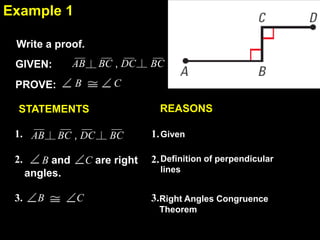
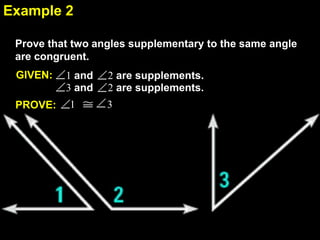
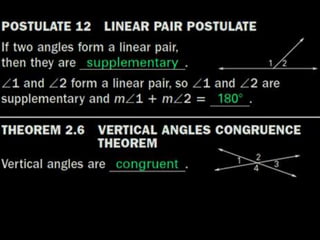
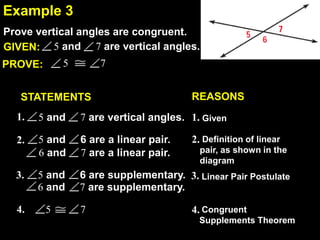
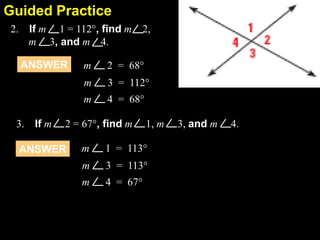
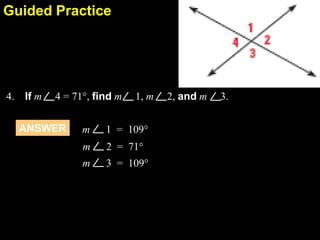
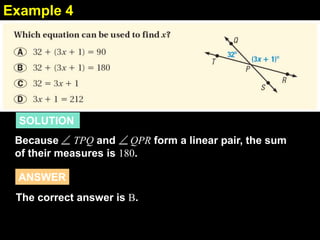
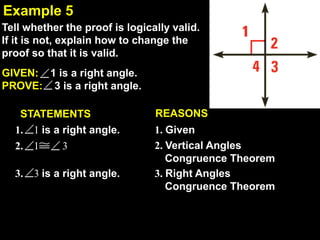
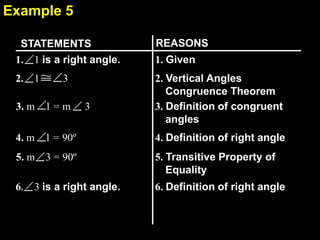
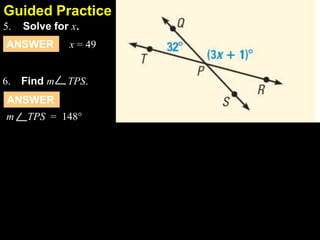
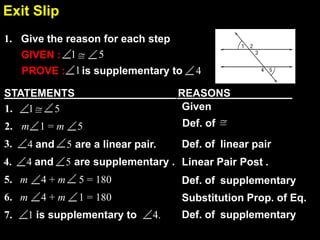
This document contains examples and explanations of angle pair relationships and angle proofs. It begins with definitions of equal angles if they are both right angles, angles formed by perpendicular lines, and congruent segment angles. Several examples of angle proofs are provided using statements and reasons. Guided practice problems ask to find missing angle measures using angle relationships. The document concludes with an exit slip and homework assignment.