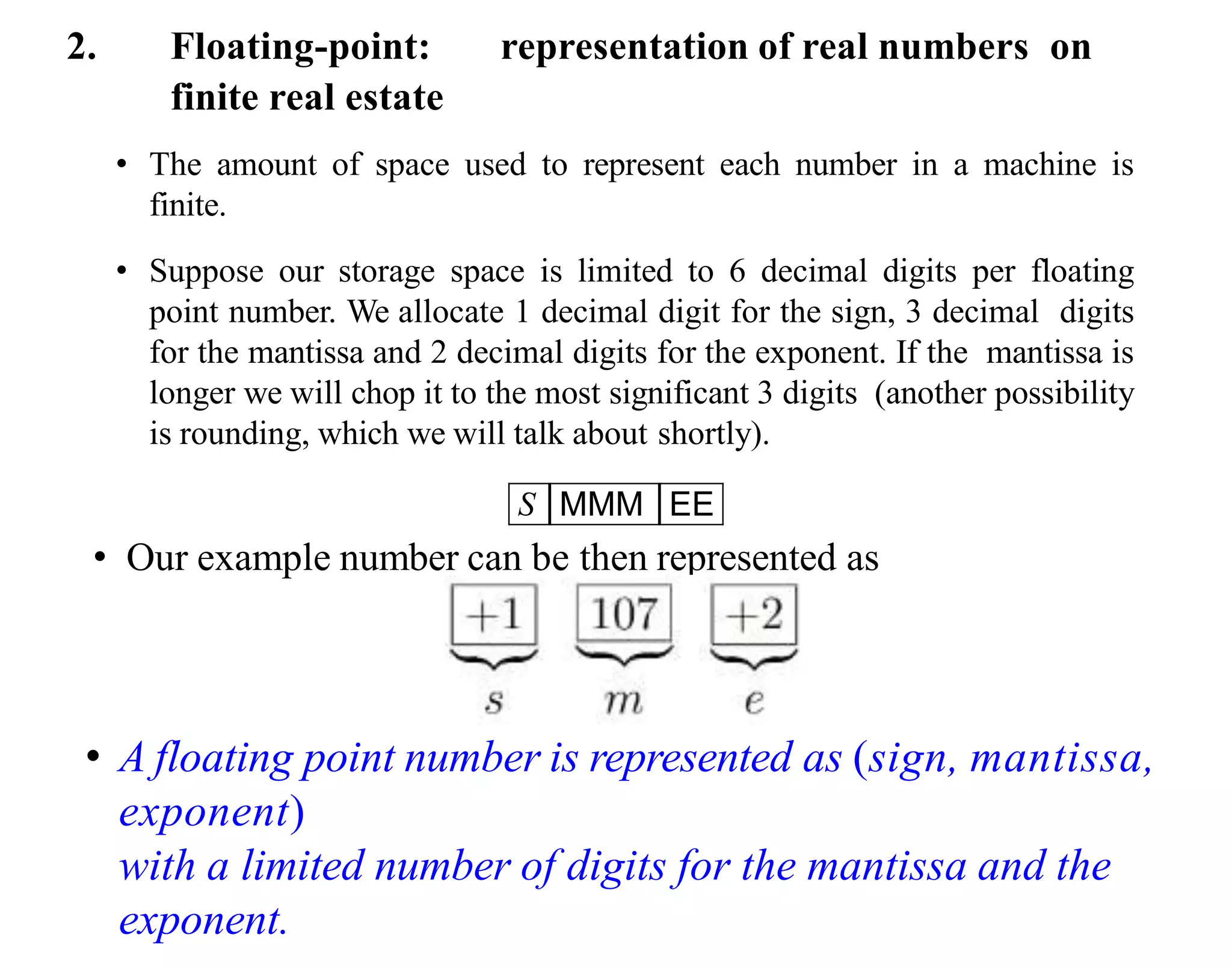
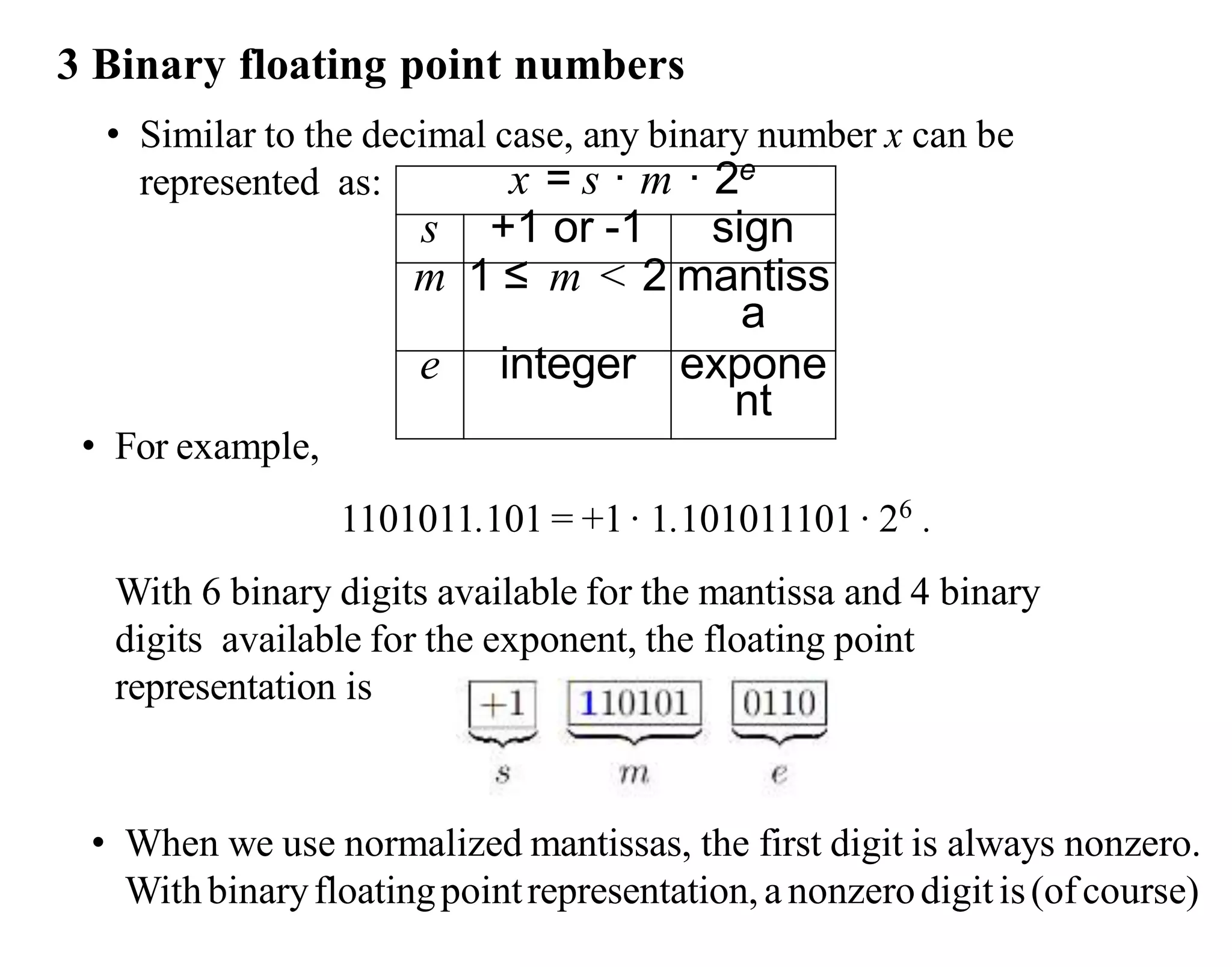
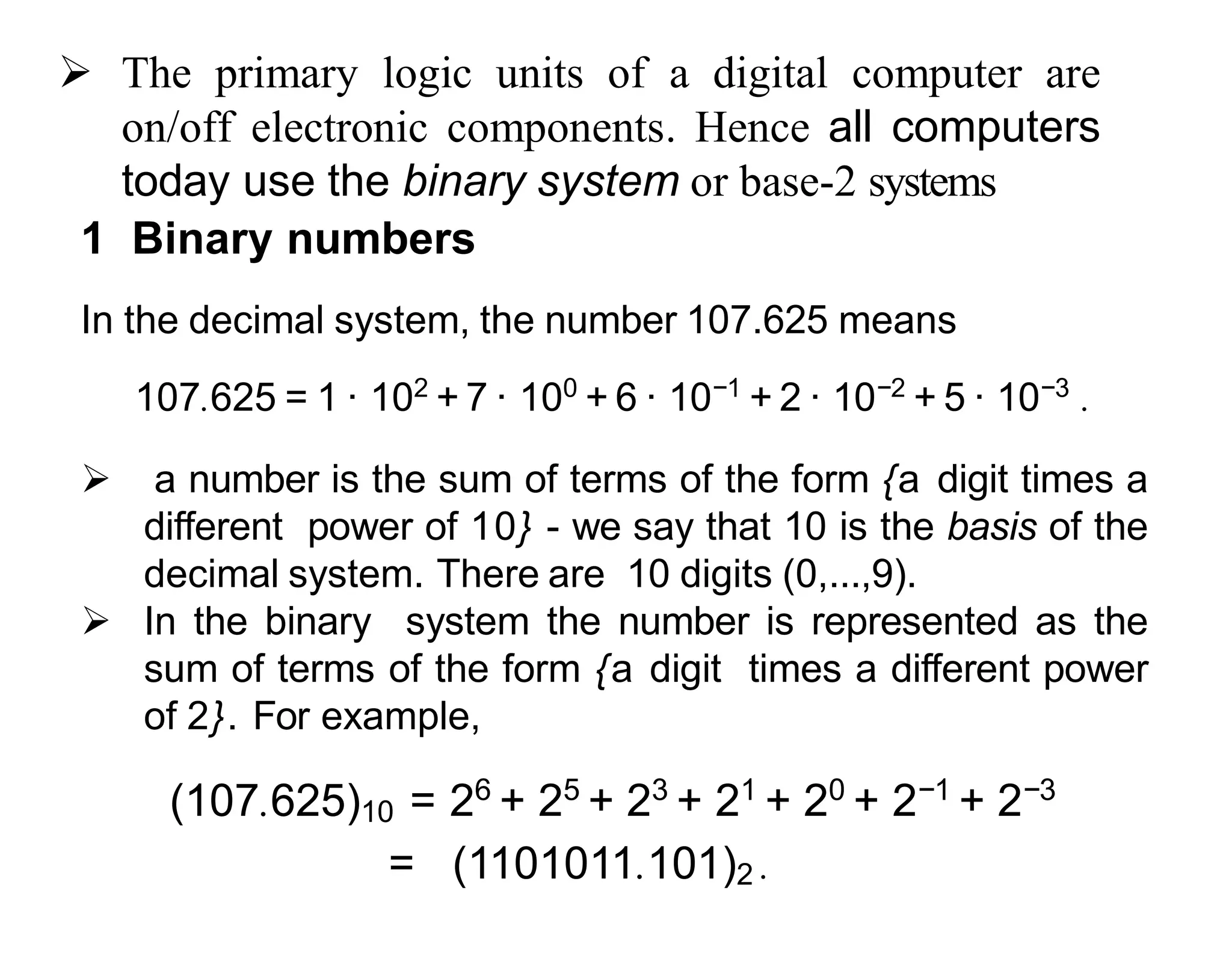
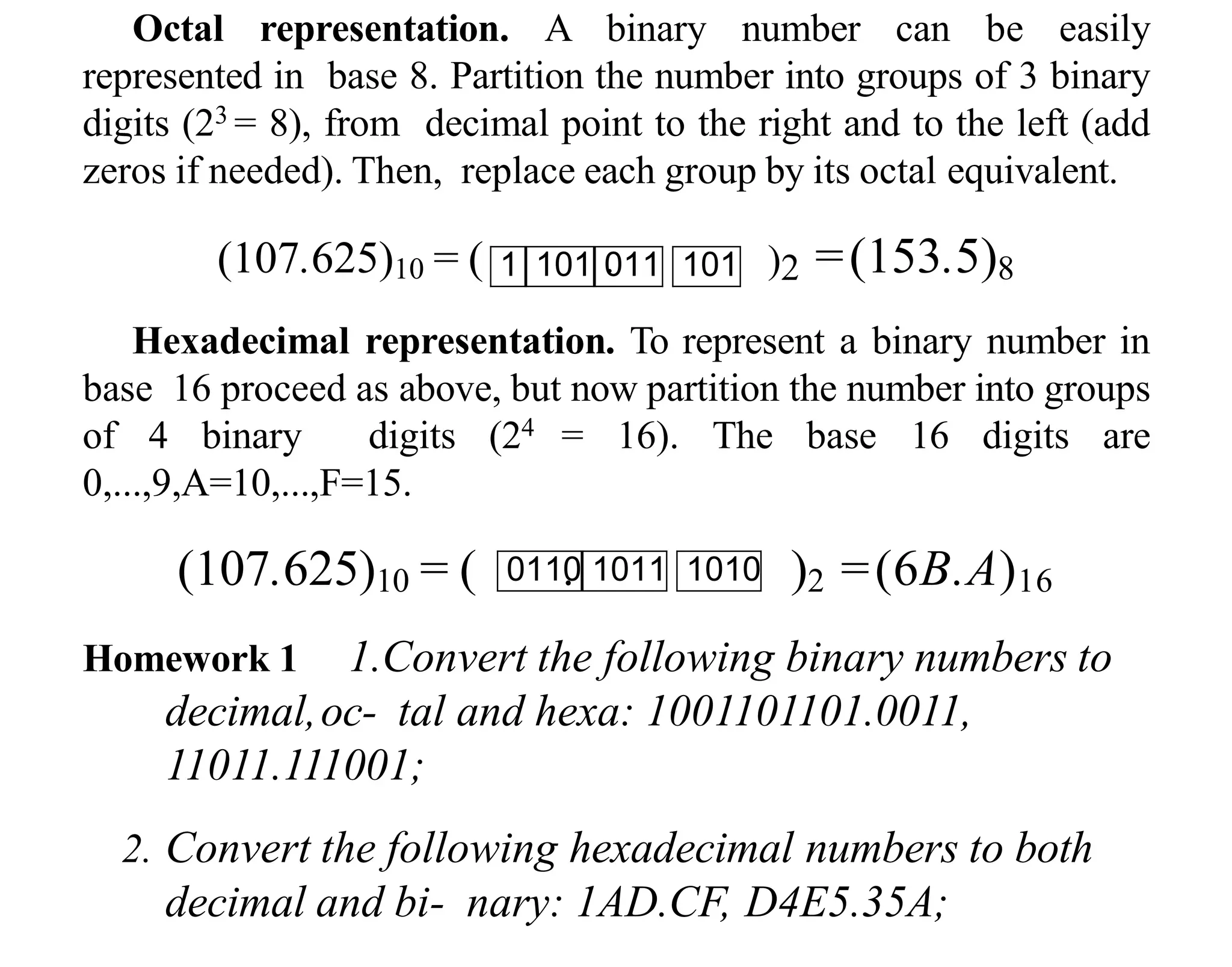
- Computers use binary to represent numbers, where each digit is either a 1 or 0. Real numbers are approximated using floating point representation with sign, mantissa, and exponent fields.
- Integers can be stored by reserving bits for the magnitude and using the first bit to indicate sign (sign-magnitude representation) or by using two's complement representation where the most significant bit indicates sign.
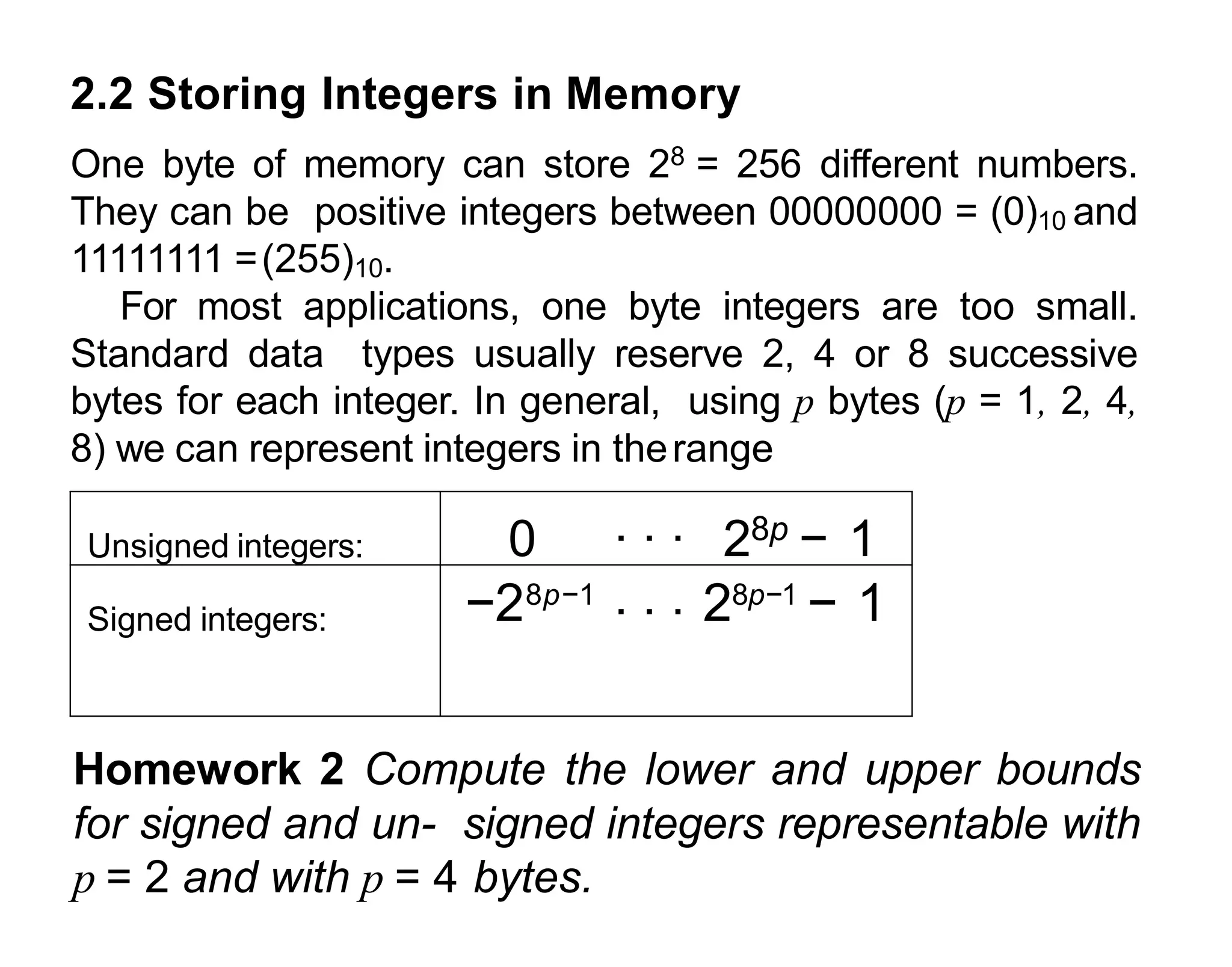
- When storing numbers in memory, multiple bytes are typically used to represent integers or floating point values to support a wider range of numbers.




![If we make the convention that the sign bit is 1
for negative numbers we have:
Number10 ([S]M)2
-3 [1]11
-2 [1]10
-1 [1]01
-0 [1]00
+0 [0]00
+1 [0]01
+2 [0]10
+3 [0]11](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/computerrepresentationofnumbersand-230524211333-616faf90/75/Computer-Representation-of-Numbers-and-pptx-7-2048.jpg)