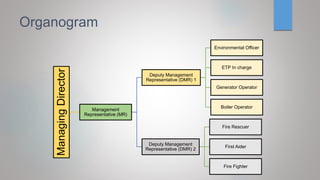
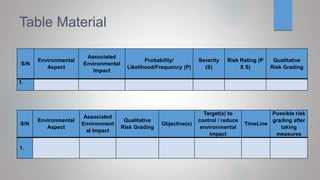
The document outlines an environmental management plan (EMP) for a project. It discusses the purpose and components of an EMP, which is to ensure environmental sustainability and compliance. The EMP covers managing environmental impacts, establishing policy, complying with laws, identifying project impacts, and minimizing negative effects. It describes monitoring environmental performance, training, and emergency response procedures. Stakeholders are mapped and an organizational structure is provided. The EMP also addresses legal requirements, risk assessment, objectives to reduce impacts, and monitoring compliance.