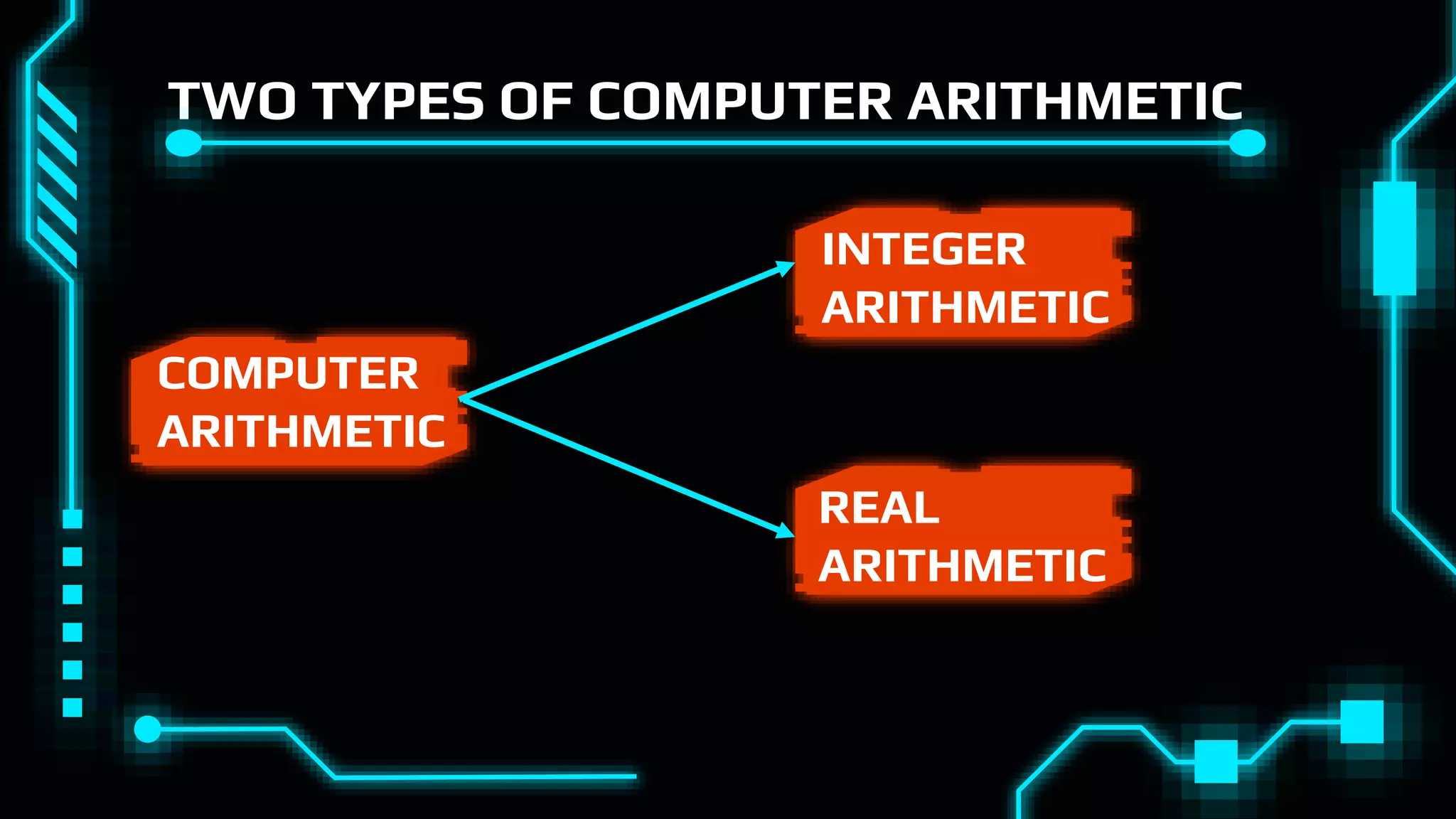
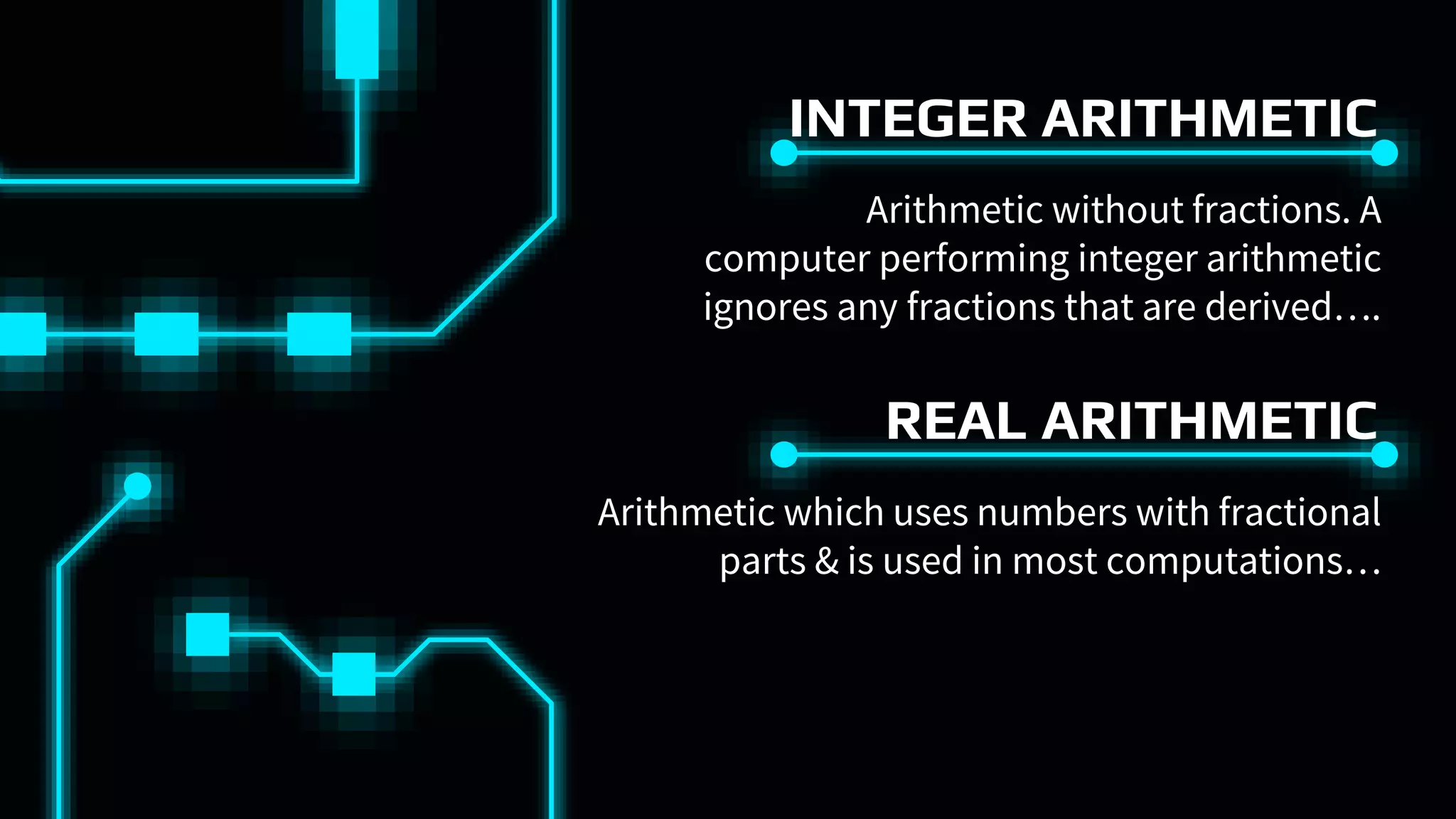
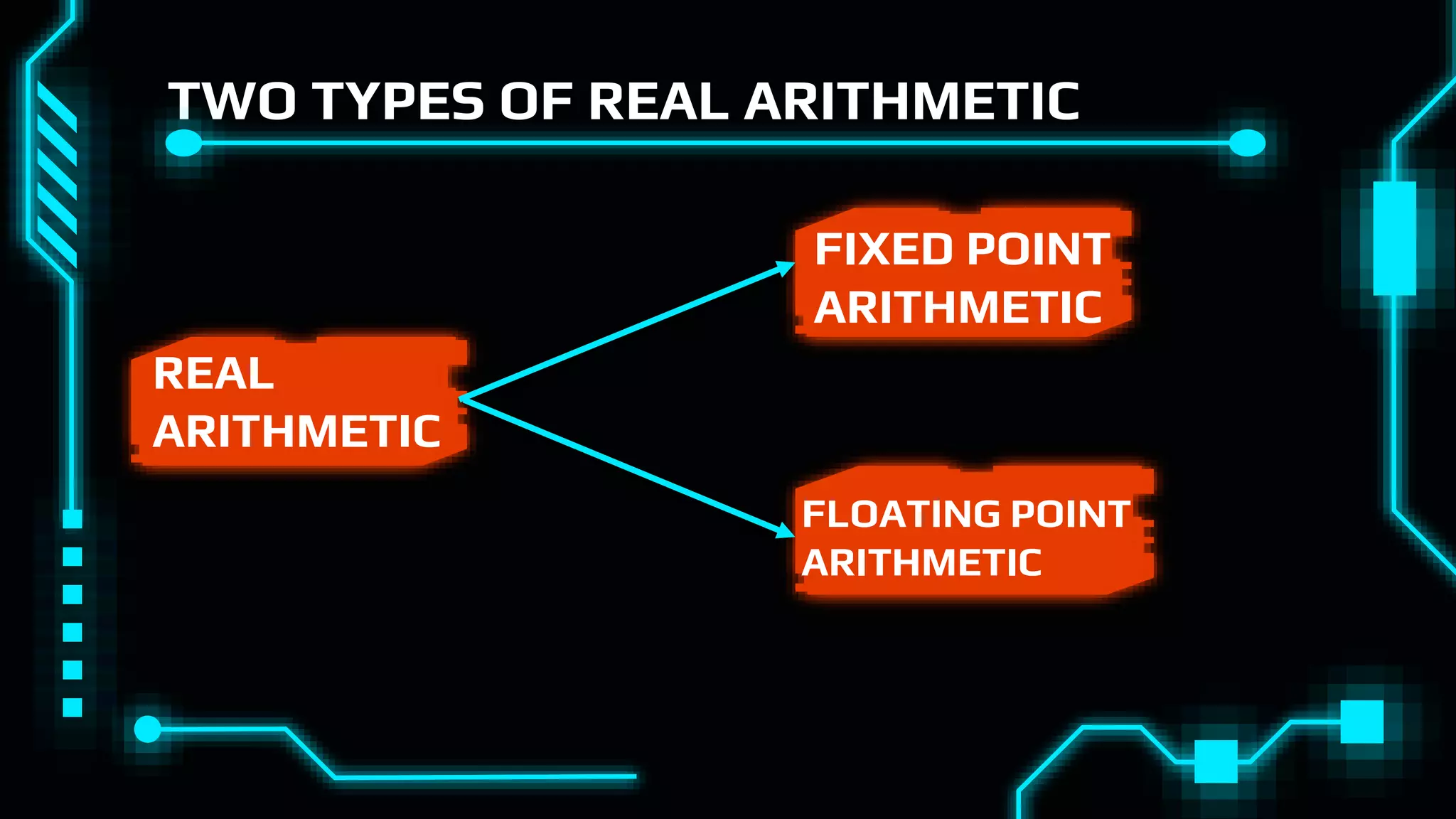
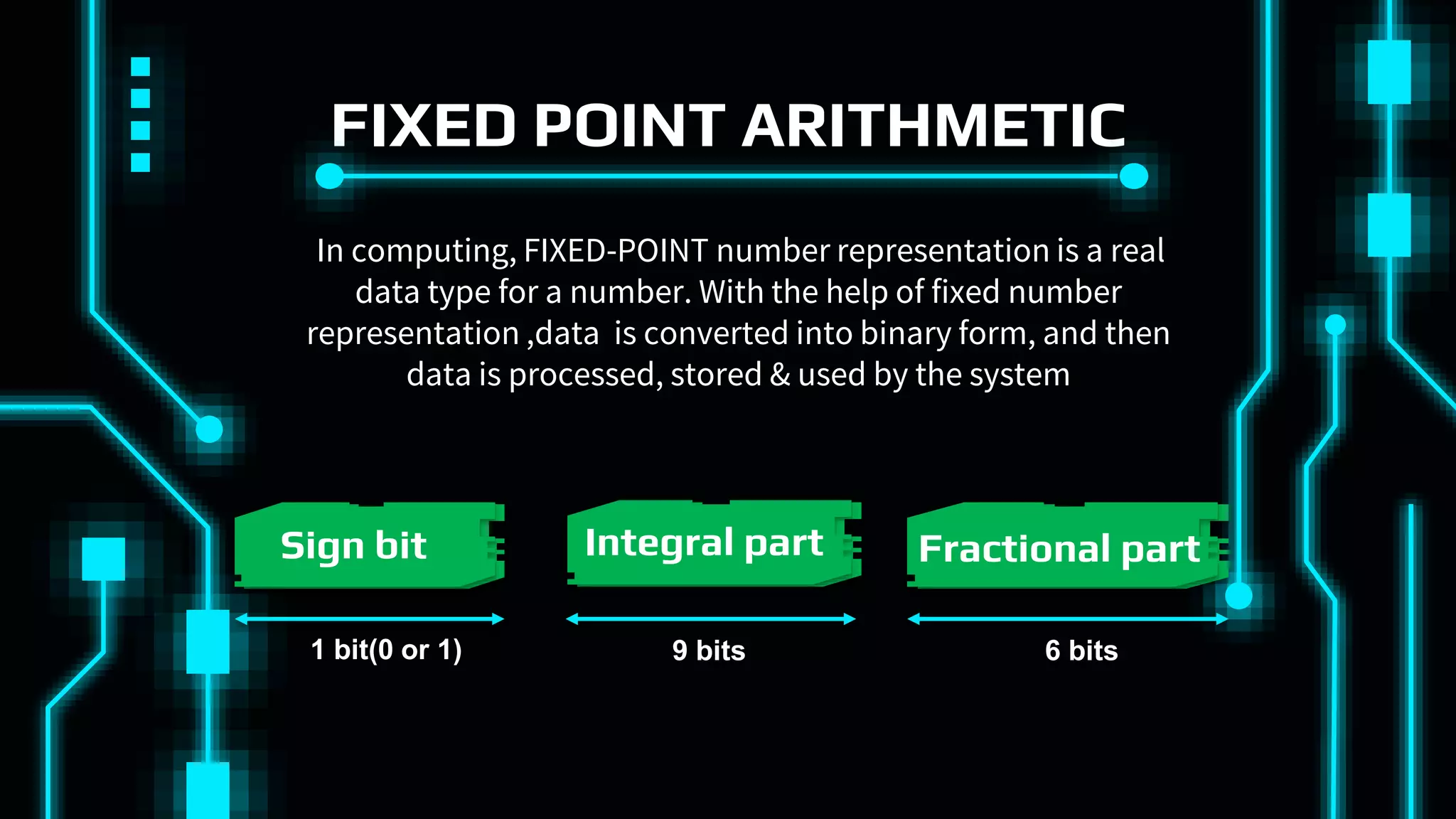
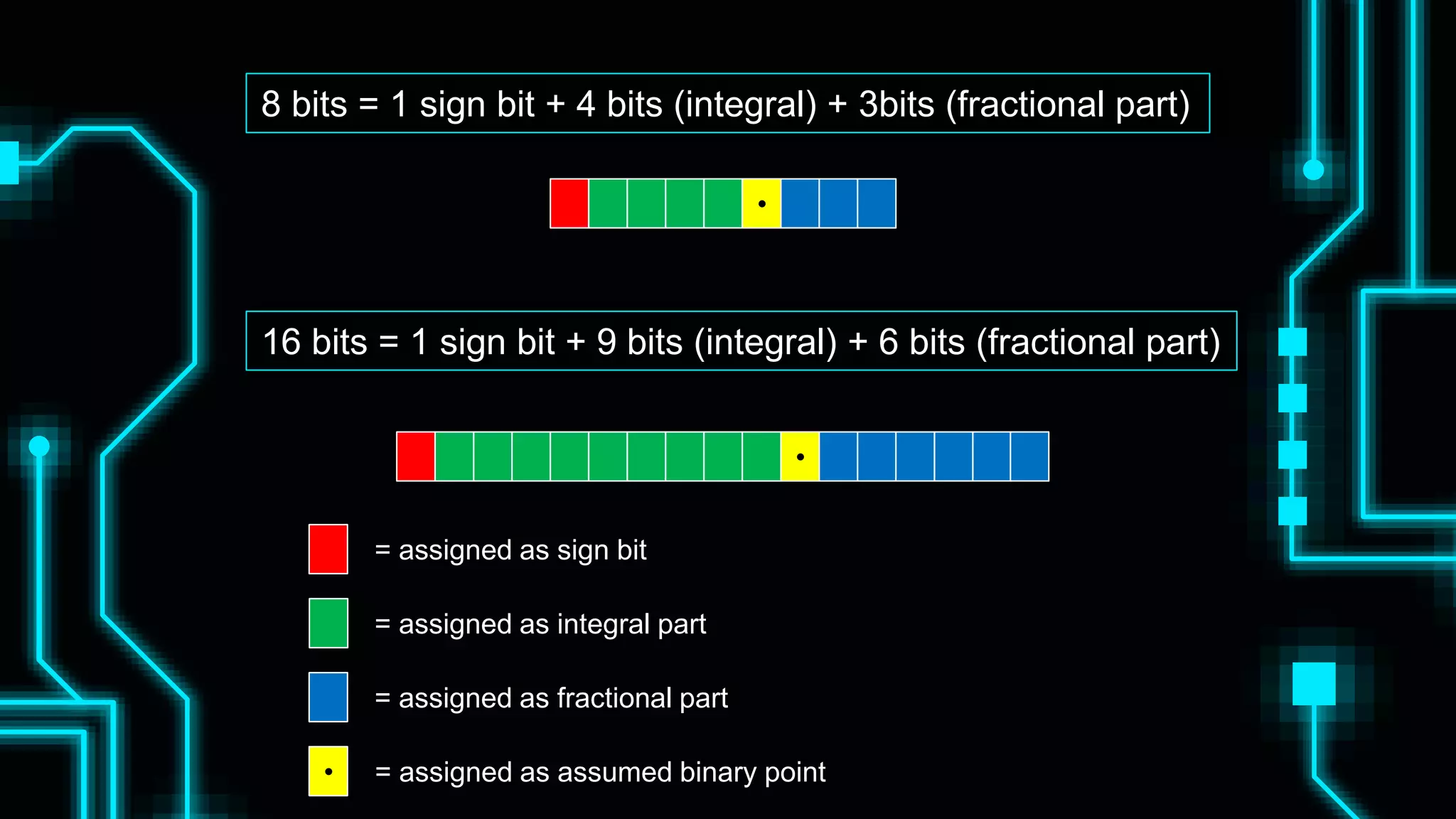
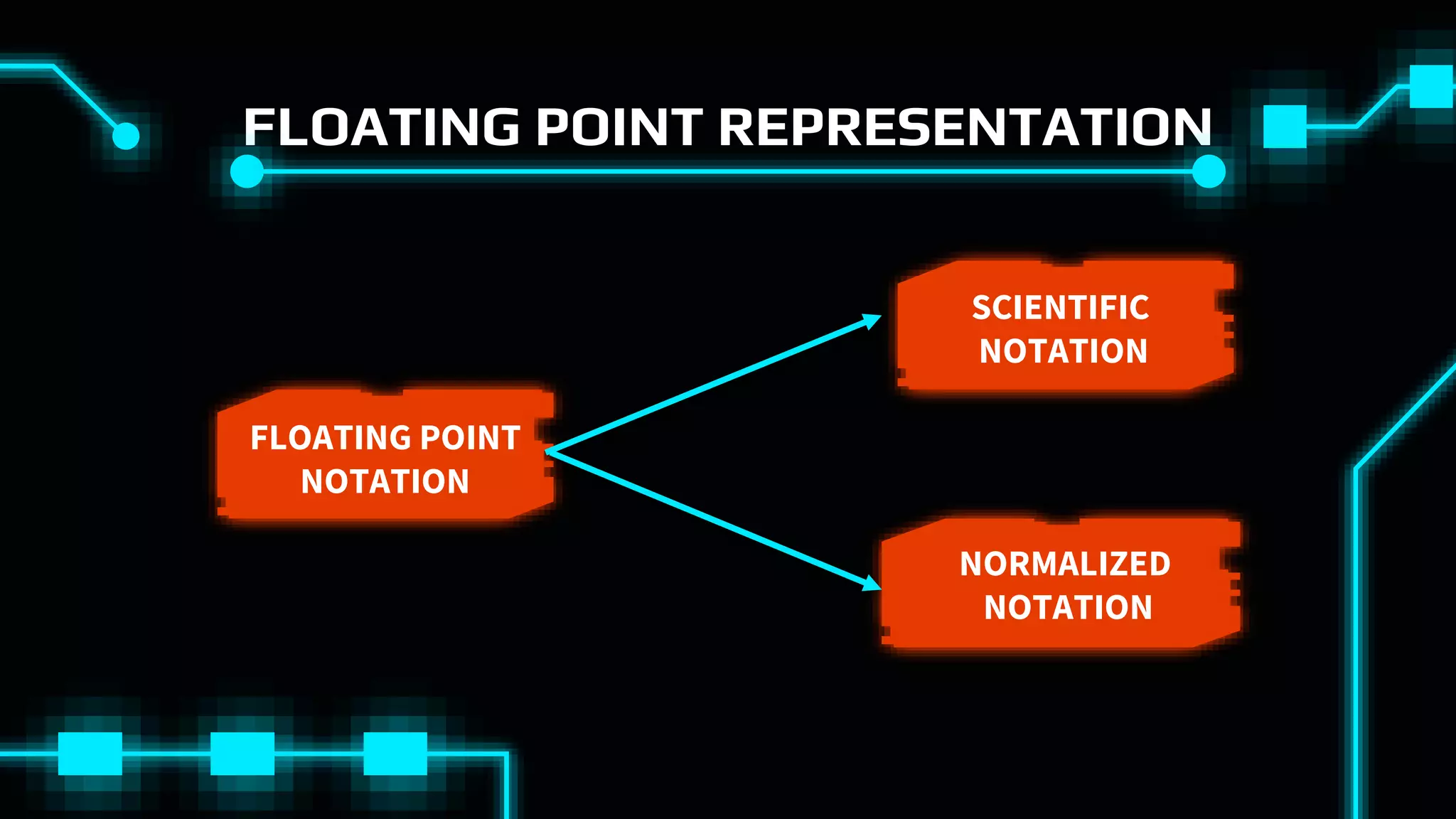
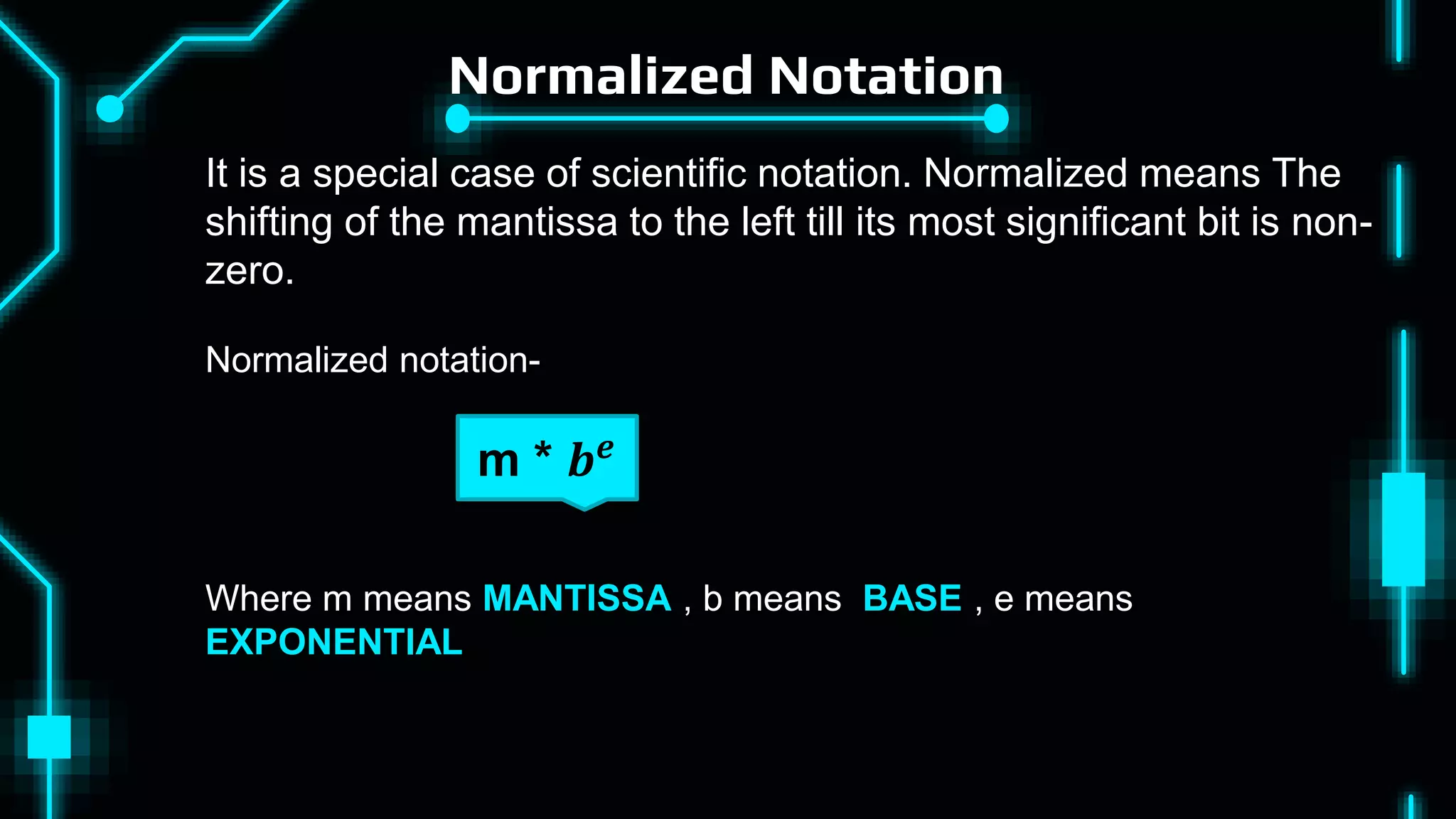
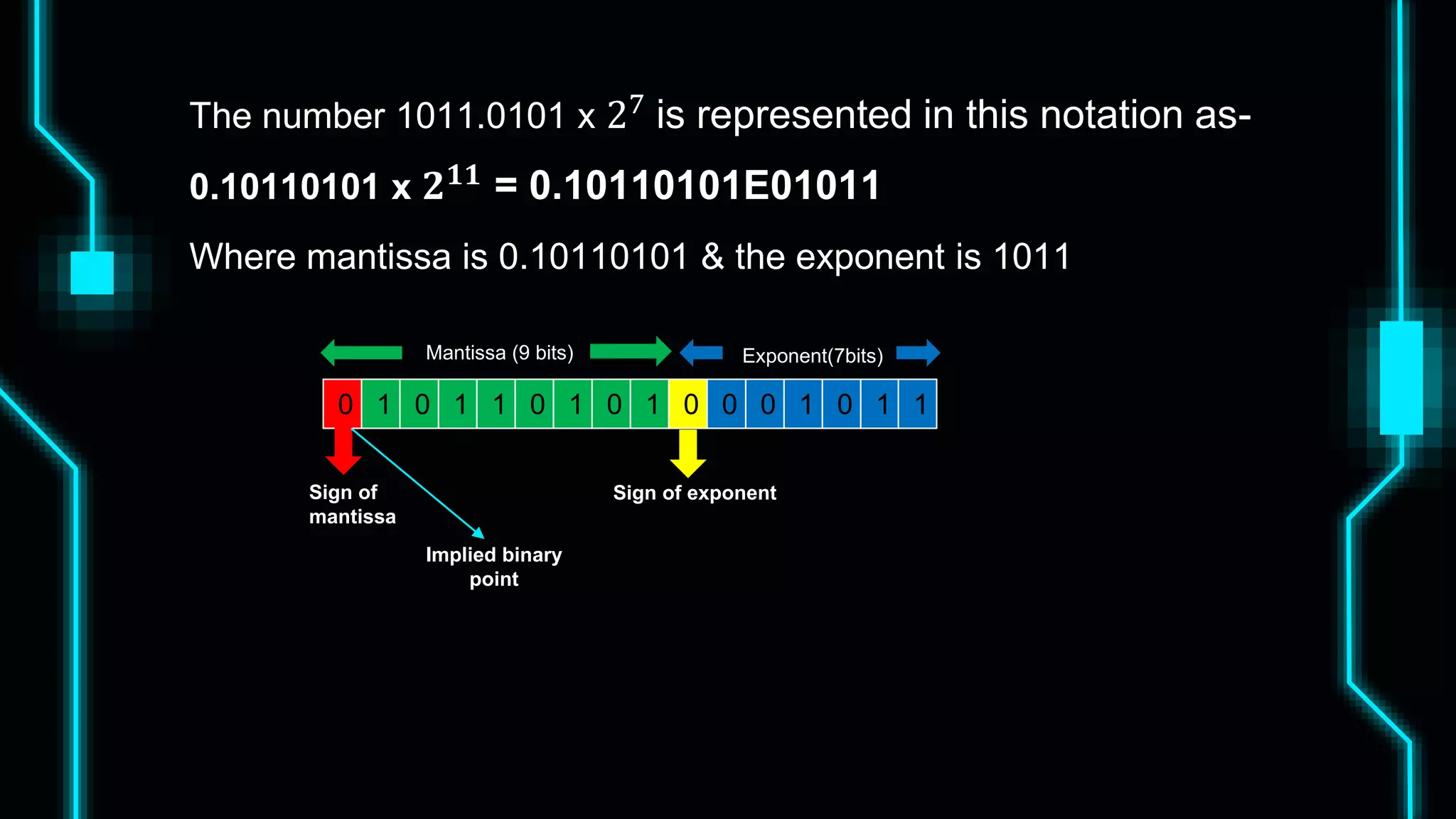
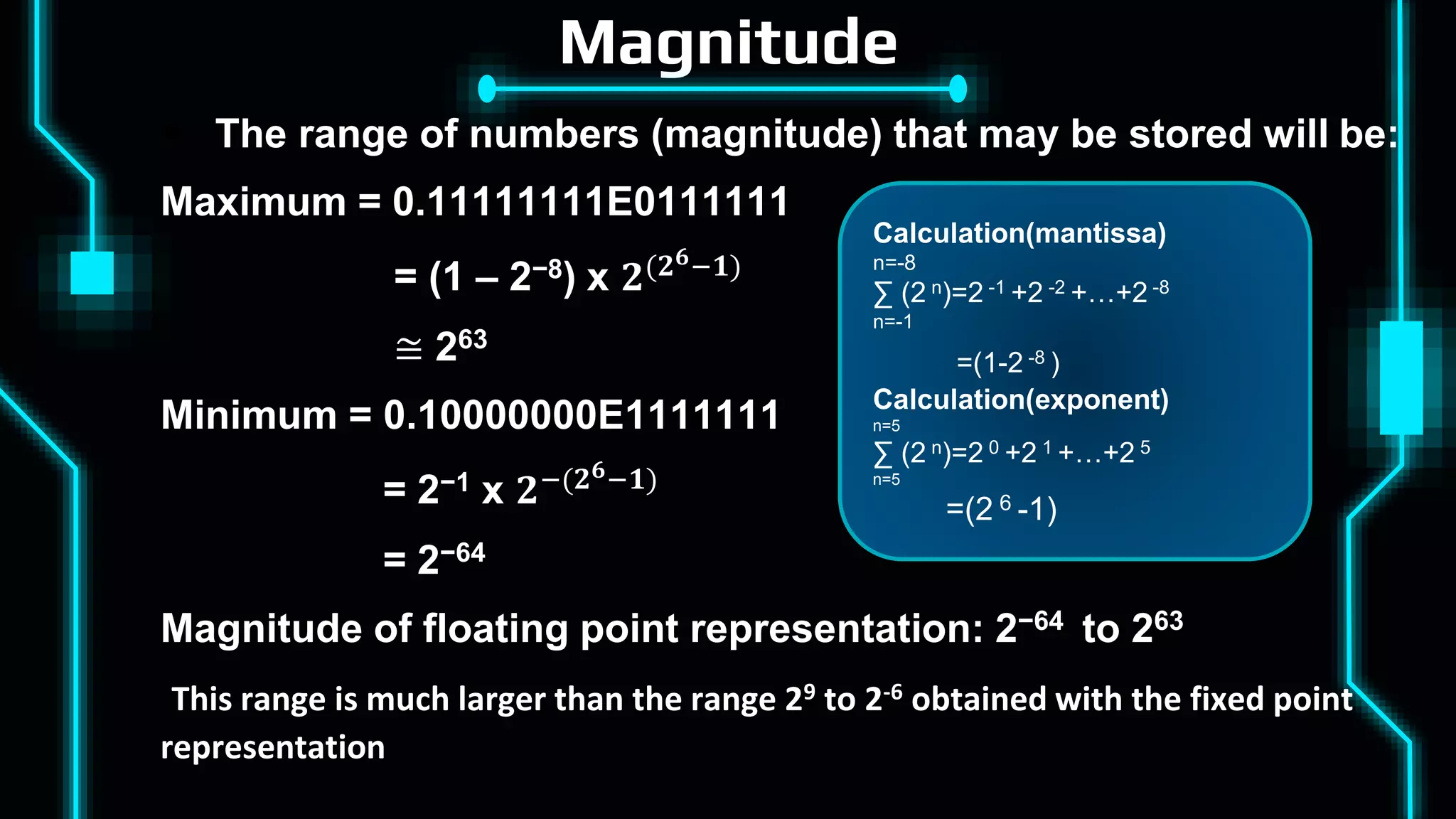
This document discusses floating point representation of numbers in computers. It explains that there are two types of computer arithmetic: integer arithmetic and real arithmetic. Real arithmetic uses numbers with fractional parts and includes fixed point arithmetic and floating point arithmetic. Fixed point arithmetic represents numbers in binary form with a sign bit, integral part, and fractional part. Floating point representation uses scientific notation and normalized notation to represent numbers with a sign bit, mantissa, and exponent. It allows for a much larger range of numbers than fixed point representation.