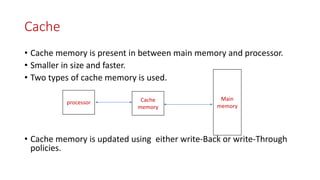
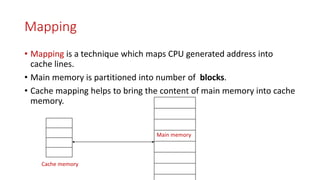
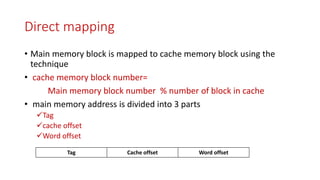
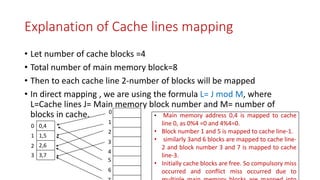
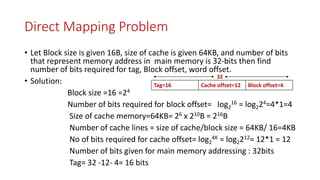
Cache memory is located between the processor and main memory. It is smaller and faster than main memory. There are two types of cache memory policies - write-back and write-through. Mapping is a technique that maps CPU-generated memory addresses to cache lines. There are three types of mapping - direct, associative, and set associative. Direct mapping maps each main memory block to a single cache line using the formula: cache line number = main memory block number % number of cache lines. This can cause conflict misses.