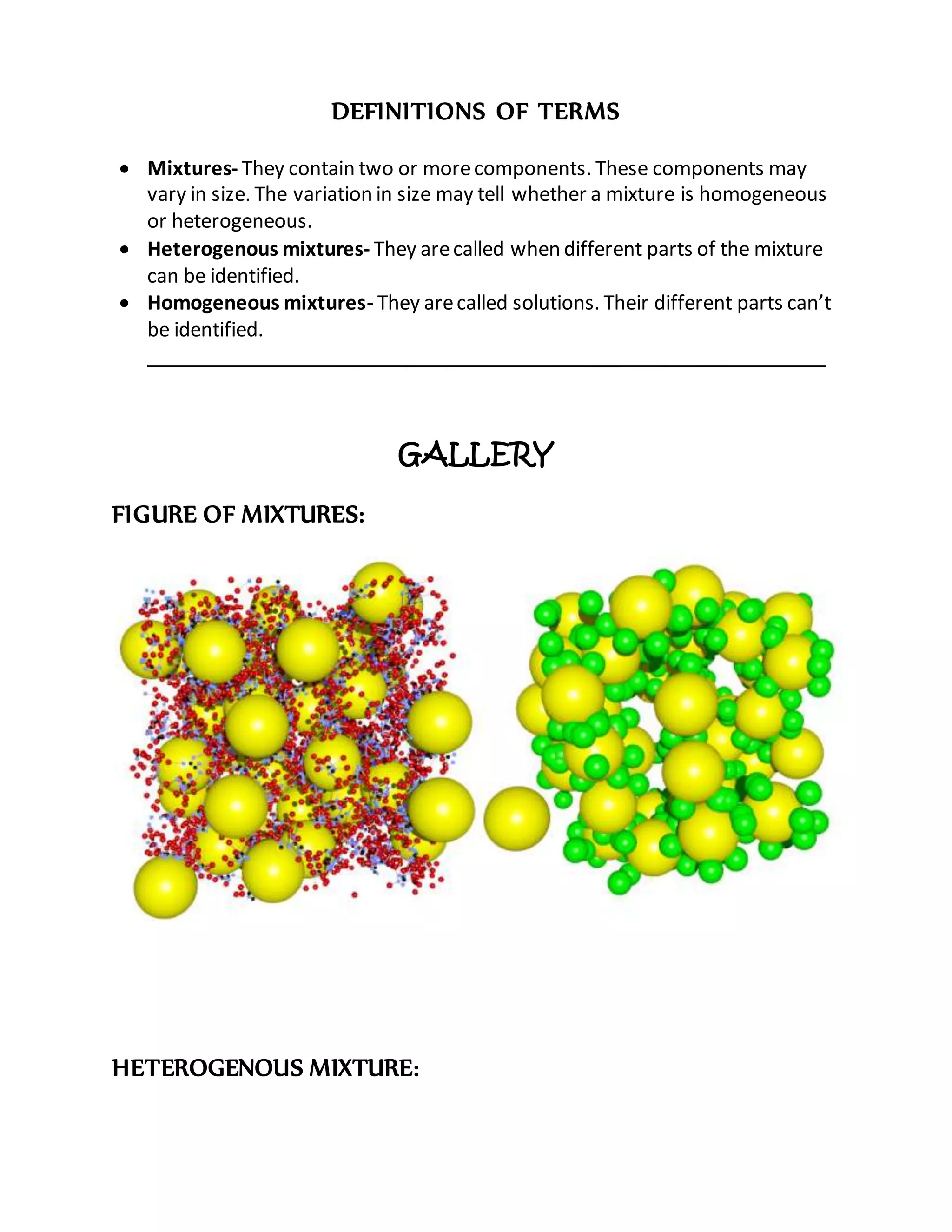
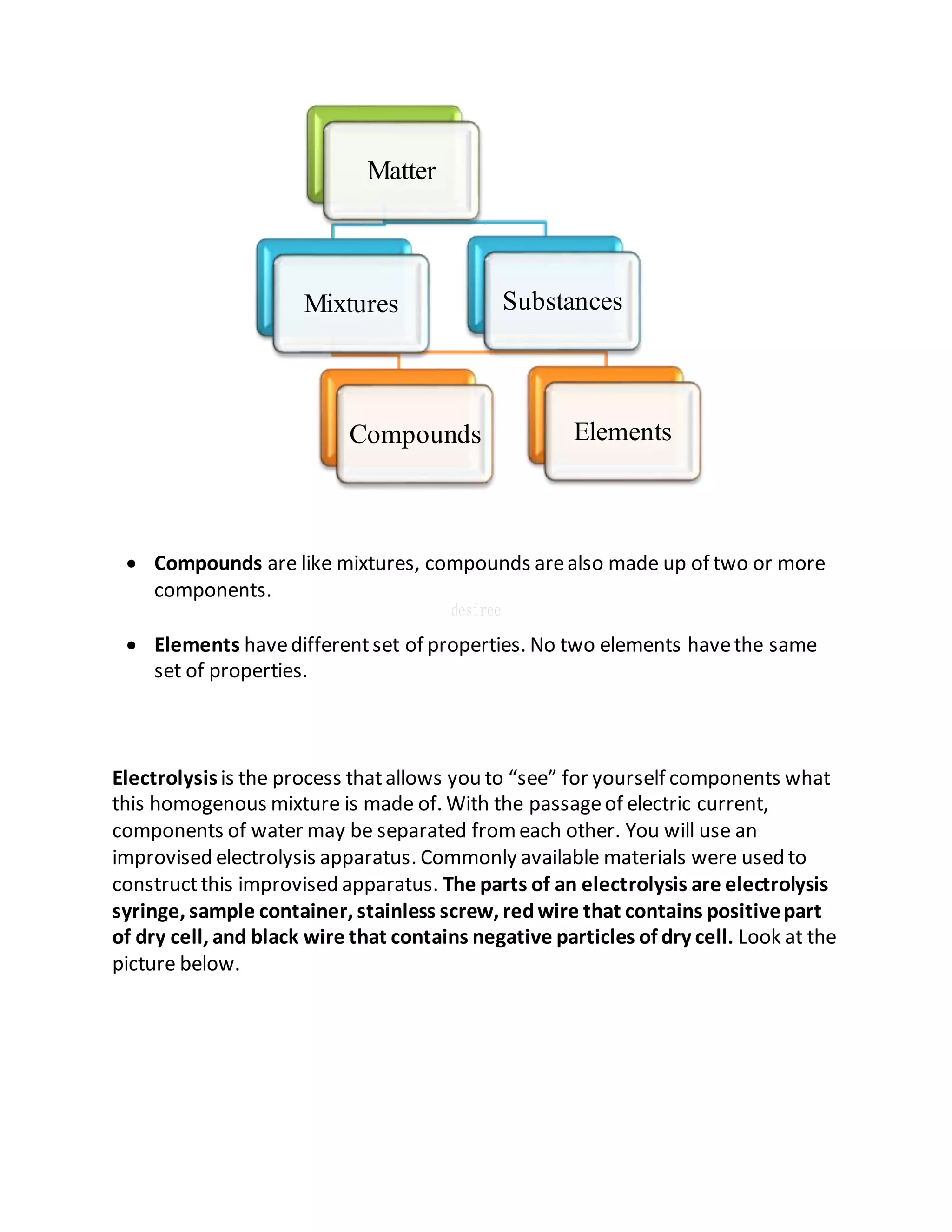
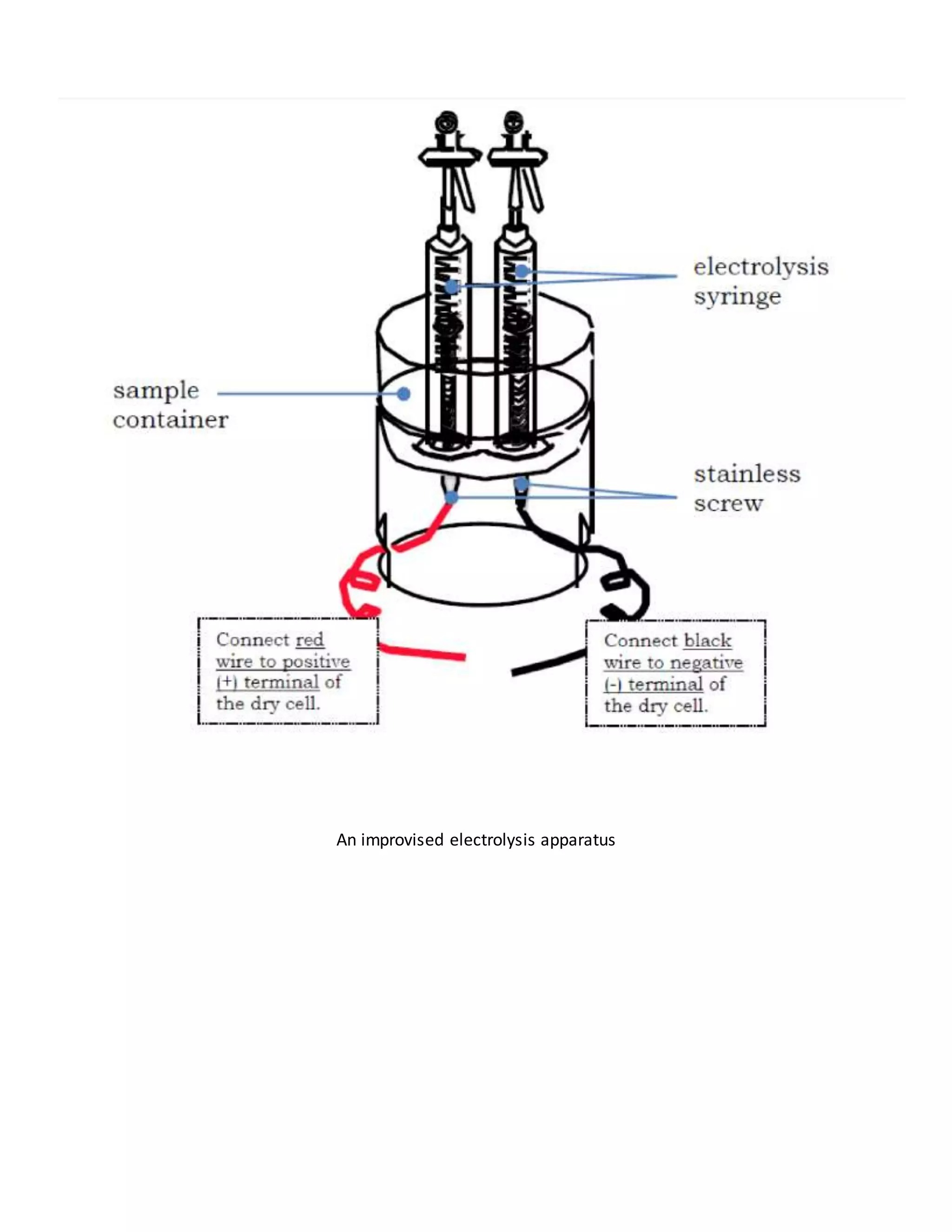
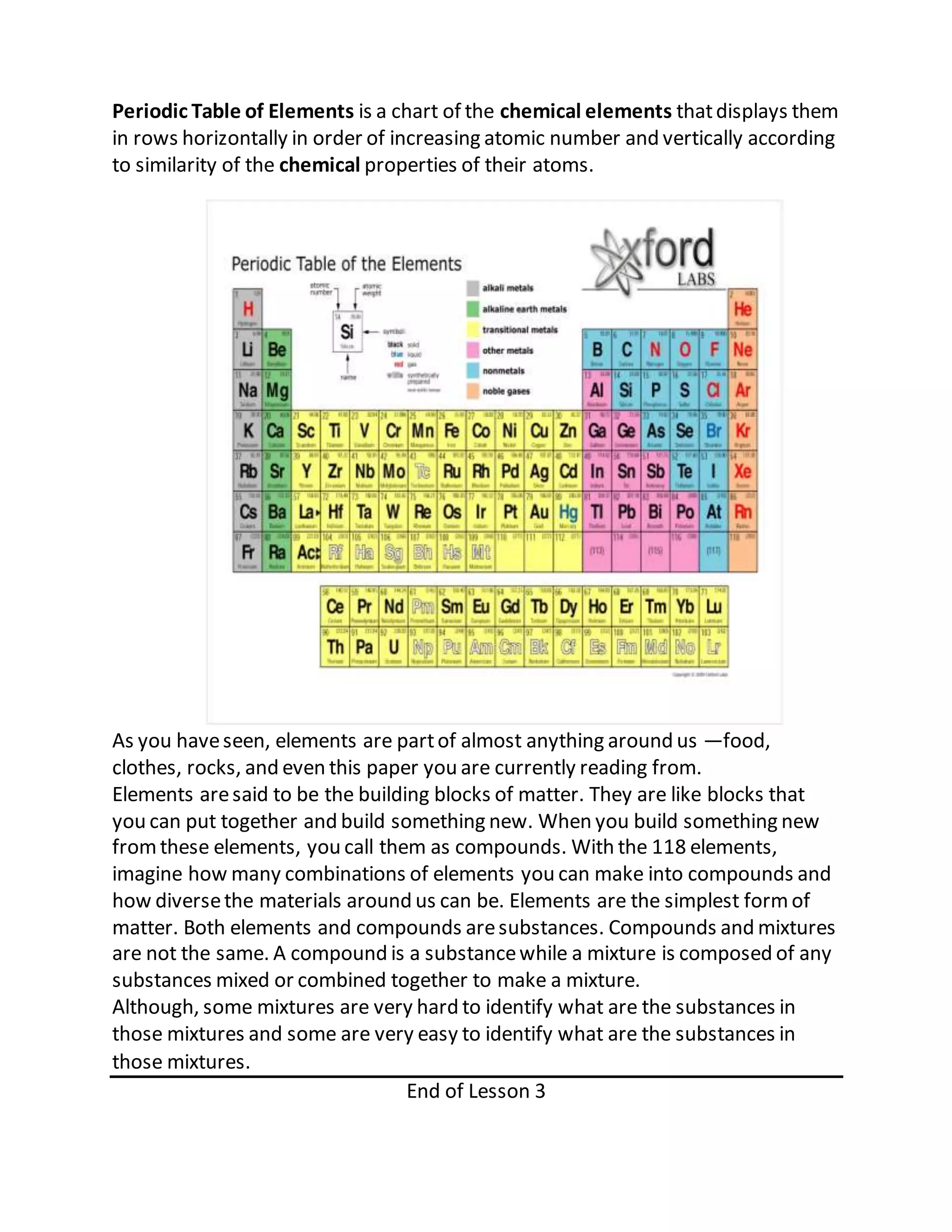
This document defines key terms related to solutions, mixtures, and substances. It discusses how homogeneous mixtures are called solutions, and that solutions can contain solids dissolved in liquids, gases dissolved in liquids, or other combinations. It also explains the difference between saturated and unsaturated solutions, and how concentration describes the relative amounts of solute and solvent in a solution.