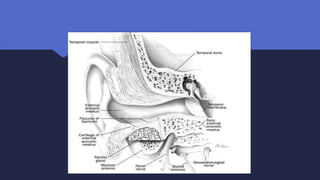
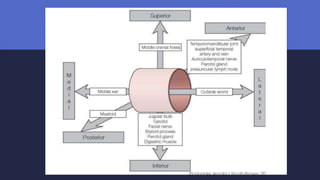
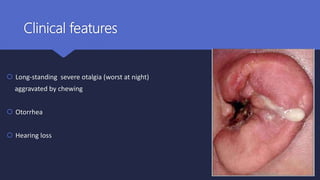
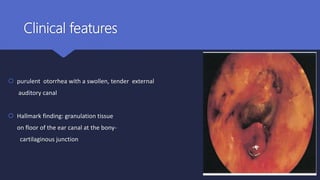
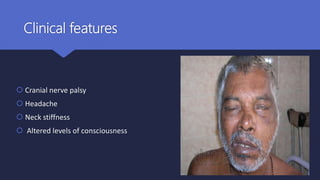
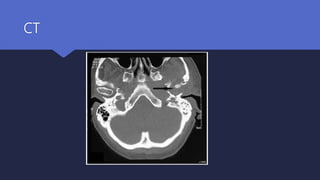
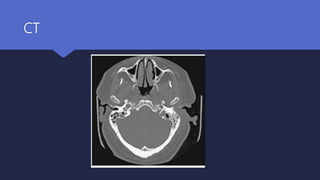
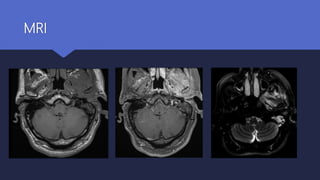
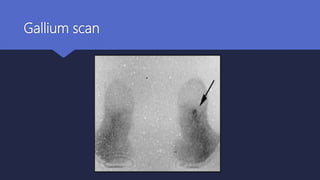
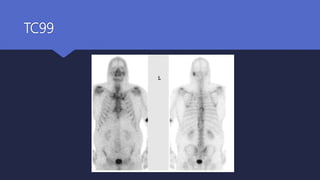
Malignant otitis externa is an aggressive infection of the external ear and skull base that commonly affects older diabetics. It is caused mainly by Pseudomonas aeruginosa bacteria invading the external ear canal and spreading through fissures in the bone. Symptoms include severe ear pain, discharge, and potentially cranial nerve palsies. Diagnosis involves culture, imaging like CT showing bone destruction, and ruling out other causes. Treatment requires long-term antibiotics like ciprofloxacin, tight blood sugar control, and sometimes hyperbaric oxygen or surgery. Prognosis has improved but mortality remains high if the infection spreads intracranially or causes multiple cranial neuropathies.