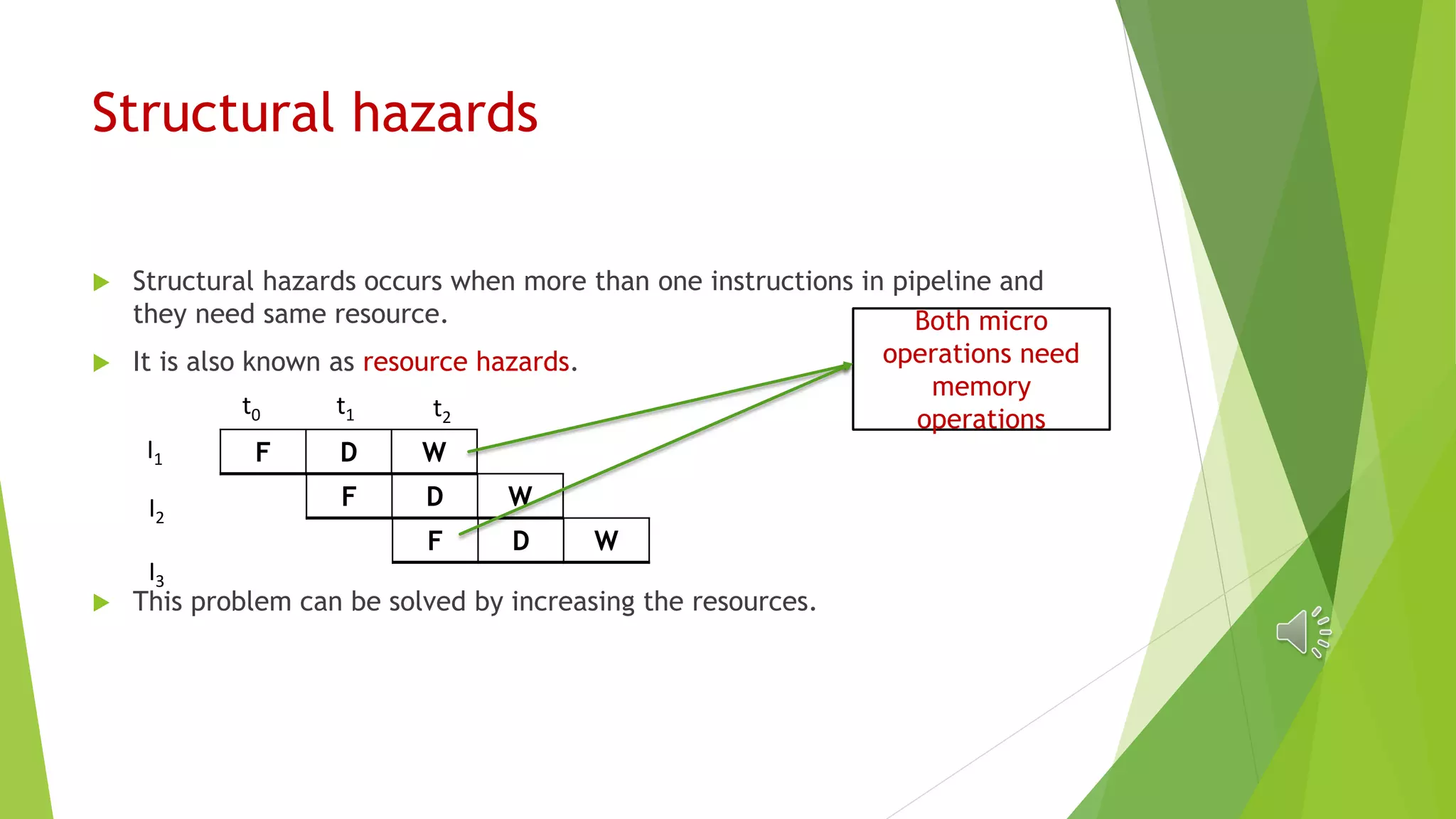
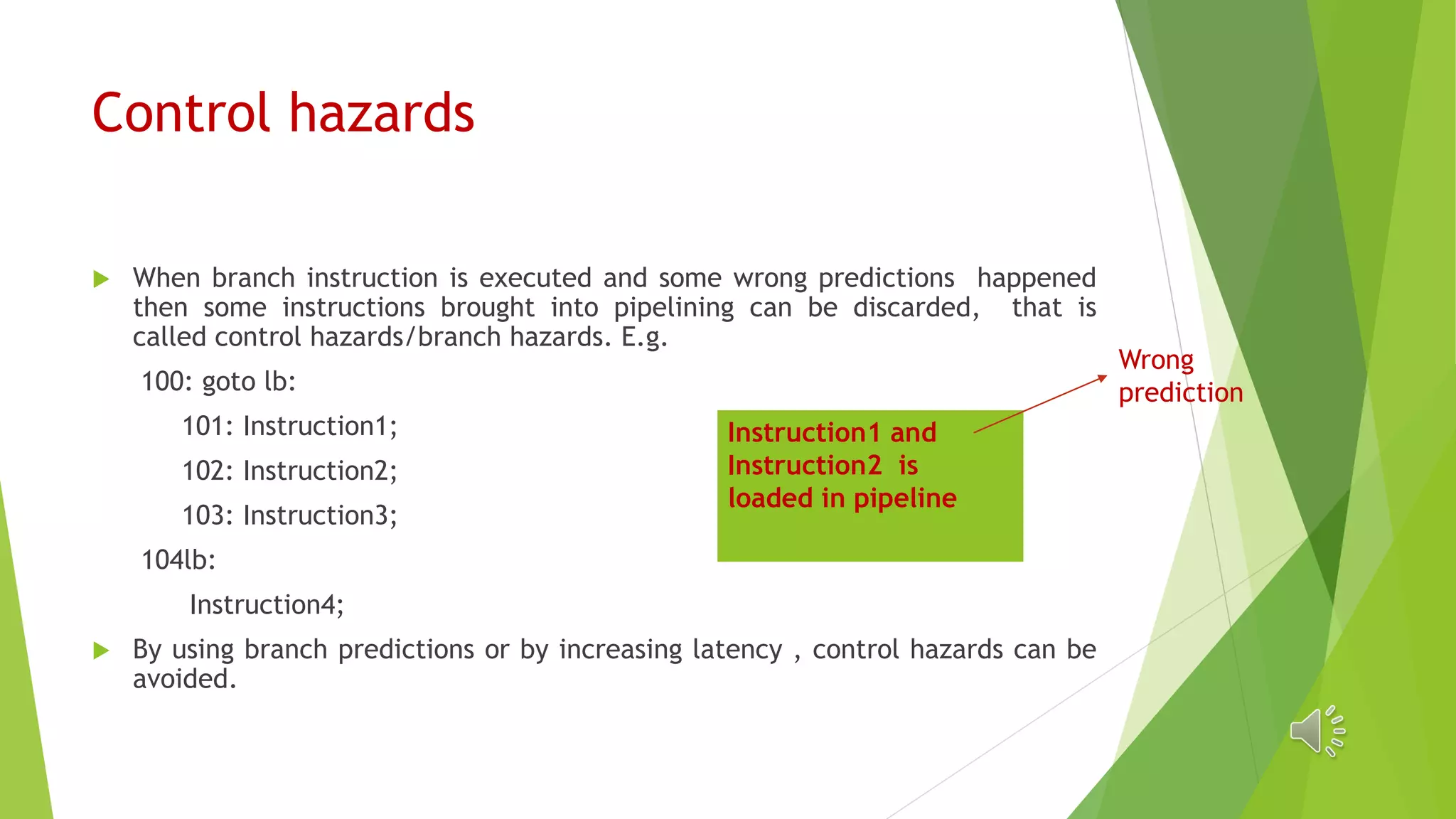
The document discusses different types of hazards that can occur in an instruction pipeline: data hazards, control hazards, and structural hazards. Data hazards include RAW (read after write), WAR (write after read), and WAW (write after write) and occur when there are dependencies between instructions. Control hazards occur due to incorrect branch predictions. Structural hazards happen when multiple instructions need the same functional unit or resource. These hazards can be avoided through techniques like operand forwarding, renaming, branch prediction, and increasing resources or latency.