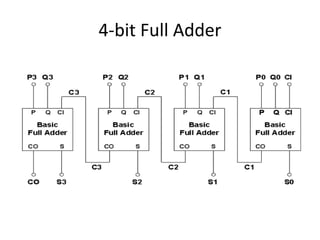
This document summarizes digital logic design lecture 4 on binary addition and signed numbers. It discusses:
1) The rules of binary addition and how to add 4-bit binary numbers using a full adder.
2) How signed numbers work in binary, including problems with the signed magnitude representation.
3) How two's complement solves the problems with signed magnitude by representing negative numbers as the binary equivalents of their positive value subtracted from 2^n.
4) Examples of adding and converting between positive and negative numbers using two's complement.