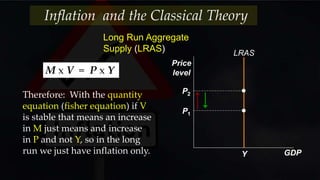
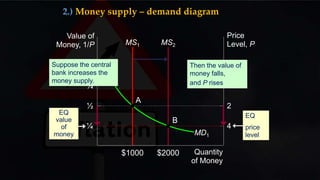
- Inflation is a sustained increase in consumer prices that results in a fall in the purchasing power of money. It is measured by changes in the Consumer Price Index (CPI) over time.
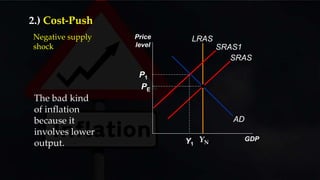
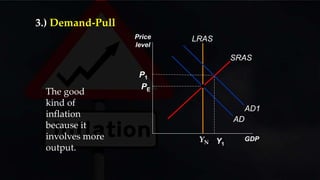
- There are two main causes of inflation - cost-push inflation which results from increases in input costs that lead firms to raise prices, and demand-pull inflation which occurs when aggregate demand grows faster than the potential output of the economy.
- The consequences of inflation include a reduction in the purchasing power of money over time, higher costs for businesses to change prices frequently ("menu costs"), and the arbitrary redistribution of income between winners and losers from inflation such as debtors and lenders.