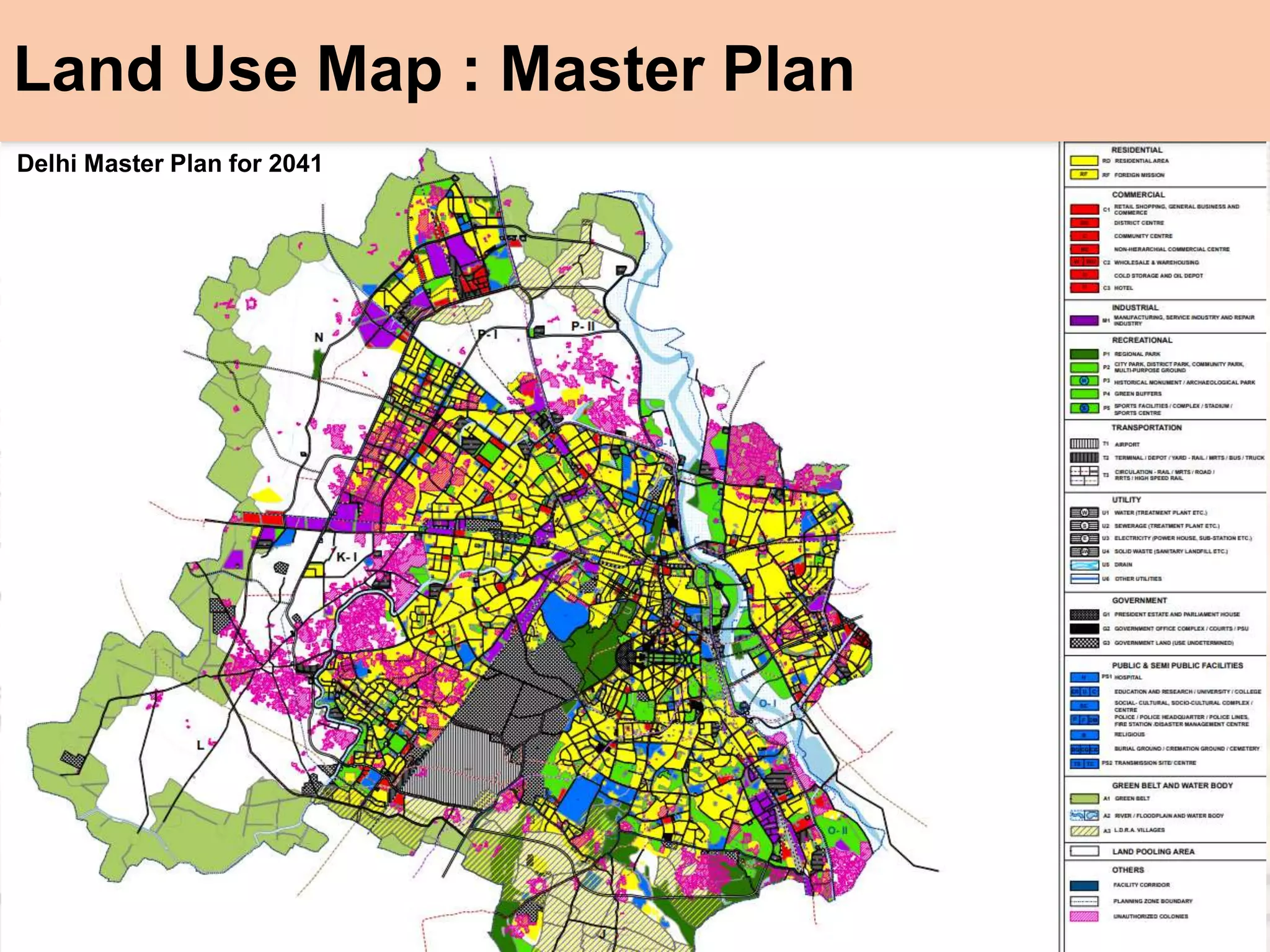
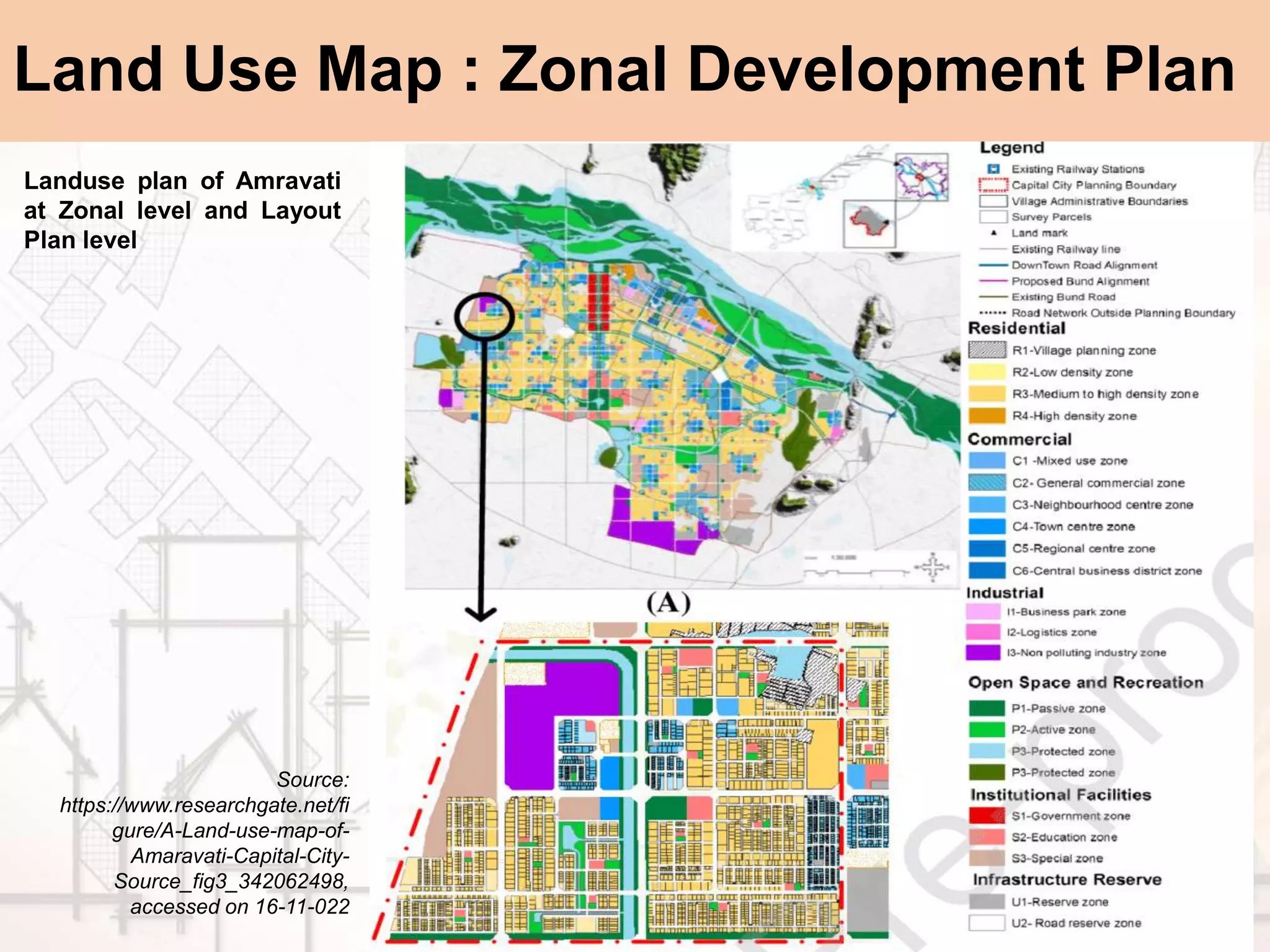
The document provides a comprehensive overview of map scales and preparation, defining a map as a diagrammatic representation of land or sea that shows various features. It discusses elements of maps, types of scales, and the preparation of base maps using GIS, emphasizing the importance of accurate representation and land-use classifications. Additionally, it references multiple sources and guidelines for effective map-making and land-use planning.