The document describes three basic models of the economy:
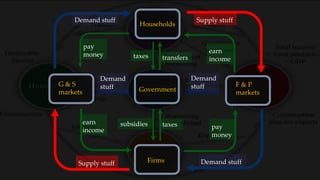
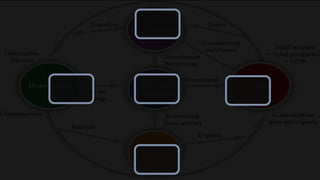
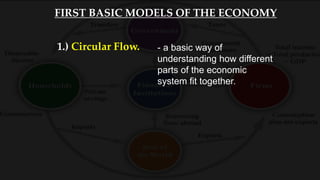
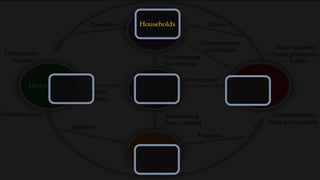
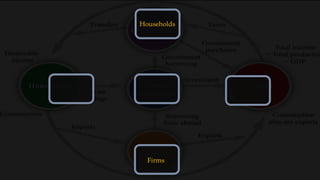
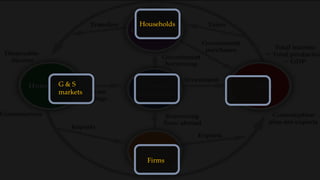
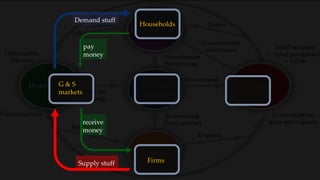
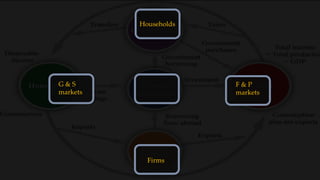
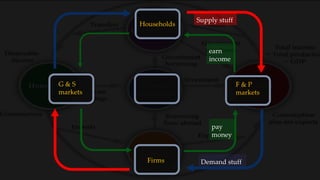
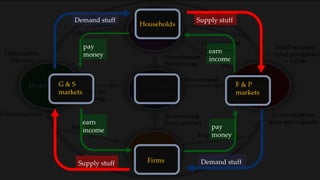
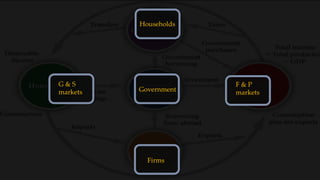
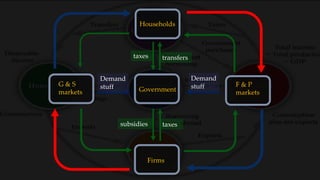
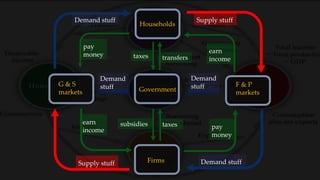
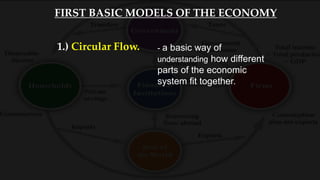
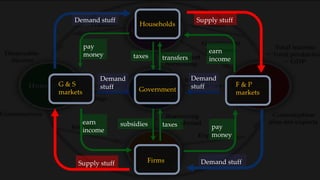
1) The circular flow model shows how households and firms interact in the goods/services and factor markets.
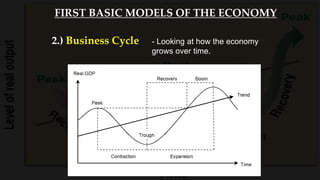
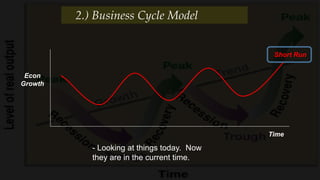
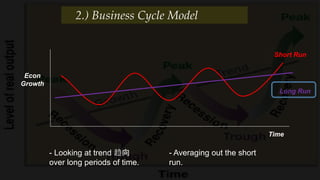
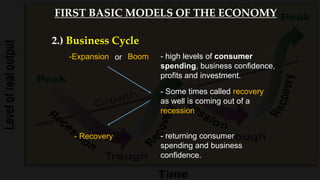
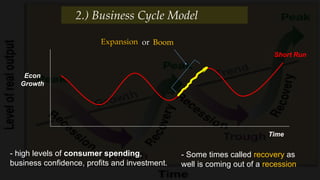
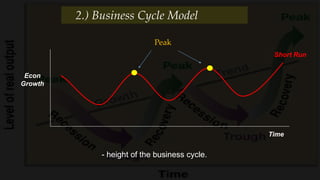
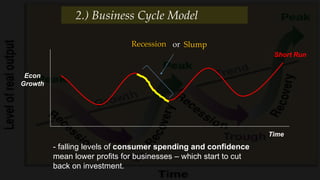
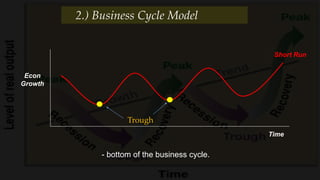
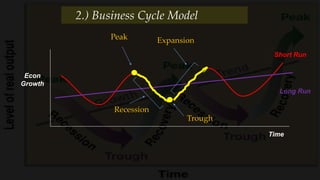
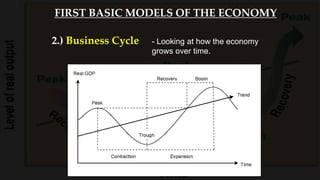
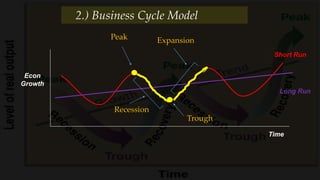
2) The business cycle model looks at how the economy fluctuates over time between periods of growth, peak, recession, and recovery.
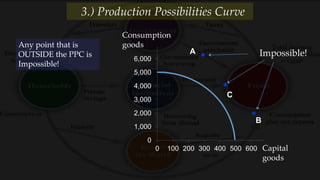
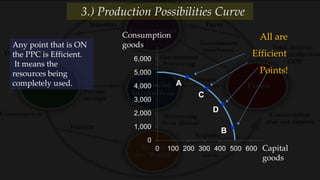
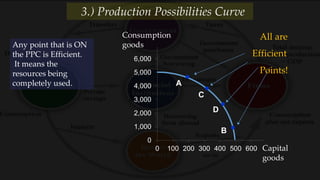
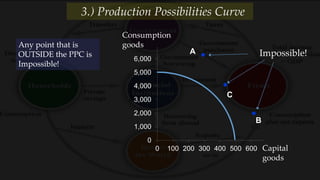
3) The production possibilities curve illustrates the tradeoffs between producing different amounts of two goods given limited resources, with points on the curve being efficient and outside being impossible.