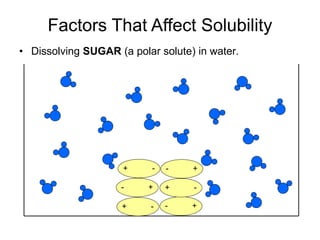
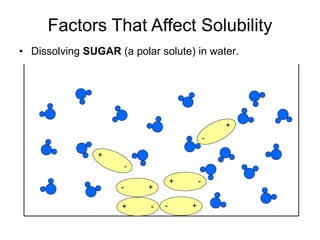
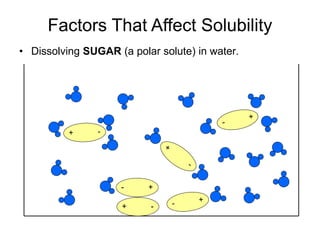
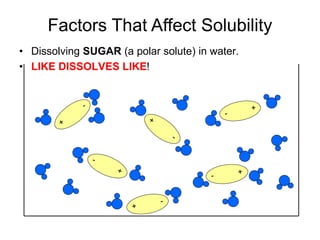
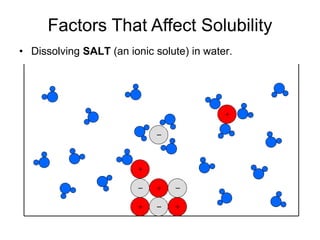
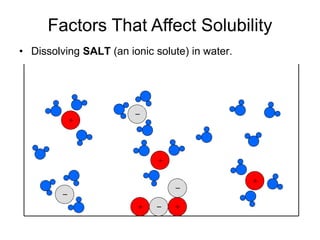
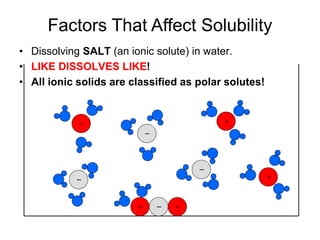
The document discusses the solubility of solutions and factors that affect solubility. It states that solubility is the maximum amount of solute that can dissolve in a solvent. The key factors are the nature of the solute and solvent, with like dissolving like (polar in polar, nonpolar in nonpolar). Temperature also affects solubility, with most solutes being more soluble in hotter solvents. Pressure only affects the solubility of gases in liquids. Examples demonstrate sugar dissolving well in water, wax not dissolving in water, and salt dissolving via ion-dipole interactions with water's polar molecules.