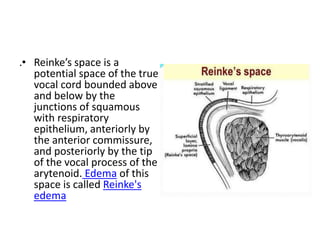
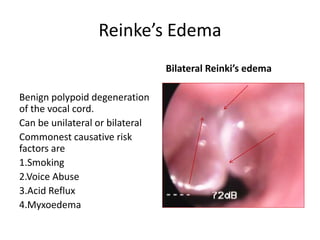
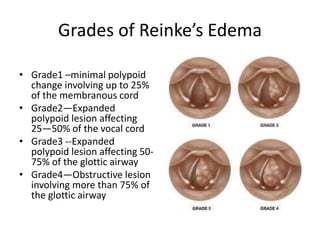
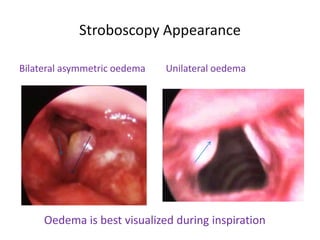
Reinke's edema is a benign polypoid degeneration of the vocal cords, commonly caused by smoking, voice abuse, acid reflux, and myxedema. It can be graded from minimal to obstructive based on the size of the edema, with symptoms including dysphonia and potential respiratory distress. Treatment involves avoiding risk factors, using steroids, and surgical options for severe cases, though dysphonia may improve but not fully normalize.