Embed presentation
Downloaded 39 times

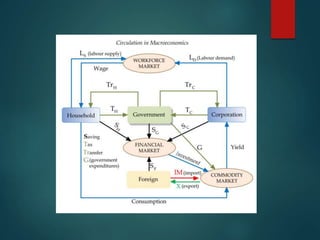








This document provides an introduction to macroeconomic concepts including consumption, investment, government spending, international trade, and applications for managers. It defines consumption as the use of goods and services to satisfy human wants, and describes the importance of consumption. It also defines investment and the different types, as well as the purposes and roles of government spending and international trade measures like exports, imports, and net exports. Finally, it discusses how macroeconomic trends can impact businesses and why managers should consider the macroeconomic environment when making decisions.








