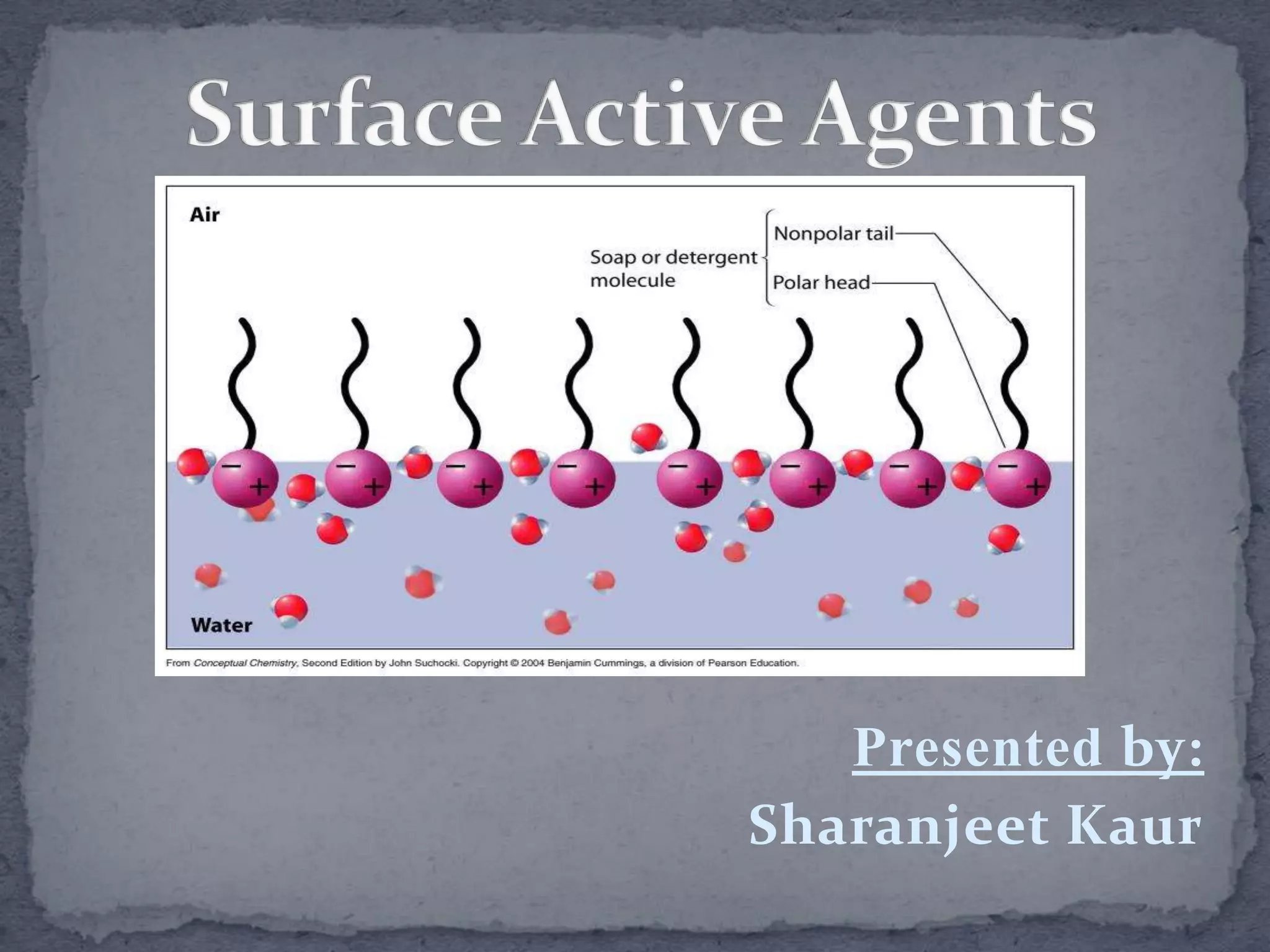
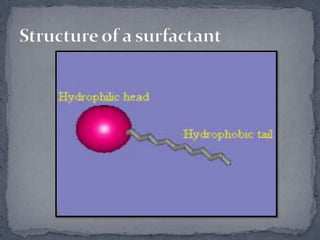
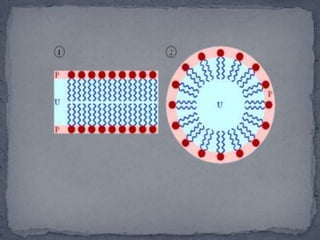
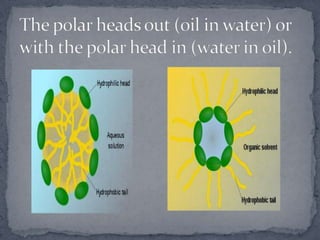
Surface active agents, also known as surfactants, are amphipathic molecules that contain both hydrophilic and hydrophobic portions. They can interact with both polar and non-polar substances, increasing the solubility of insoluble substances. In water, surfactant molecules form spherical clusters called micelles with the non-polar ends on the inside and polar ends on the outside. Surfactants are classified as anionic, cationic, non-ionic, or amphoteric based on their charge, and can be used as detergents, emulsifiers, wetting agents, and other products.