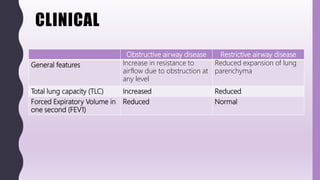
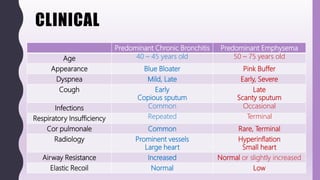
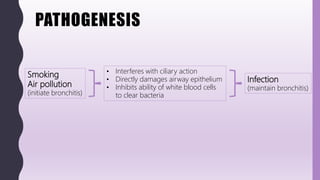
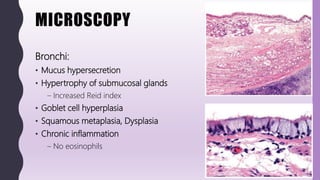
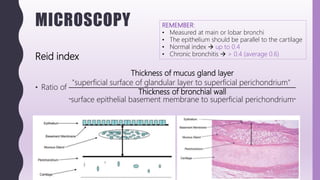
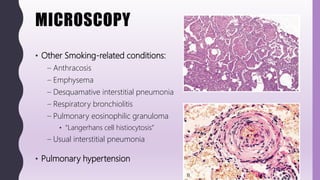
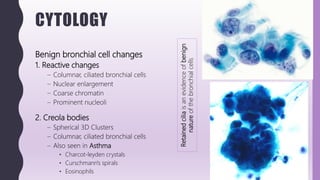
This document discusses chronic bronchitis, which is an obstructive lung disease characterized by a persistent productive cough for at least three months in consecutive years. Chronic bronchitis is often caused by cigarette smoking and air pollution and is clinically grouped with emphysema as chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD). The document describes the clinical features, pathogenesis, gross and microscopic pathology, cytology, differential diagnosis, and management of chronic bronchitis. Chronic bronchitis involves inflammation and mucus hypersecretion in the large airways that can lead to bronchial dilation over time.