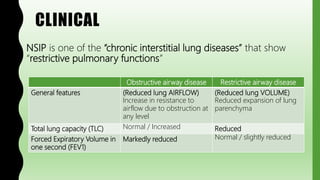
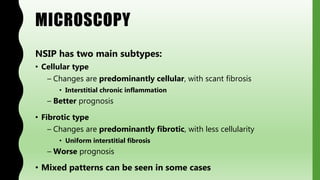
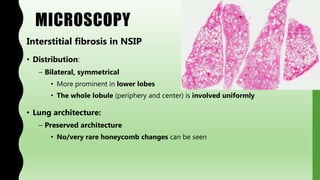
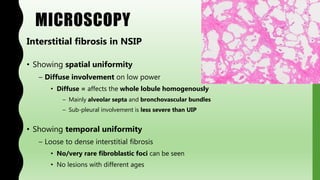
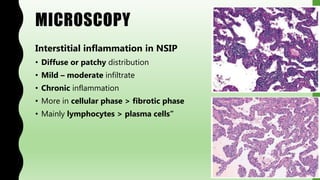
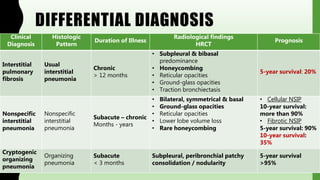
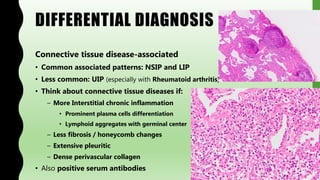
This document provides information on nonspecific interstitial pneumonia (NSIP), including its clinical features, radiological and pathological findings, differential diagnosis, and prognosis. NSIP is a chronic lung disease that presents with cough, dyspnea and fatigue. Radiologically, it appears as bilateral ground-glass opacities and reticular opacities predominantly in the lower lobes. Pathologically, NSIP has a uniform interstitial fibrosis without honeycombing. It has two subtypes, cellular and fibrotic, with the cellular type having a better prognosis. The diagnosis of NSIP is made after excluding other interstitial lung diseases.