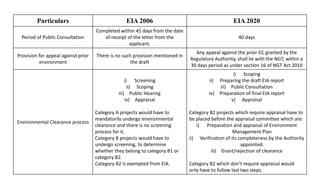
The document outlines the Environmental Impact Assessment (EIA) process as regulated by the Ministry of Environment, Forest and Climate Change, focusing on the 2020 draft amendments. Key changes include categories for project classification, reduced requirements for public consultation, and the controversial allowance for post-facto approvals. The new draft also alters compliance reporting requirements and raises concerns about the transparency and accountability of EIA procedures.