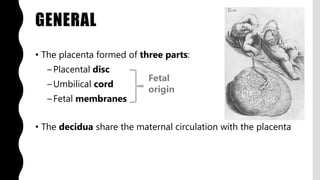
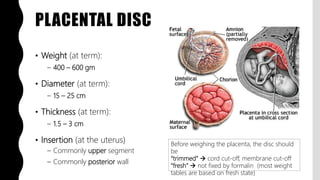
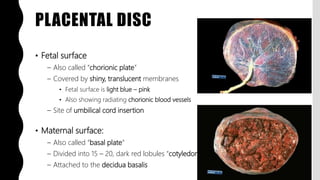
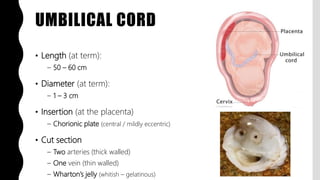
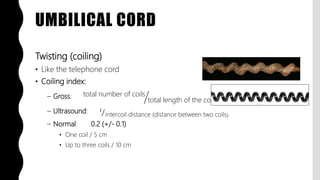
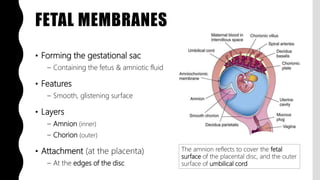
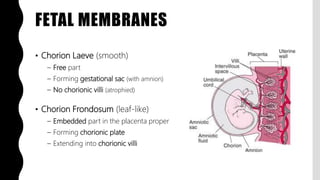
The placenta is a temporary organ that develops during pregnancy to support the growth and development of the fetus. It has protective, vascular, and endocrine functions, including delivering nutrients and oxygen to the fetus and removing waste. The placenta is composed of the placental disc, which attaches to the uterine wall, the umbilical cord that connects to the fetus, and fetal membranes surrounding the fetus. At term, the placenta weighs 400-600 grams and is 15-25 centimeters in diameter. It exchanges gases, nutrients, and waste between the mother and developing fetus through chorionic villi in the placenta and maternal blood in the uterine wall.