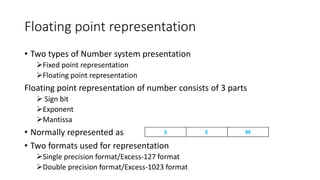
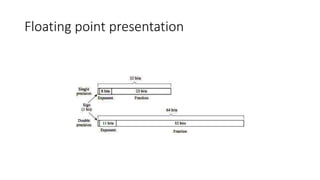
This document discusses floating point number representation in IEEE-754 format. It explains that floating point numbers consist of a sign bit, exponent, and mantissa. It describes single and double precision formats, which use excess-127 and excess-1023 exponent biases respectively. Examples are given of representing sample numbers in both implicit and explicit normalized forms using single and double precision formats.



![Explanation of Exponent
• Exponent is of two types :- original exponent [e]
• - Stored Exponent [E’]
• E’ is computed using formula:-
• Bias is same as Excess-X code. E.g. Excess-3 code means 0 will be counted
as 0+3=3, 1 as 1+3=4.
• Similarly if original bias is e and biased exponent is in the form Excess-32
then Biased Exponent is e+32.
• If exponent is presented in k-bits then bias value is 2k-1 -1.
• Note -: Biased Exponent means Exponent is not stored directly. It is stored
as original bias + Excess-x format.[x value is anything.]
E’ =e+ bias](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/floatingpointpresentation-210731062429/85/Floating-point-presentation-6-320.jpg)
![Mantissa
• Mantissa is number after the point.
• When we are going to present mantissa in memory it is presented in
normalised format.
• In Explicit normalised form number is present after the point. E.g.
1011.1 -> number can be normalise as 0.10111 x 2 4 . [instead of 10 base 2 is used]
Implicit
Normalized
form
Explicit
Normalised
Form](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/floatingpointpresentation-210731062429/85/Floating-point-presentation-7-320.jpg)
![Cont…
• In Explicit normalised form point is present by leaving one bit value
and that value is 1. Means presented as 1.---
• Let the number is 1011.1 .
• Implicit Presentation of number in memory 1.0111 x 2 3.
• Original exponent(e) is 3.
• Biased exponent is(E’)= 127+3=130 [As we are presenting using
excess-127 format]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/floatingpointpresentation-210731062429/85/Floating-point-presentation-8-320.jpg)

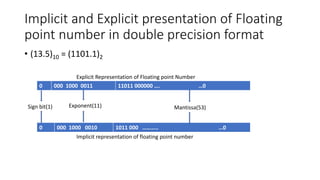
![Floating point representation using implicit
normalised form
• Floating point number=13.5 .
• Binary presentation of number (13.5)10 = (1101.1)2 .
• Now implicit normalised form of the number is 1101.1 = 1.1011 x23 .
• So original bias[e] = 3 .
• Stored bias[E’] = 127+3 = 130 = 10000010
• Mantissa is .1011
• Now floating point presentation of number is
0 10000010 1011000……………0
Sign bit Exponent Mantissa](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/floatingpointpresentation-210731062429/85/Floating-point-presentation-10-320.jpg)