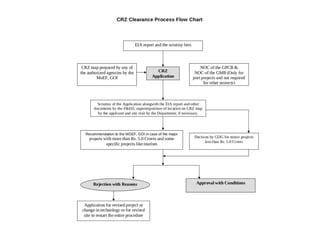
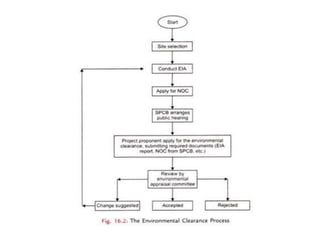
The document discusses India's key environmental clearance acts and the process for obtaining environmental clearance to set up industrial units or projects. The process involves screening projects to determine if clearance is needed, scoping environmental impact assessments, submitting applications and environmental statements, conducting public hearings, evaluation by pollution control boards and environmental appraisal committees, and issuance of no-objection certificates if standards are met. The main purpose is to assess environmental impacts and minimize them.