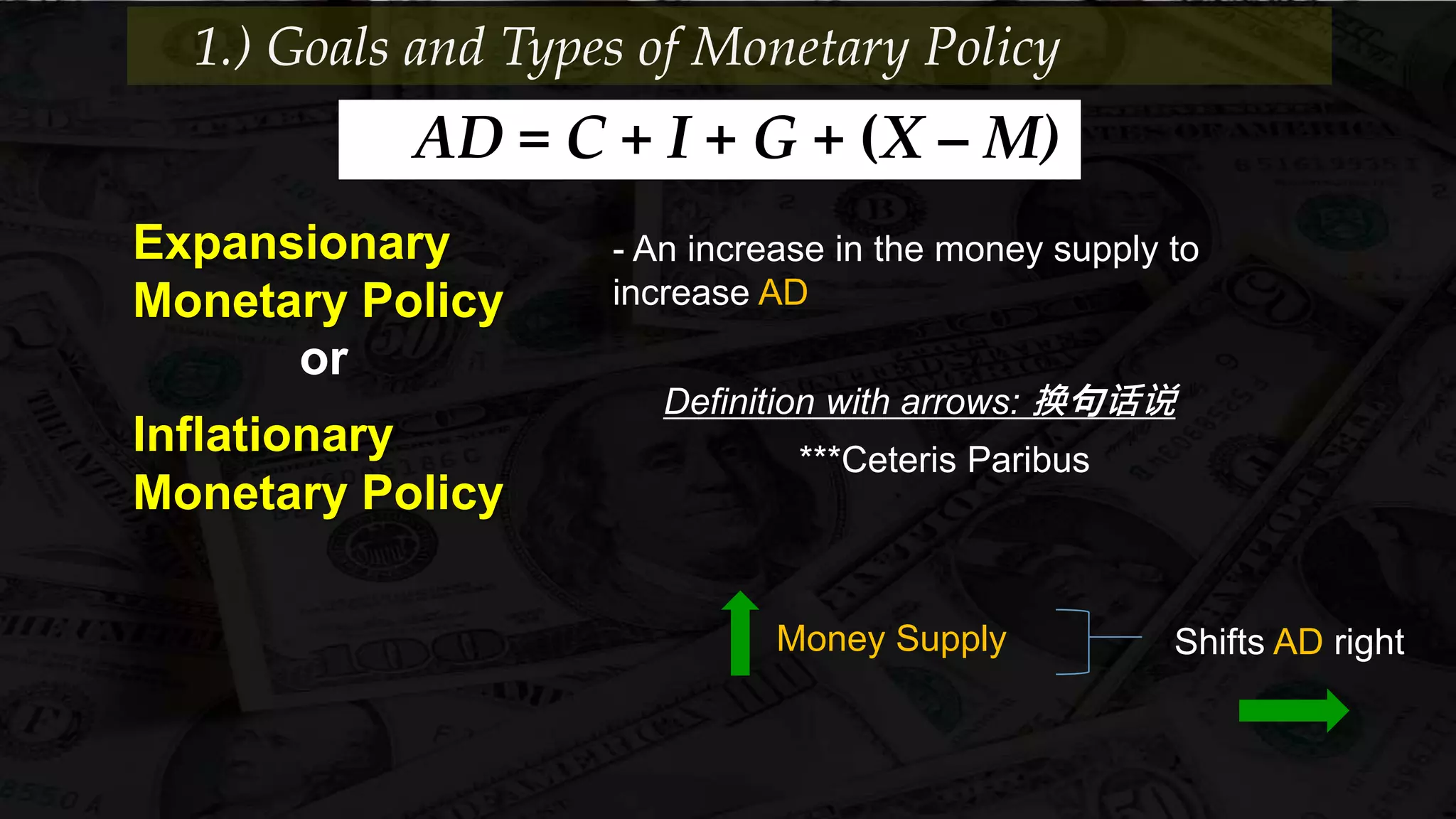
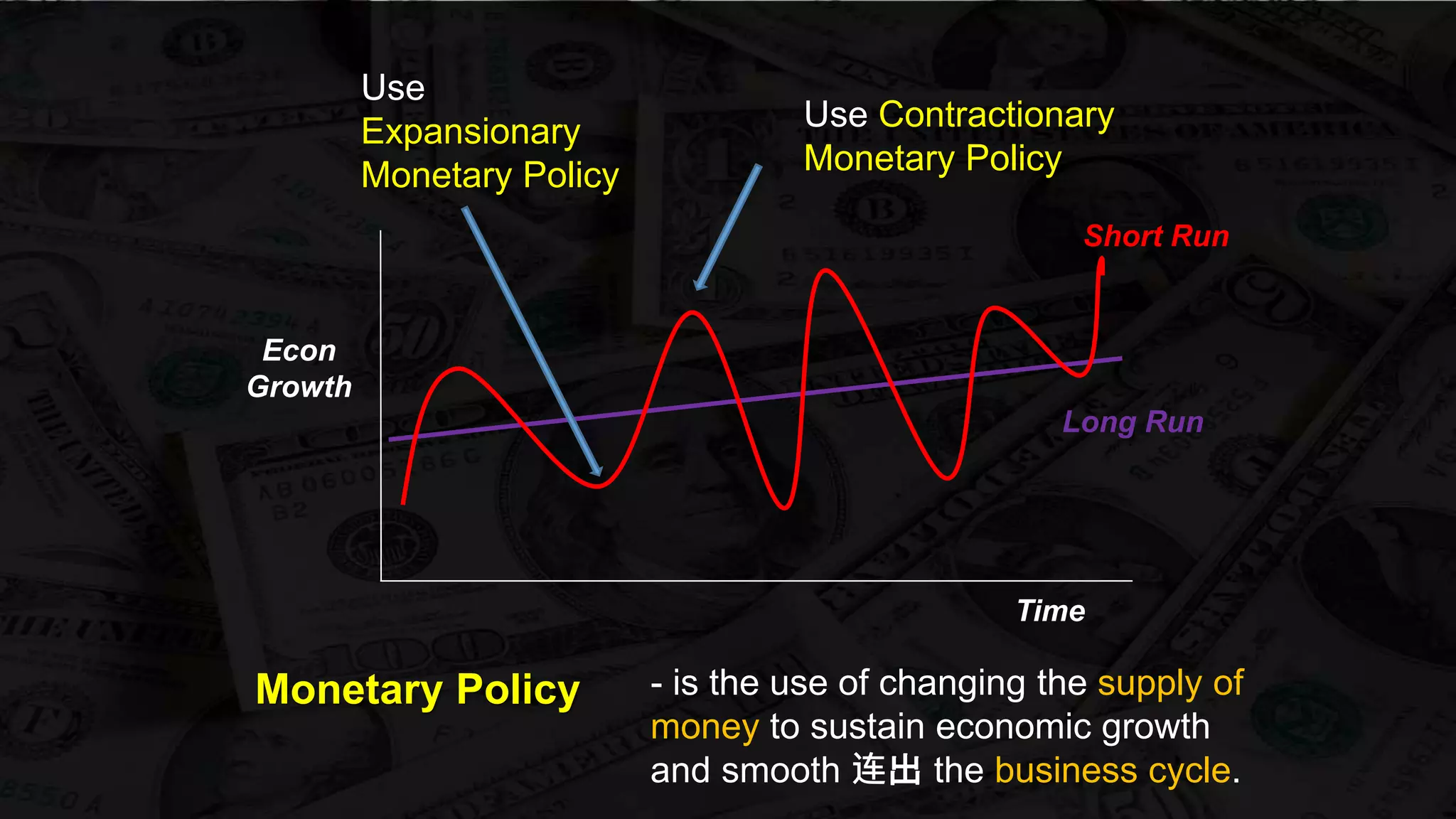
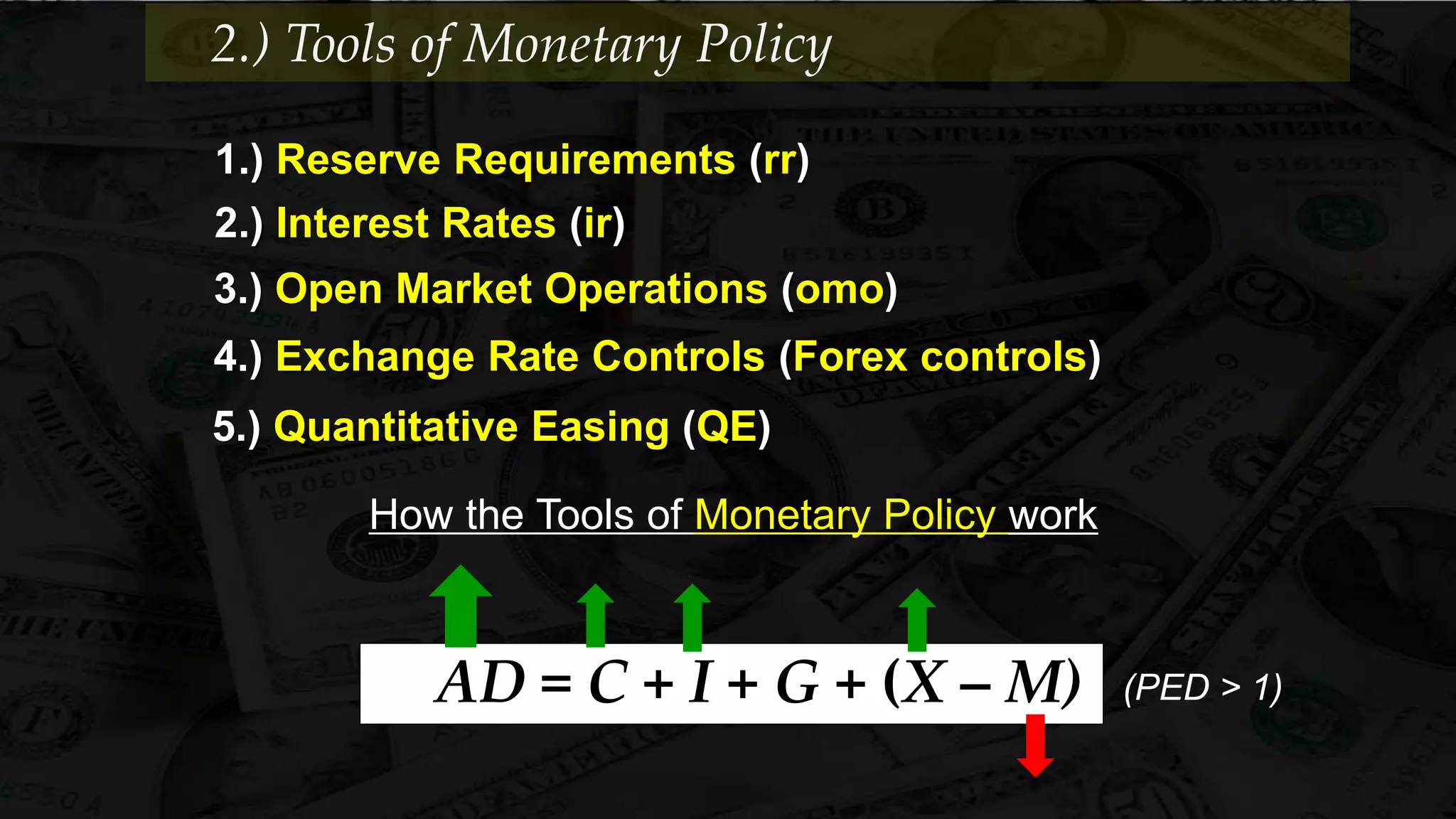
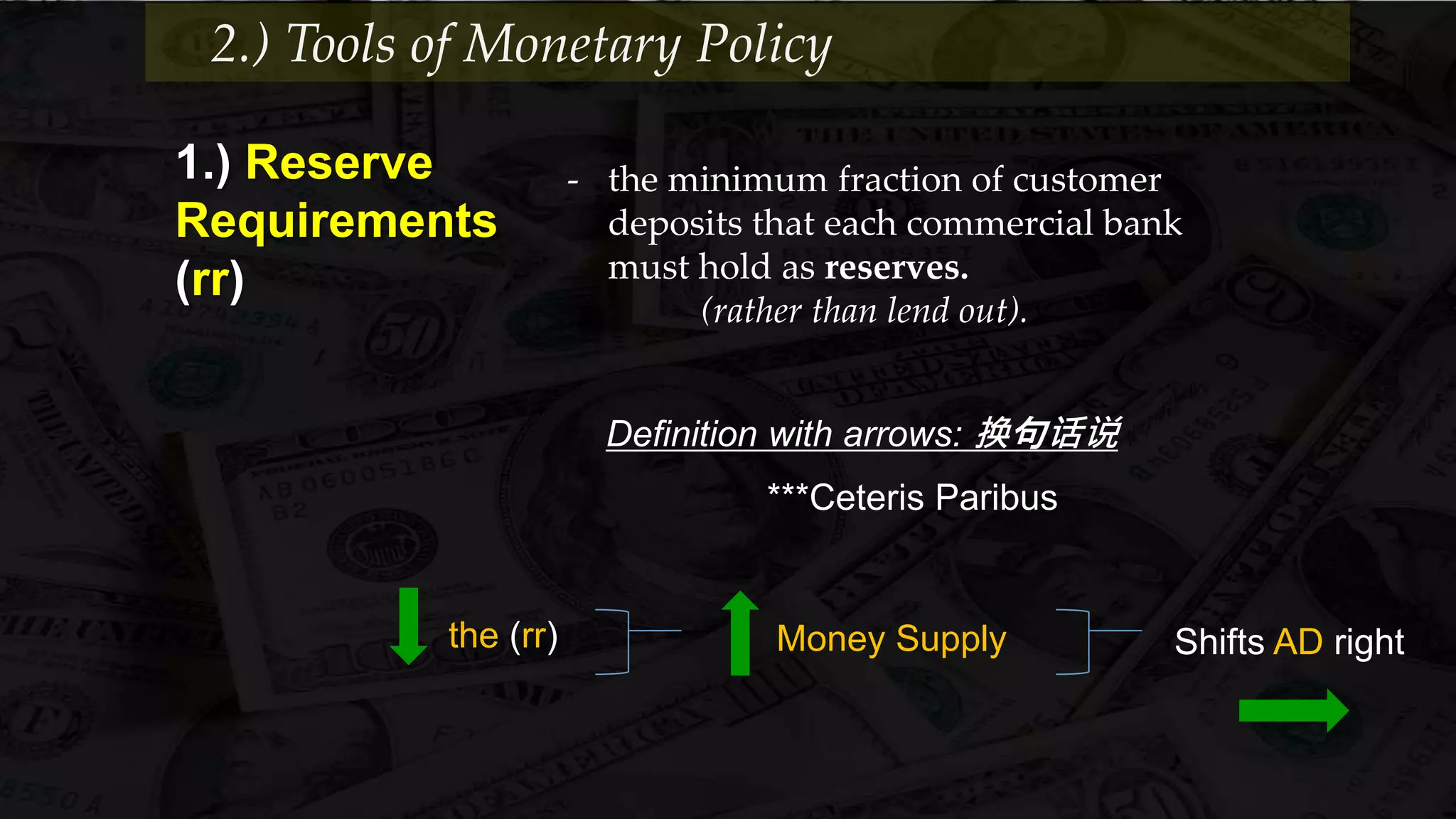
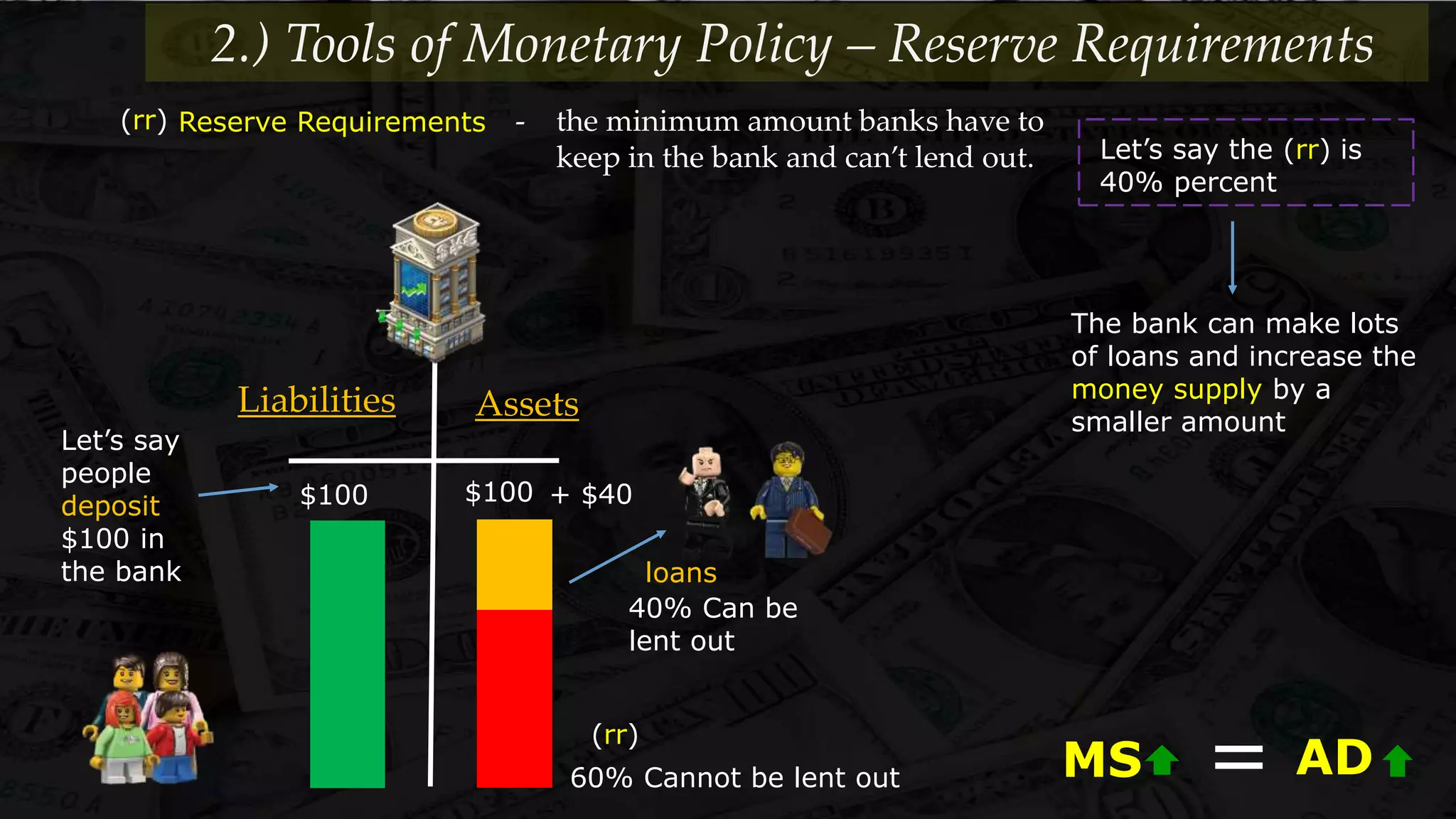
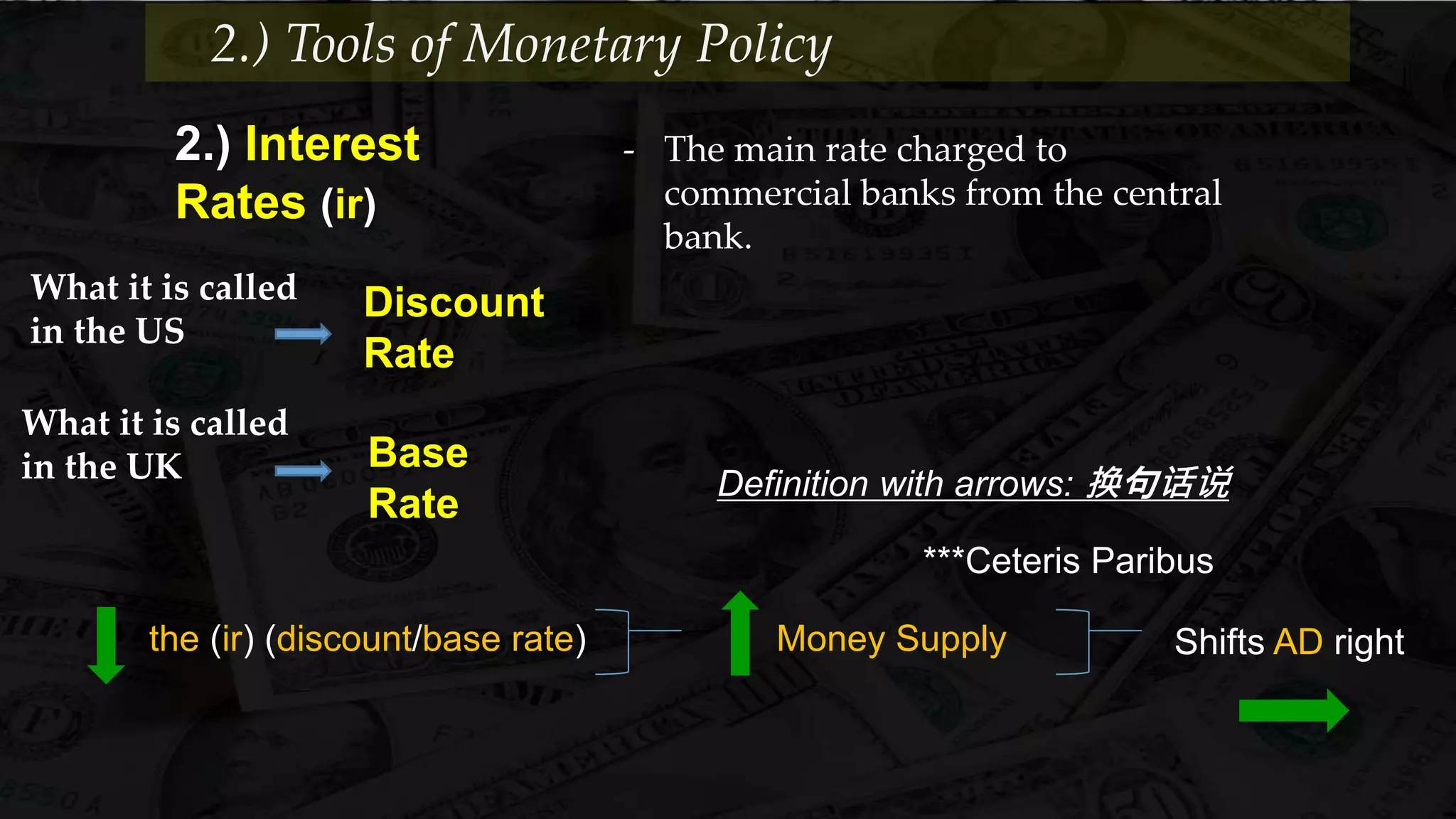
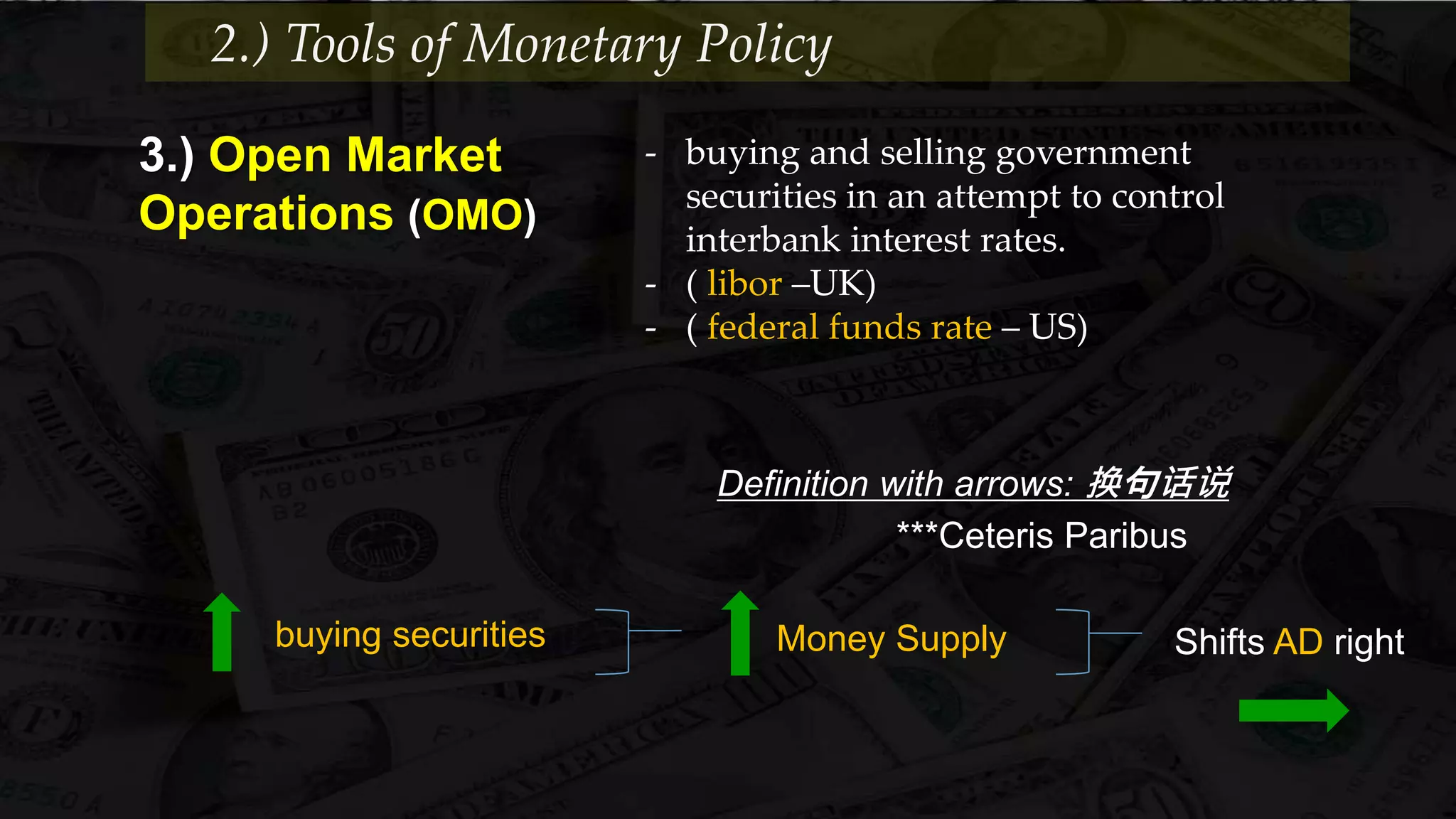
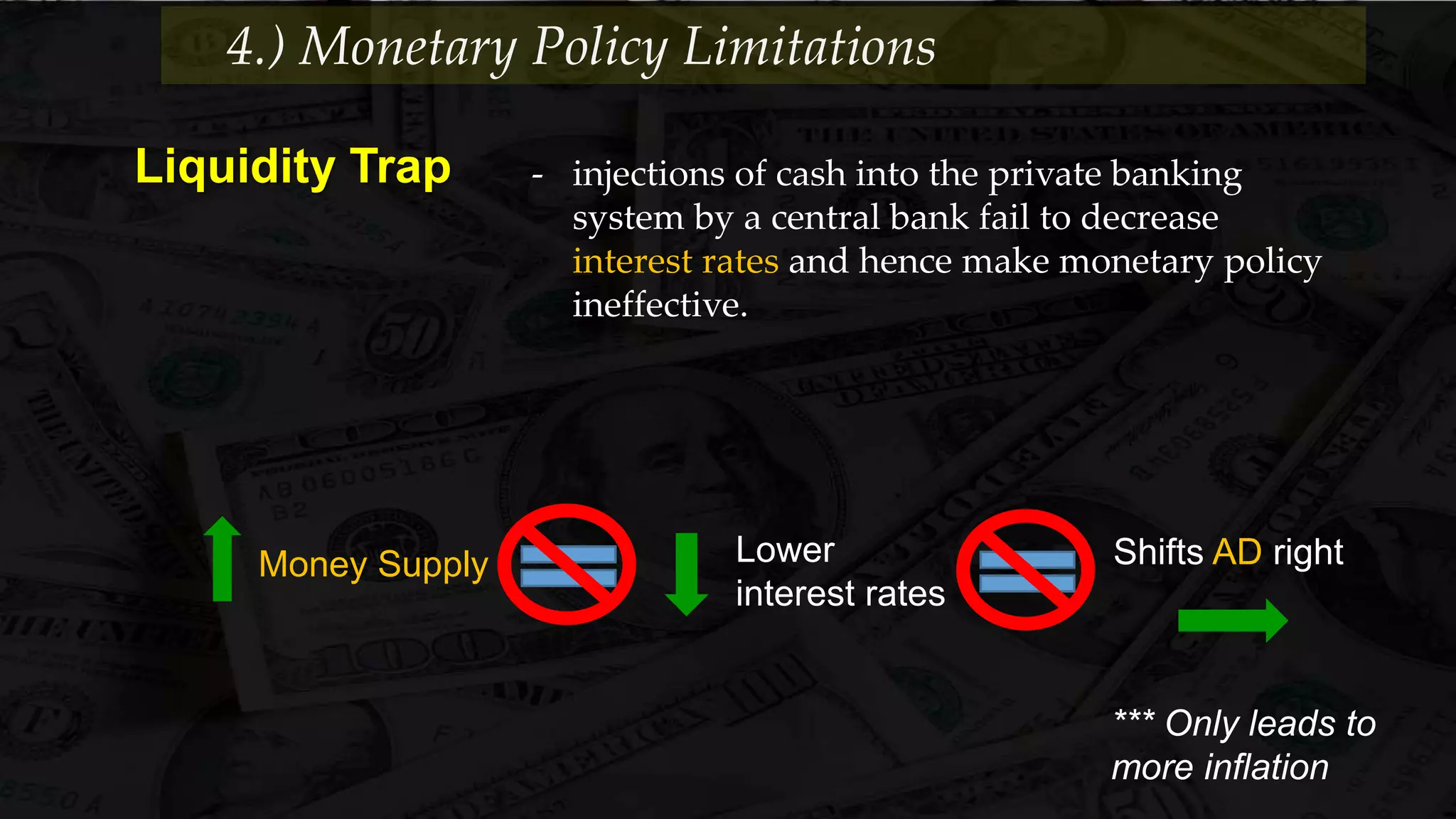
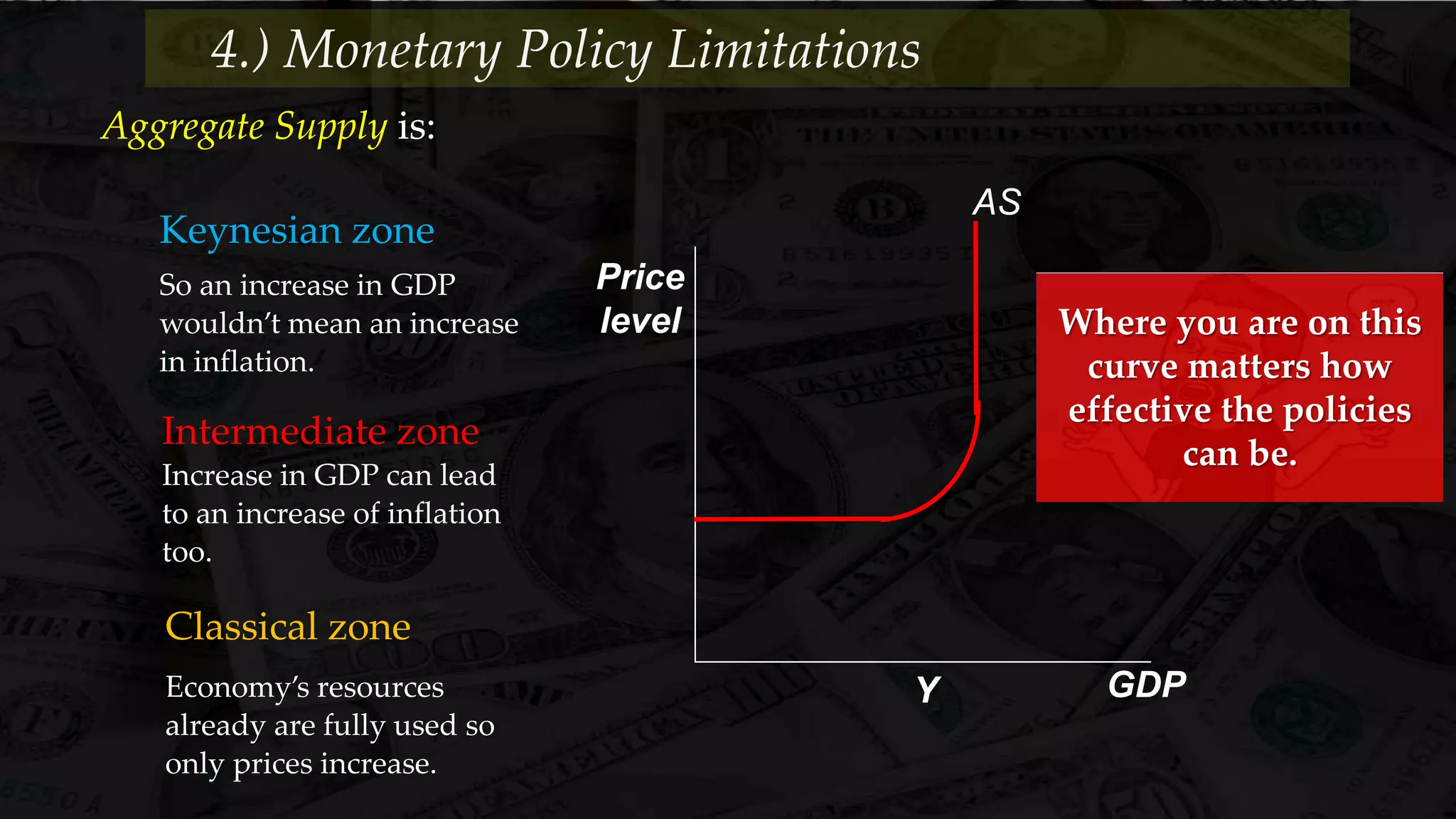
Monetary policy uses tools like interest rates, reserve requirements, and open market operations to influence the money supply and shift the aggregate demand curve to achieve goals like economic growth and stable prices. Banks create money through fractional reserve banking by lending out deposits while holding only a portion as reserves, multiplying the original money supply. However, monetary policy faces limitations when interest rates hit zero and the economy is already at full employment, as further stimulus only causes inflation without increasing output.