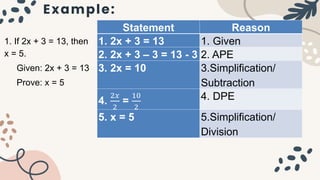
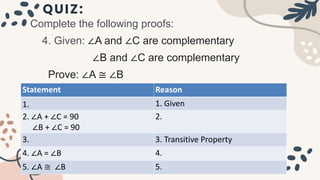
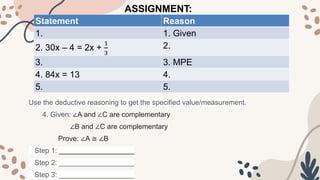
The document discusses deductive and inductive reasoning. It provides examples of using deductive reasoning to prove mathematical statements through a series of logical steps. Deductive reasoning uses facts and properties to reach a conclusion, while inductive reasoning observes patterns to form a conclusion. The document also contains examples of multi-step proofs involving geometry concepts like complementary angles. Students are assigned to identify given and prove statements, complete proofs using properties of equality and geometry, and distinguish between deductive and inductive reasoning.