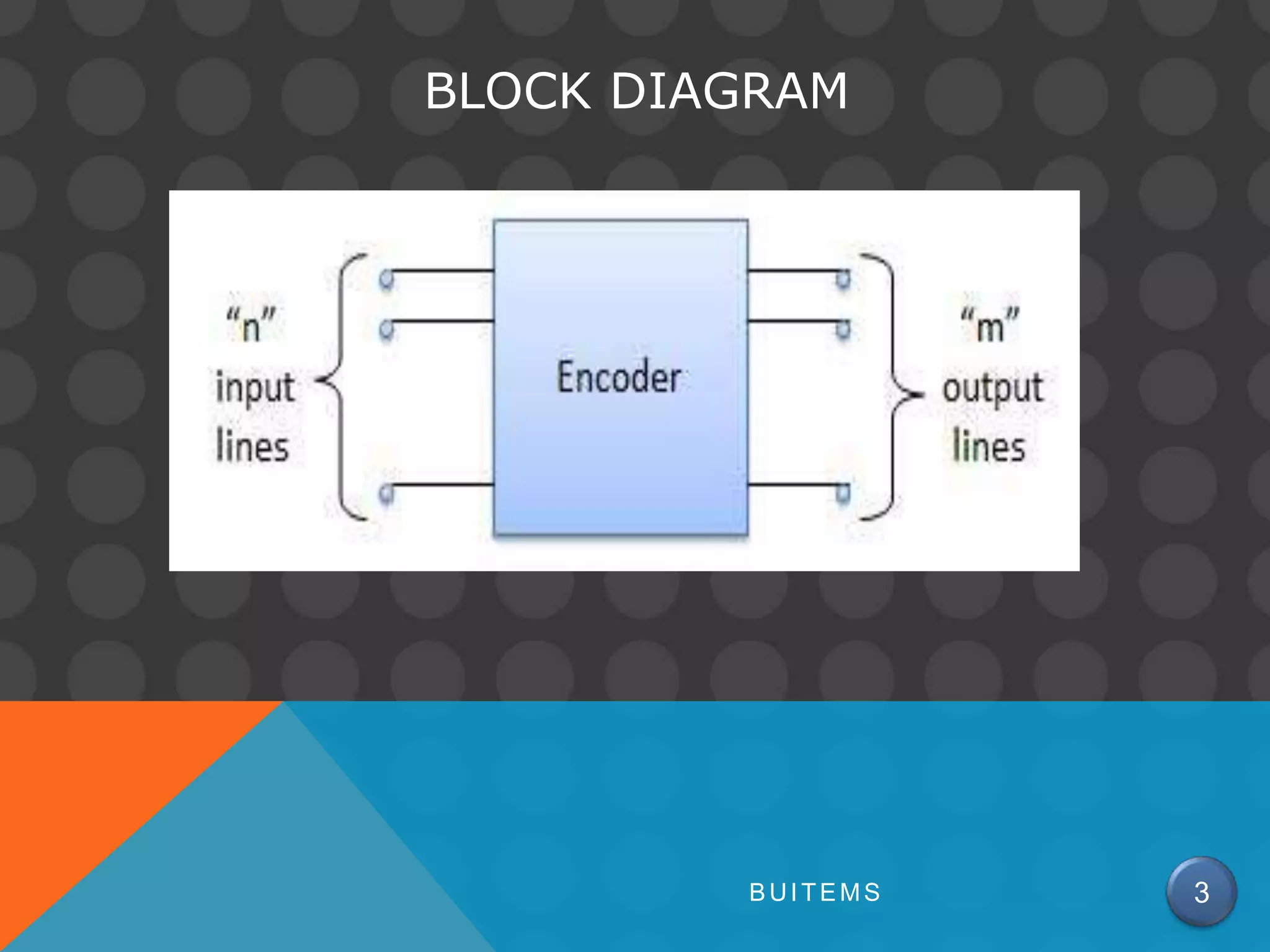
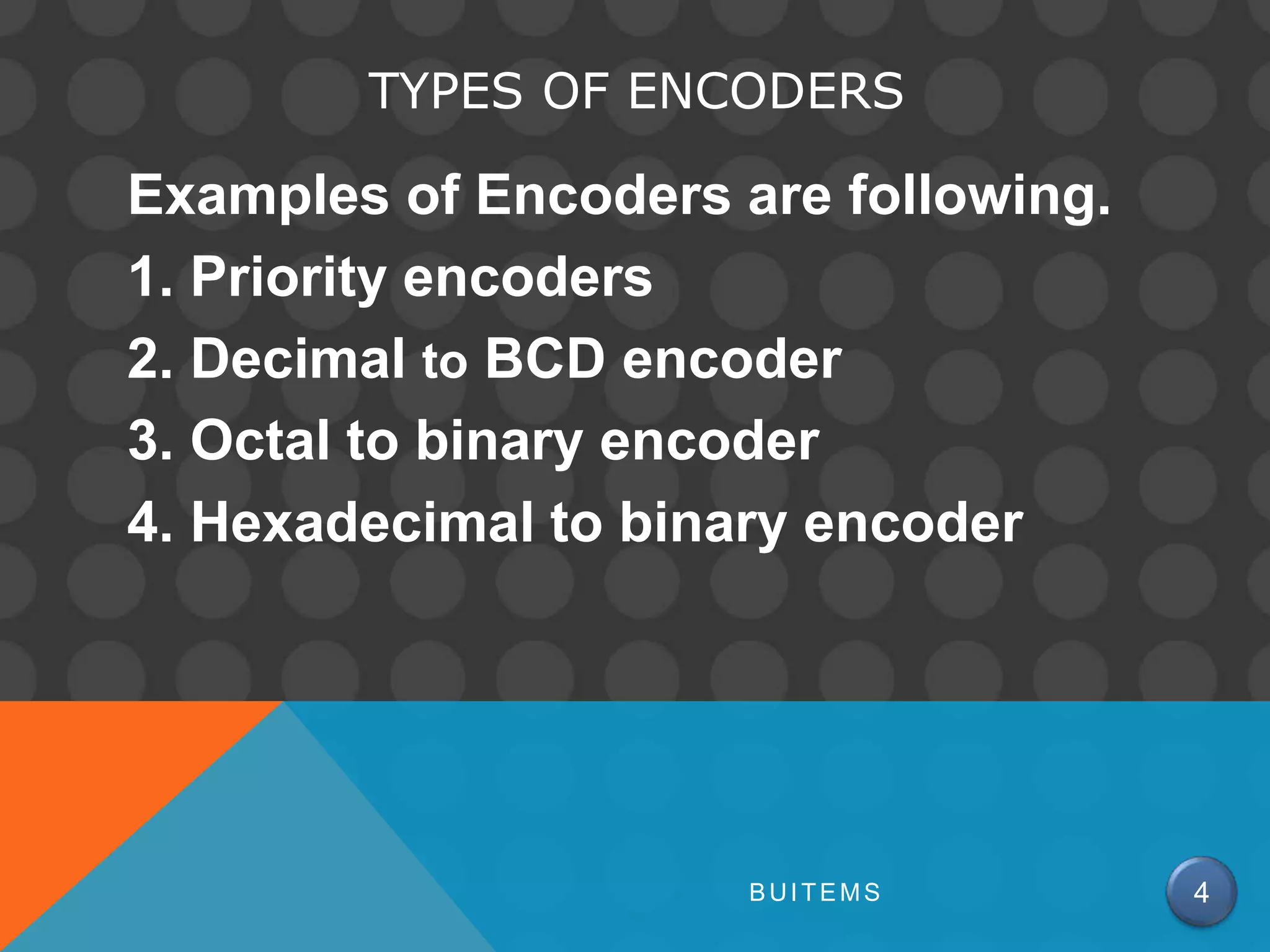
An encoder is a circuit that takes a digital input and converts it to a binary code output. It performs the inverse operation of a decoder. There are different types of encoders like priority encoders, decimal to binary coded decimal encoders, and hexadecimal to binary encoders. A priority encoder gives priority to certain input lines such that if multiple lines are high, the output corresponds to the highest priority line. A decimal to BCD encoder takes a 10-bit decimal input and produces a 4-bit binary coded decimal output corresponding to each decimal value. Standard encoder integrated circuits like the 74HC147 implement common encoder functions.