Fiscal Policy ppt include:
1. WHAT IS FISCAL POLICY?
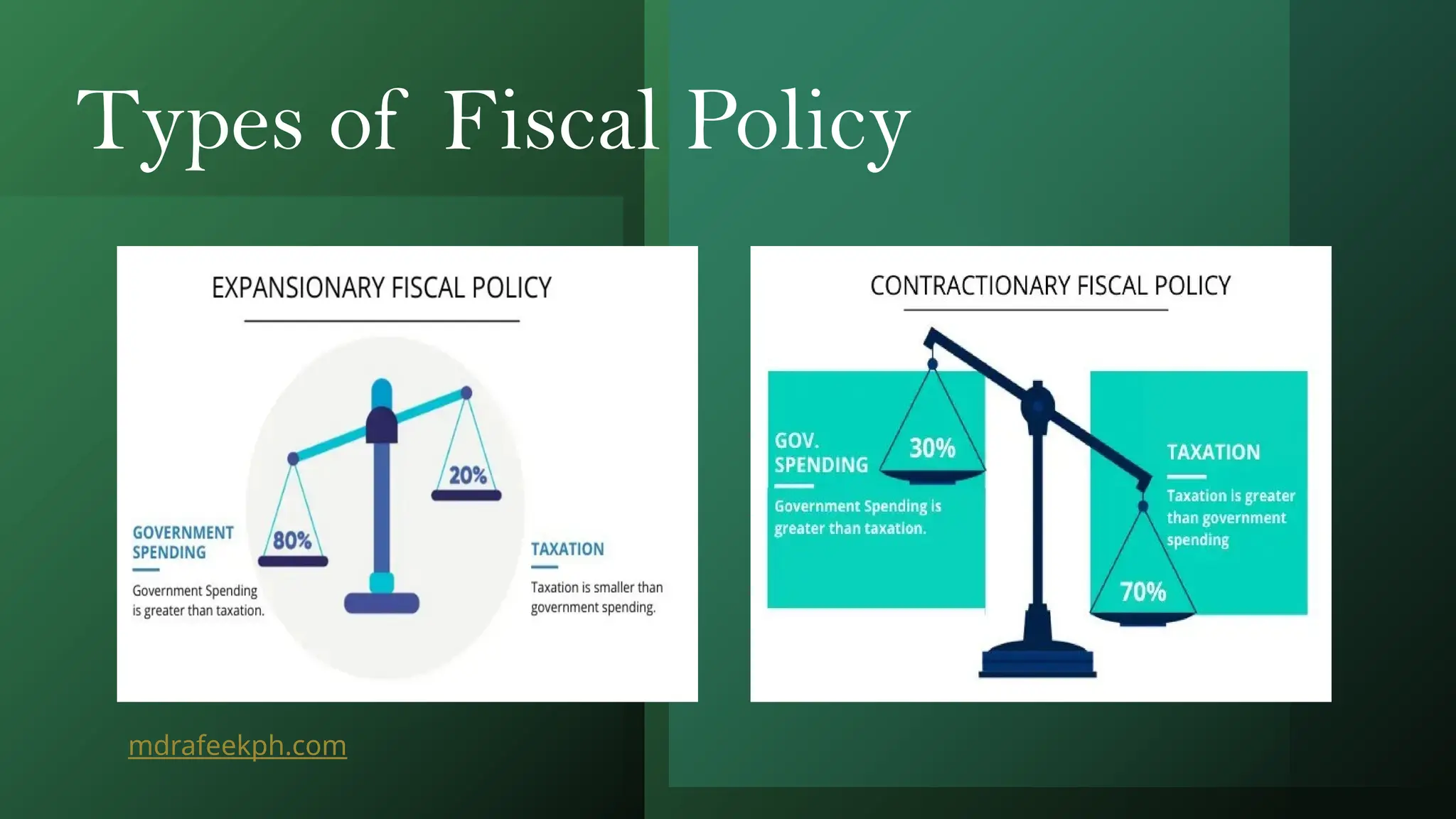
2. Types of Fiscal Policy
3. Objectives of Fiscal Policy
4. Historical Example of Fiscal Policy
5. Role of Politics in Fiscal Policy
6. FISCAL POLICY OF INDIA
7. EXAMPLES OF FISCAL POLICES OF INDIA
This is Fiscal Policy Power Point created, developed Digital Marketing Freelancer in Dubai