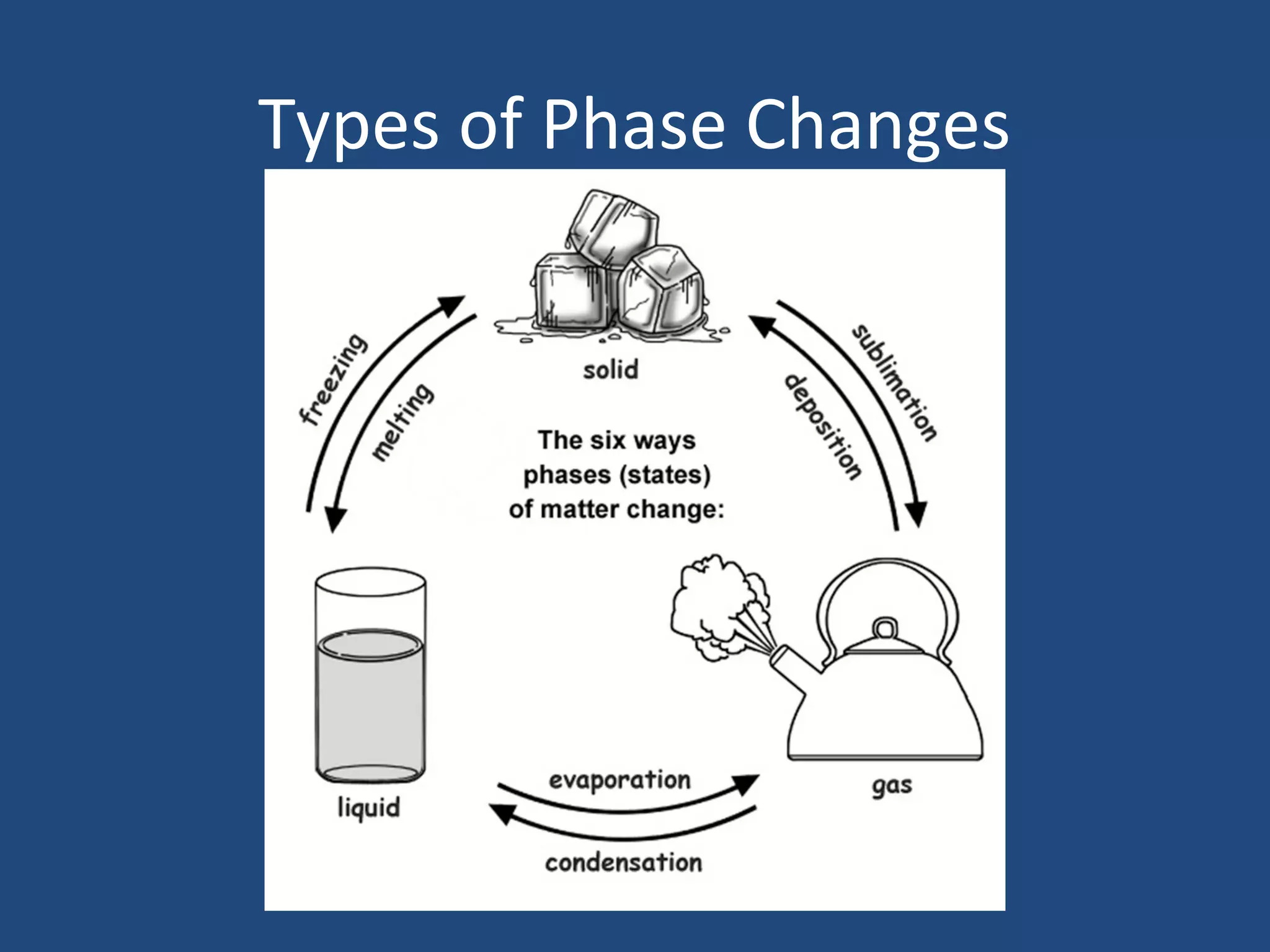
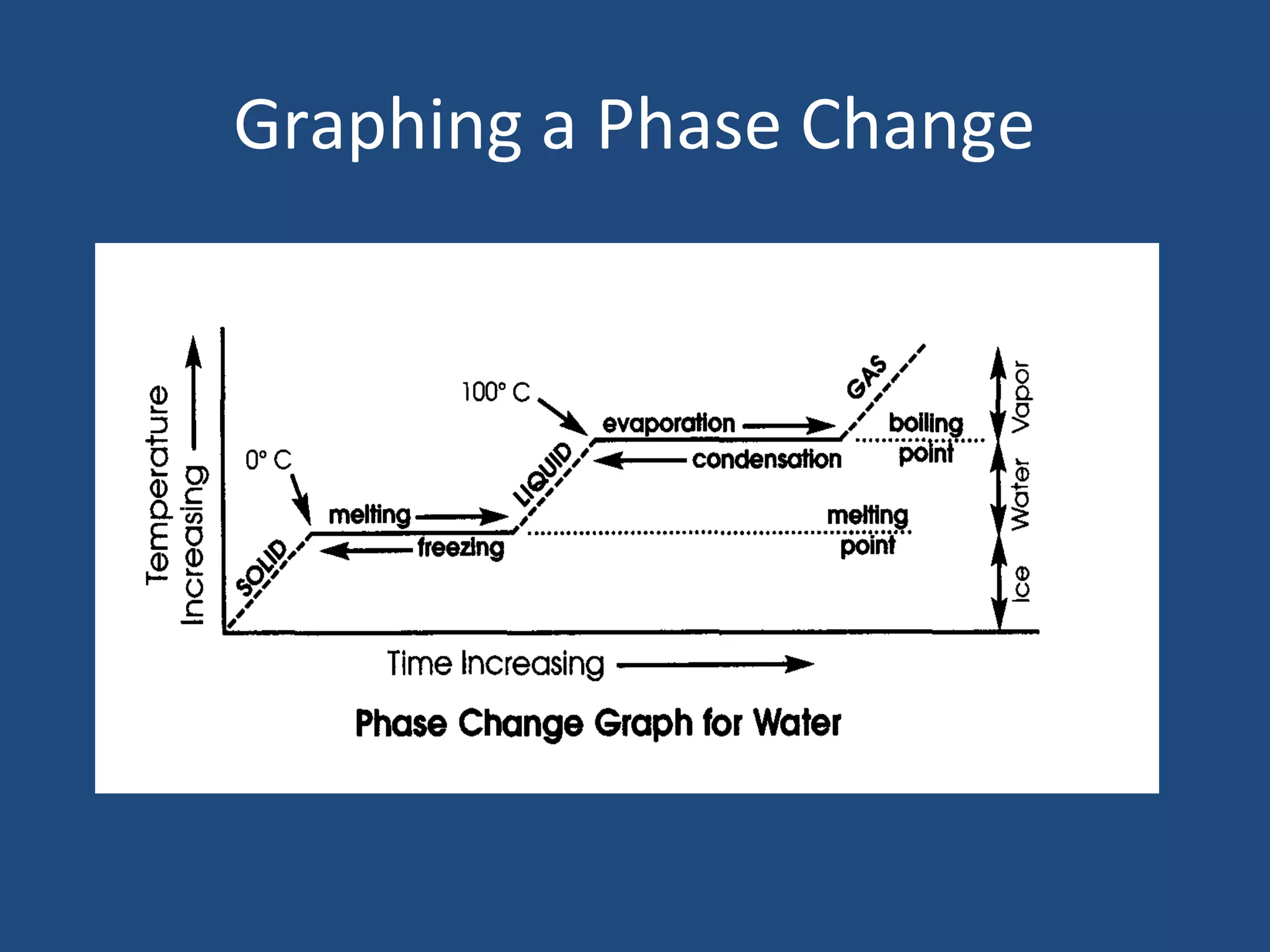
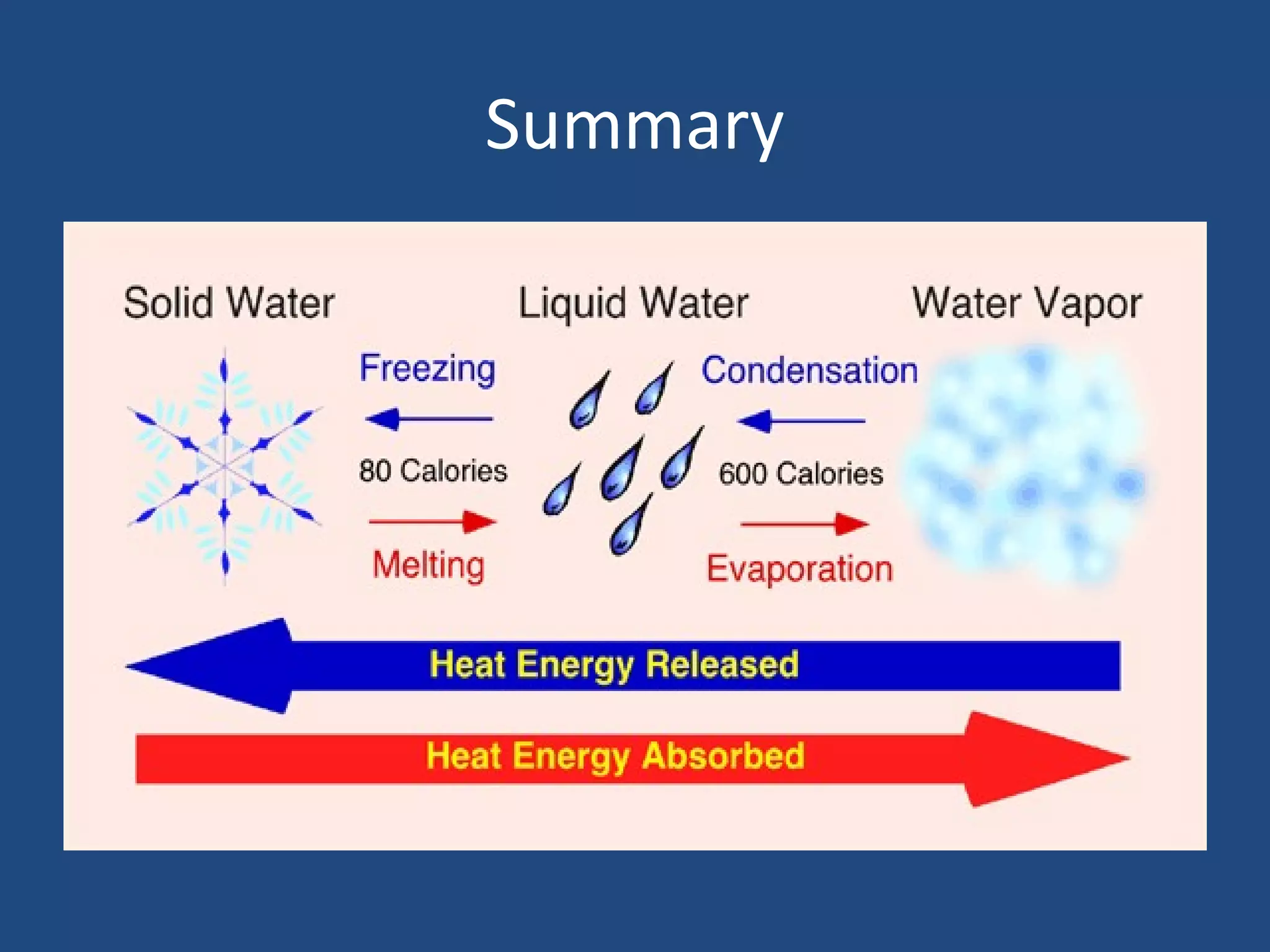
Phase changes occur when matter transitions between solid, liquid, and gas states. During a phase change, molecules either absorb or release heat energy as they speed up or slow down. There are several types of phase changes, including melting (solid to liquid), freezing (liquid to solid), vaporization/boiling (liquid to gas), evaporation, condensation, and sublimation. A key characteristic of phase changes is that the temperature remains constant despite an exchange of heat energy, as the molecules rearrange their structure.