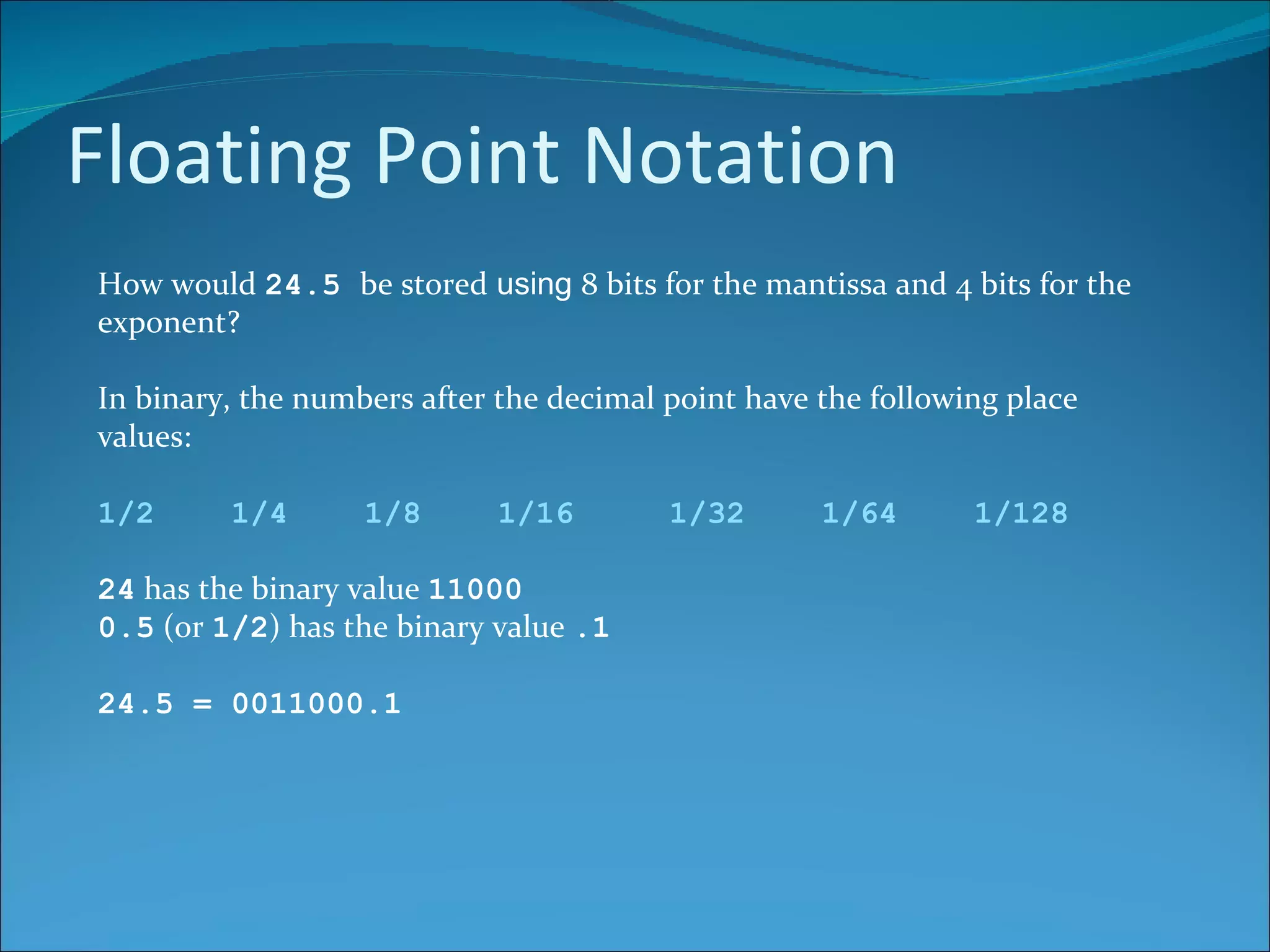
Real numbers include whole numbers, rational numbers like fractions and decimals, and irrational numbers like pi. They can be positive, negative or zero. In computing, real numbers are represented using floating point notation, which stores numbers as a mantissa and exponent. The mantissa holds the significant digits of the number, while the exponent tracks the decimal place. Increasing the bit size of the mantissa improves accuracy, while increasing the exponent size expands the representable range of numbers.