1. Thailand's economy grew rapidly in the 1990s due to liberalization, foreign investment, and a fixed exchange rate policy. However, this growth was not balanced and did not strengthen Thailand's industrial base.
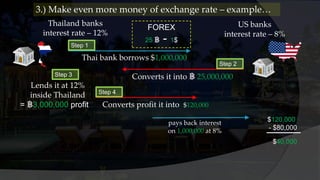
2. When other Asian currencies depreciated against the dollar in 1997 due to economic changes, Thailand could no longer maintain its fixed exchange rate. Investors fled the country and speculators attacked the baht.
3. Thailand used its dollar reserves to support the baht, but eventually ran out. It was forced to float the currency, causing a financial crisis as property values and banks collapsed under non-performing loans.