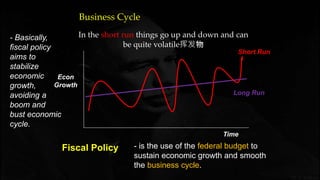
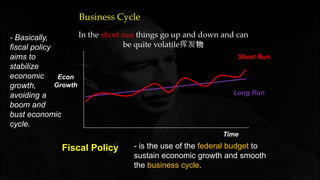
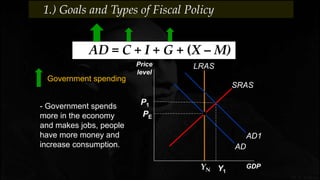
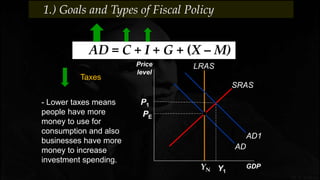
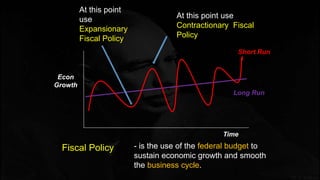
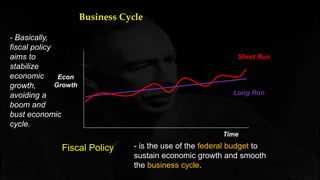
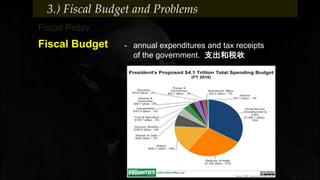
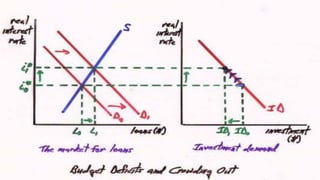
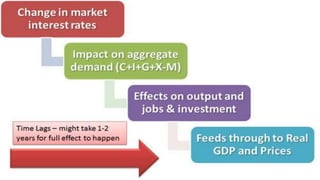
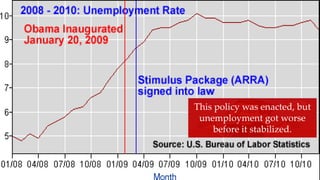
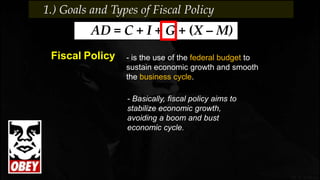
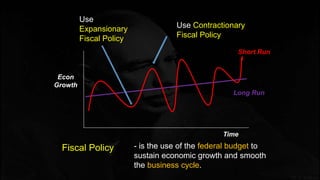
Fiscal policy aims to stabilize economic growth and smooth the business cycle using the federal budget. It can use expansionary or contractionary fiscal policy to respectively increase or decrease aggregate demand by increasing or decreasing government spending and taxes. Expansionary policy is used to stimulate the economy during recessions, while contractionary policy is used during booms. Fiscal policy implementation involves both automatic stabilizers and discretionary changes to policy and faces limitations such as political conflicts, time lags, and potential budget deficits.