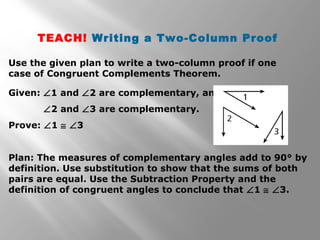
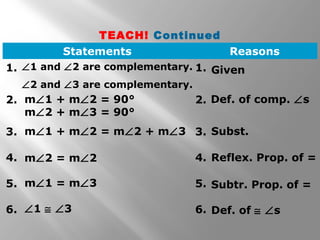
This document contains geometry content on indirect proofs, two-column proofs, and properties of angles. It includes examples of writing indirect proofs, two-column proofs, and solving equations. It quizzes the reader with problems involving justifying steps in solving equations and identifying properties such as the transitive property of equality.