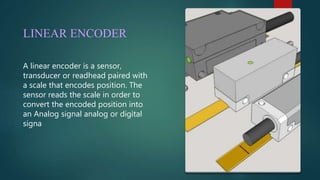
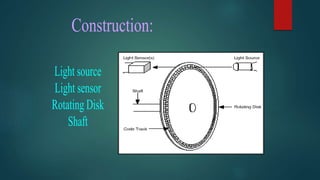
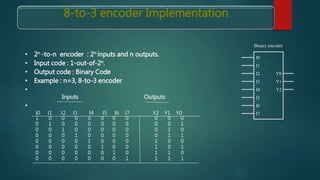
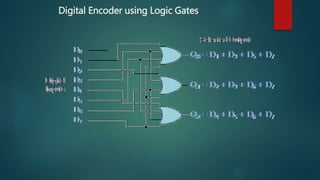
The document discusses different types of encoders. It defines an encoder as a device, circuit, transducer, software, algorithm, or person that converts information from one format to another. It provides examples of linear encoders that encode position and digital encoders that convert multiple inputs into a binary coded output. Specifically, it describes an n-bit binary encoder that has 2n inputs and n outputs, and provides truth tables for 8-to-3 and 4-to-2 bit encoders. It also discusses priority encoders that prioritize inputs and output the code of the highest priority active input.