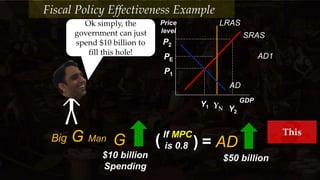
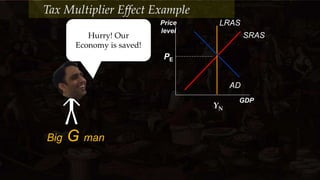
The document discusses fiscal policy effectiveness and the multiplier effect. It uses an example where the government representative, Big G Man, wants to increase aggregate demand (AD) by $10 billion to reach the GDP goal. Big G Man learns that a $1 billion increase in government spending will actually increase AD by $5 billion due to the multiplier effect, where each dollar of initial spending recirculates in the economy and generates further spending. The multiplier depends on the marginal propensity to consume (MPC), and is calculated as 1/(1-MPC). The example illustrates how the multiplier amplifies the impact of fiscal policy on AD and GDP.