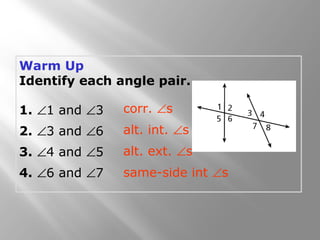
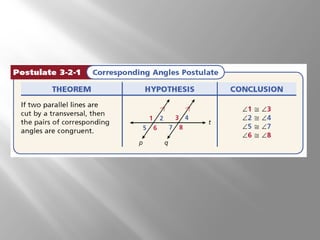
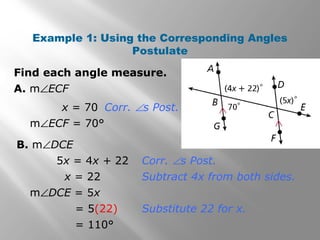
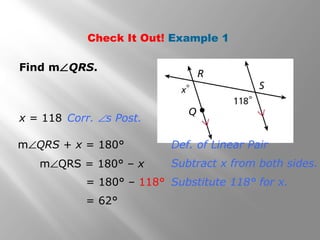
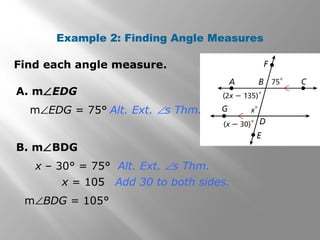
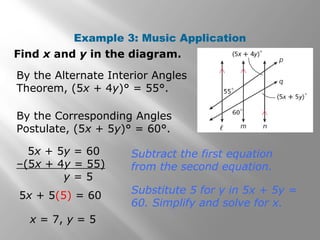
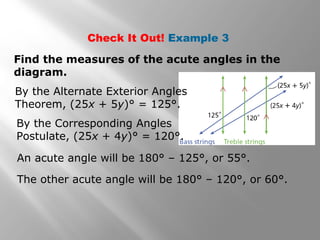
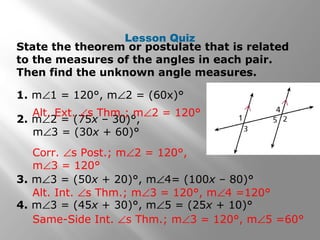
This document discusses properties of parallel lines and angles formed when lines are cut by a transversal. It defines key angle terms such as corresponding angles, alternate interior angles, and alternate exterior angles. Examples show how to use postulates and theorems about parallel lines to calculate unknown angle measures. Theorems addressed include the corresponding angles postulate and theorems about alternate interior and exterior angles. The document provides examples finding specific angle measures and asks students to identify the theorem or postulate used in different problems.