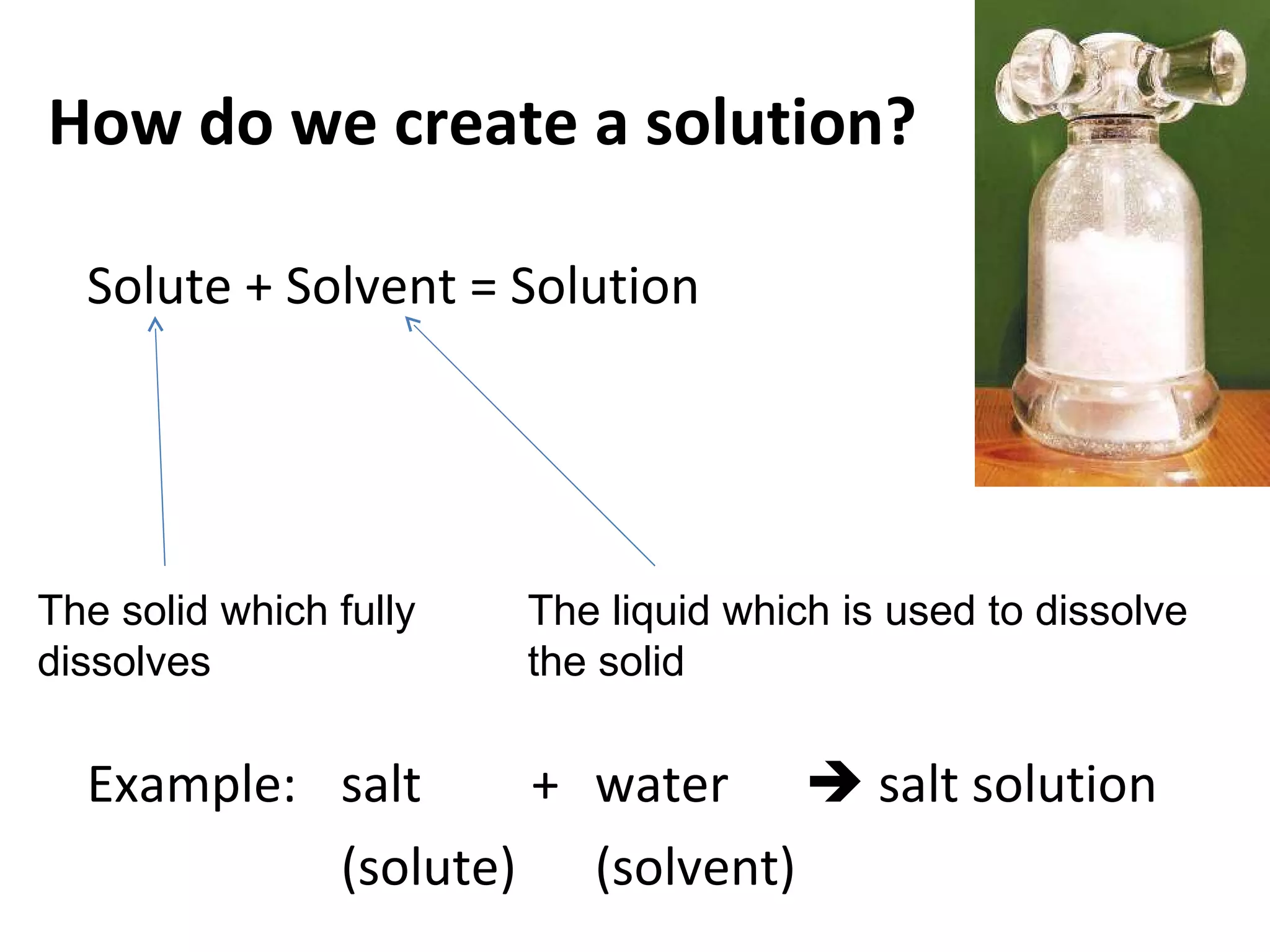
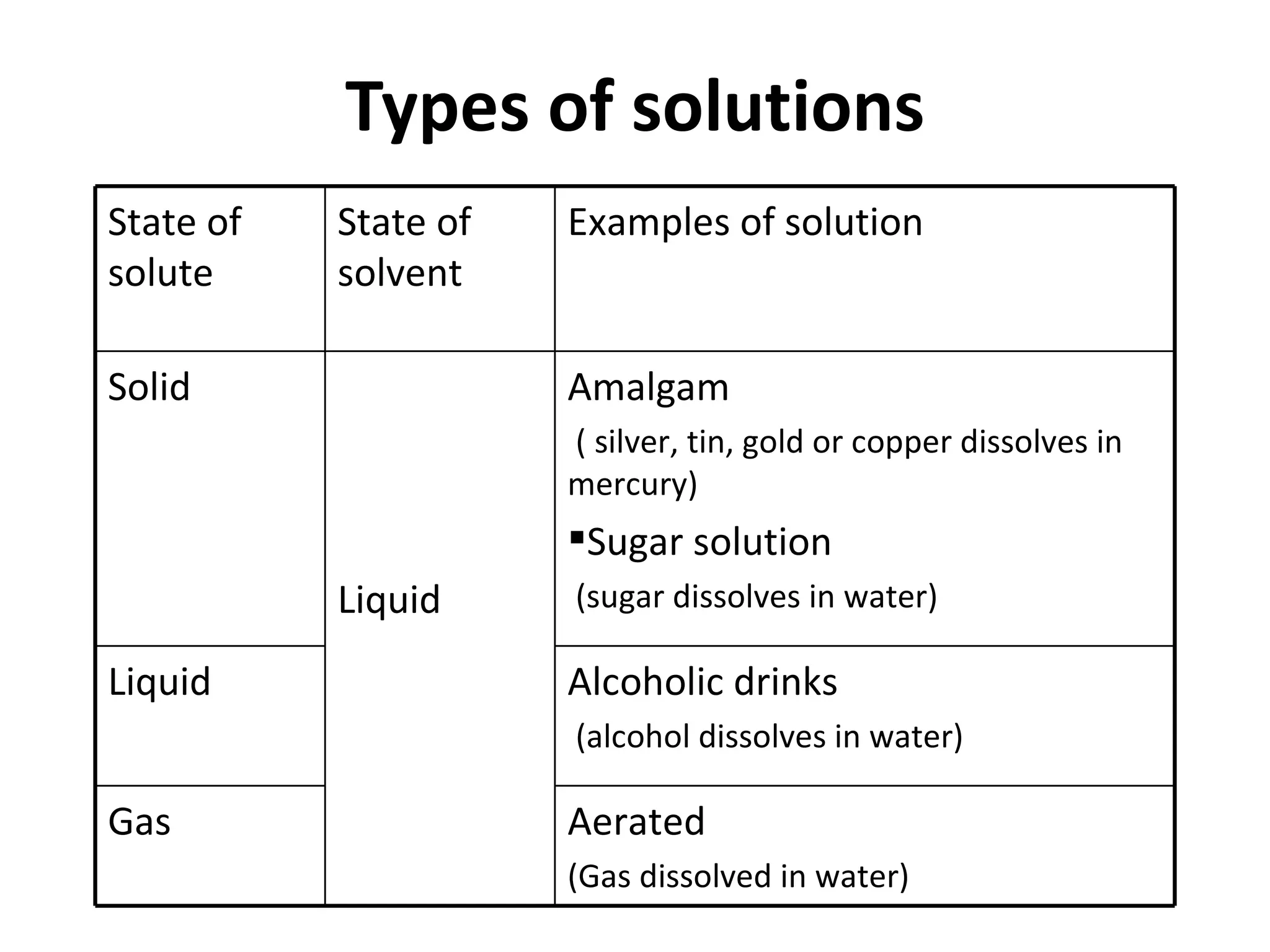
Solutions are homogeneous mixtures where solute particles are evenly distributed throughout a solvent. A solution is formed when a solute dissolves completely in a solvent such as dissolving salt in water. Solutions are used widely in homes and industries, for example soap dissolving in water for washing and dyes dissolving in water for fabric coloring. Solutions can have solutes and solvents that are solids, liquids or gases.