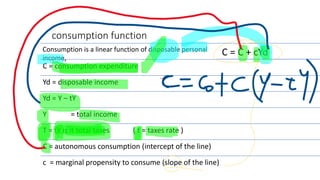
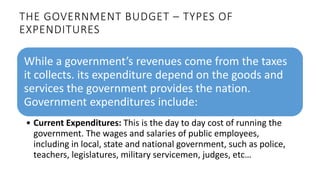
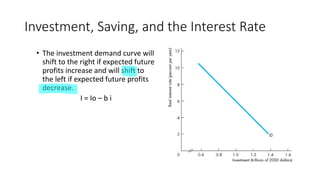
This document discusses macroeconomic concepts related to fiscal and monetary policy. It defines monetary policy as how central banks control money supply and interest rates to influence price stability and trust in currency. Fiscal policy refers to how governments use spending and taxes to influence demand, employment, inflation, and growth. The goods market is modeled using the IS curve and Keynesian cross diagram, where equilibrium income equals planned expenditure. An increase in government purchases using this model leads to a multiplier effect that increases income more than the initial change in purchases.