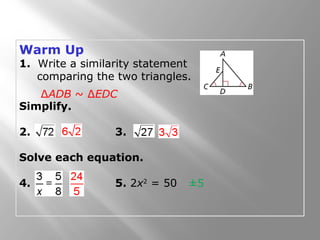
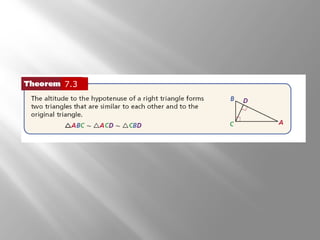
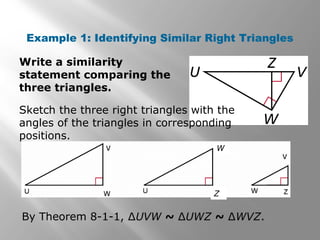
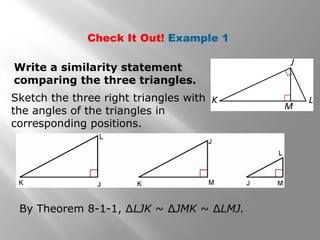
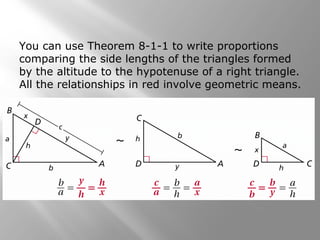
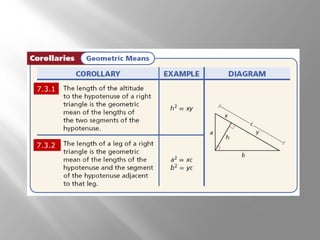
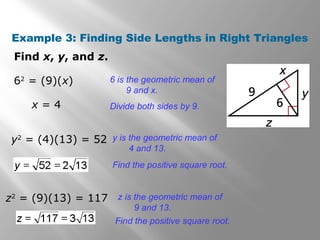
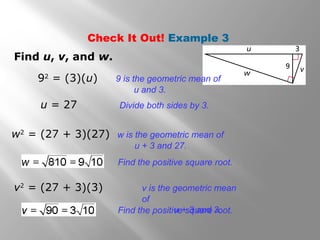
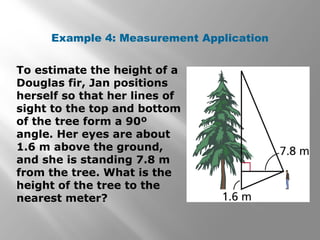
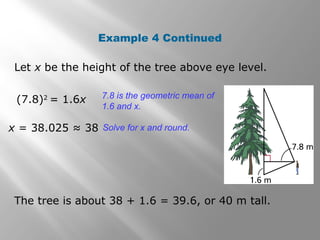
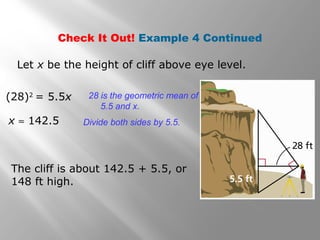
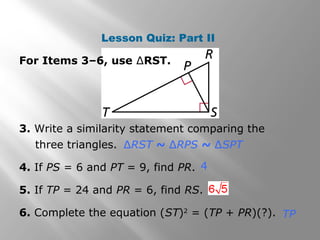
This document is from a geometry textbook and covers similarity in right triangles. It begins with objectives and vocabulary, then provides examples of identifying similar right triangles, finding geometric means, using geometric means to find unknown side lengths in right triangles, and an application to estimating height. Examples are included with step-by-step work shown. Students are then given a quiz to assess their understanding.