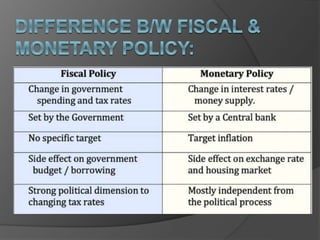
Fiscal policy refers to a government's spending and tax policies. It aims to stabilize economic growth and avoid booms and busts. Fiscal policy tools include government spending, taxation, and borrowing. Governments use these tools to influence aggregate demand and influence goals like economic growth, inflation, and unemployment. Fiscal policy plays a crucial role in mobilizing resources, boosting employment and development, and stabilizing an economy.