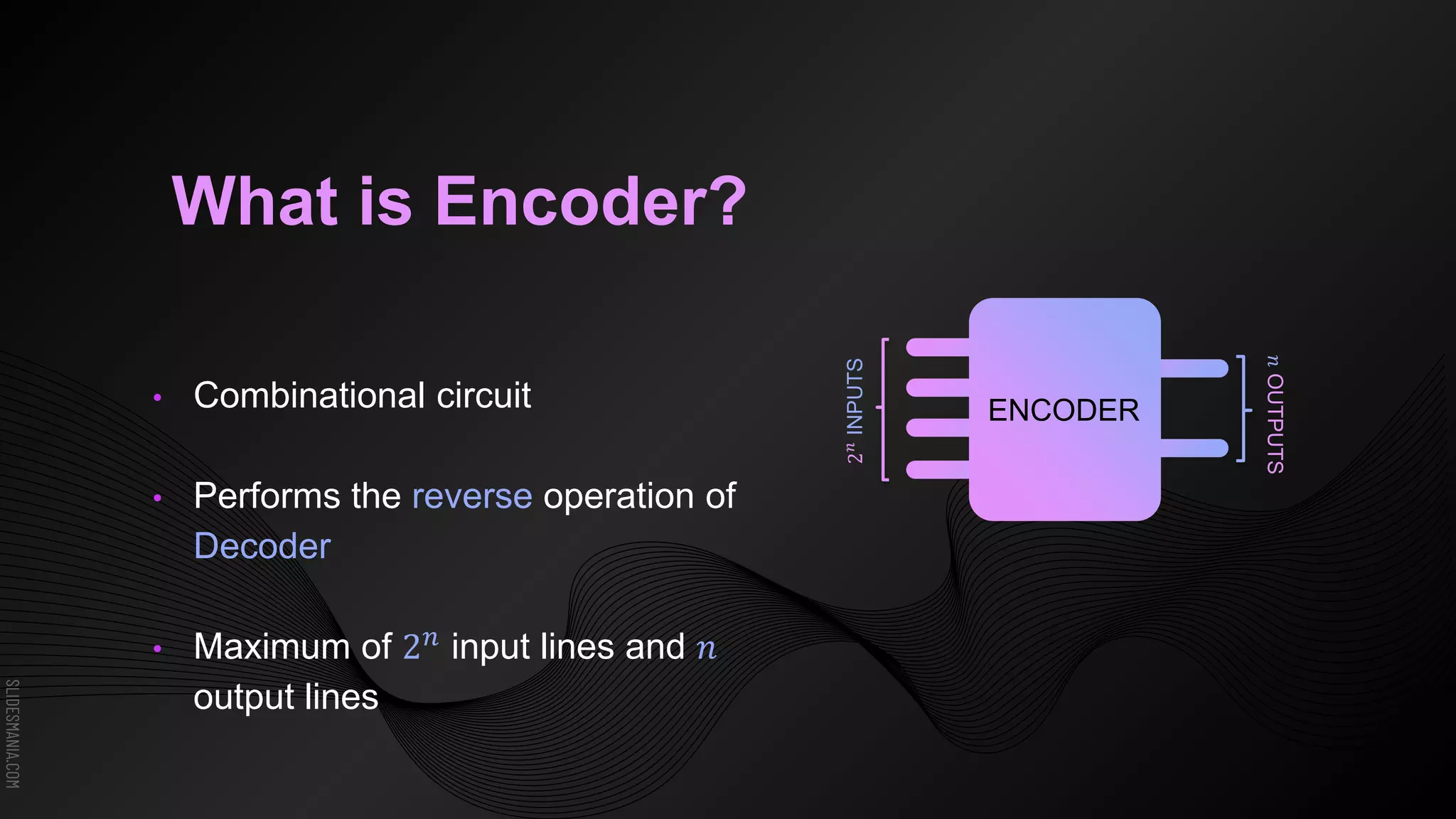
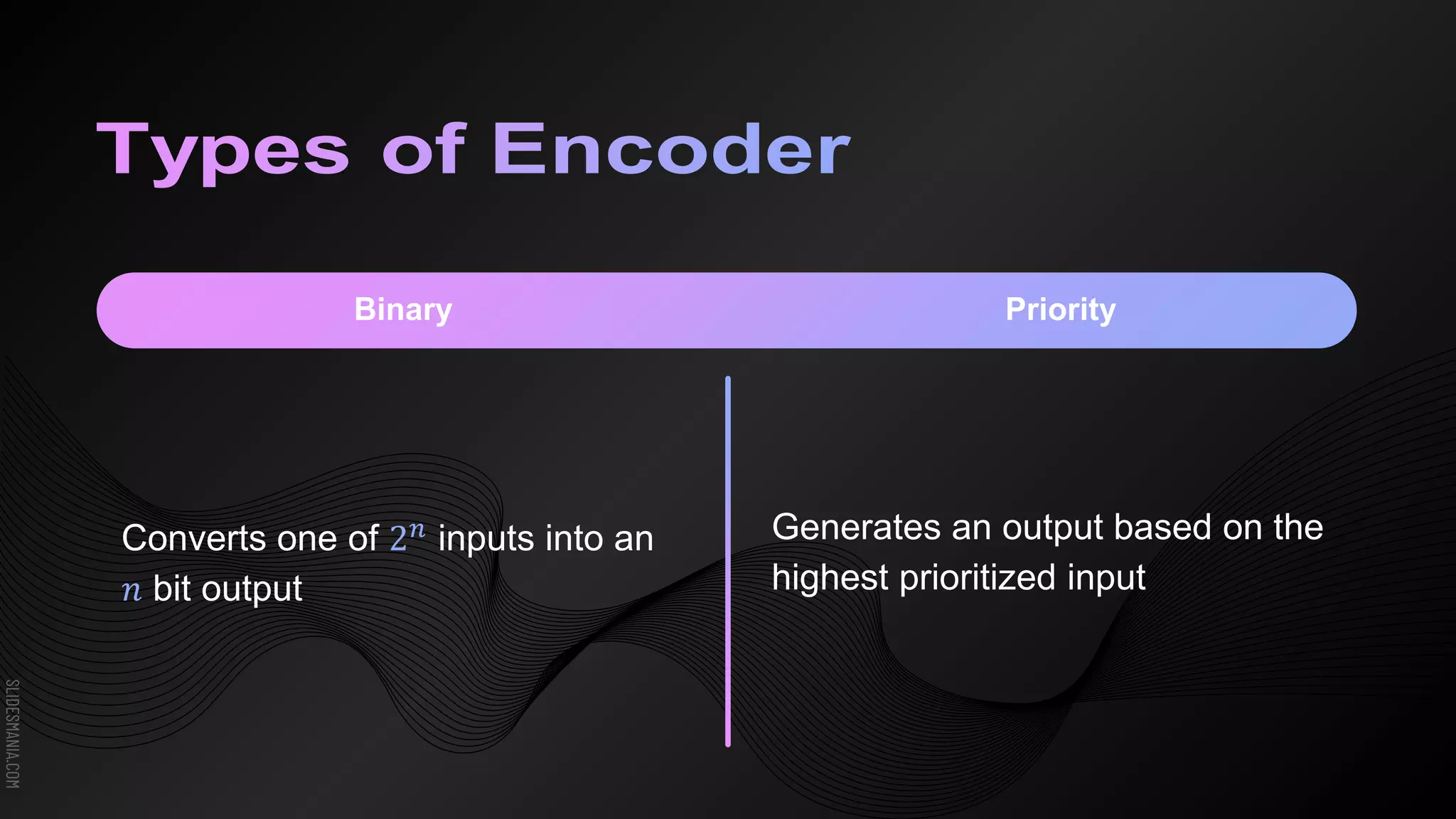
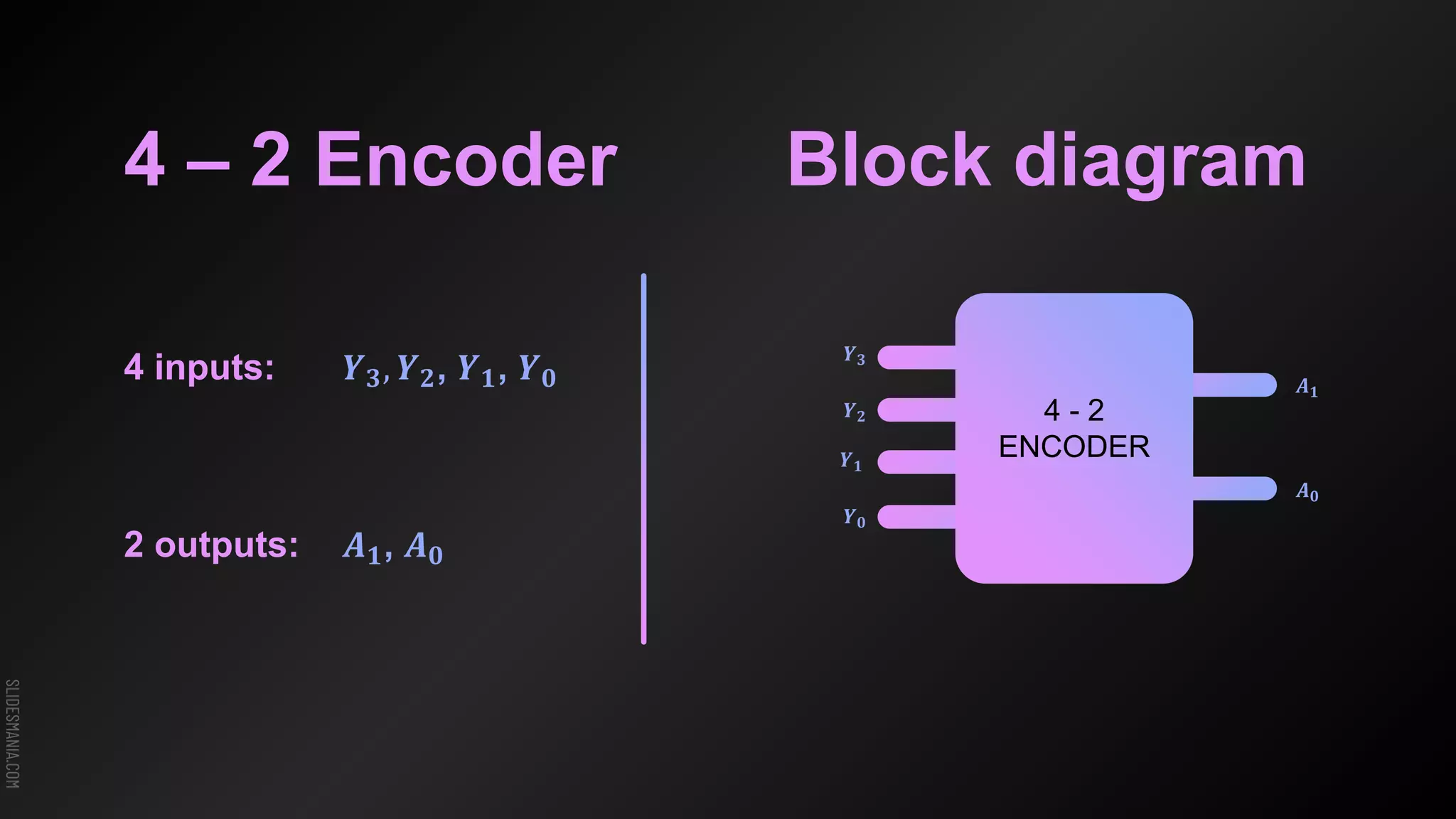
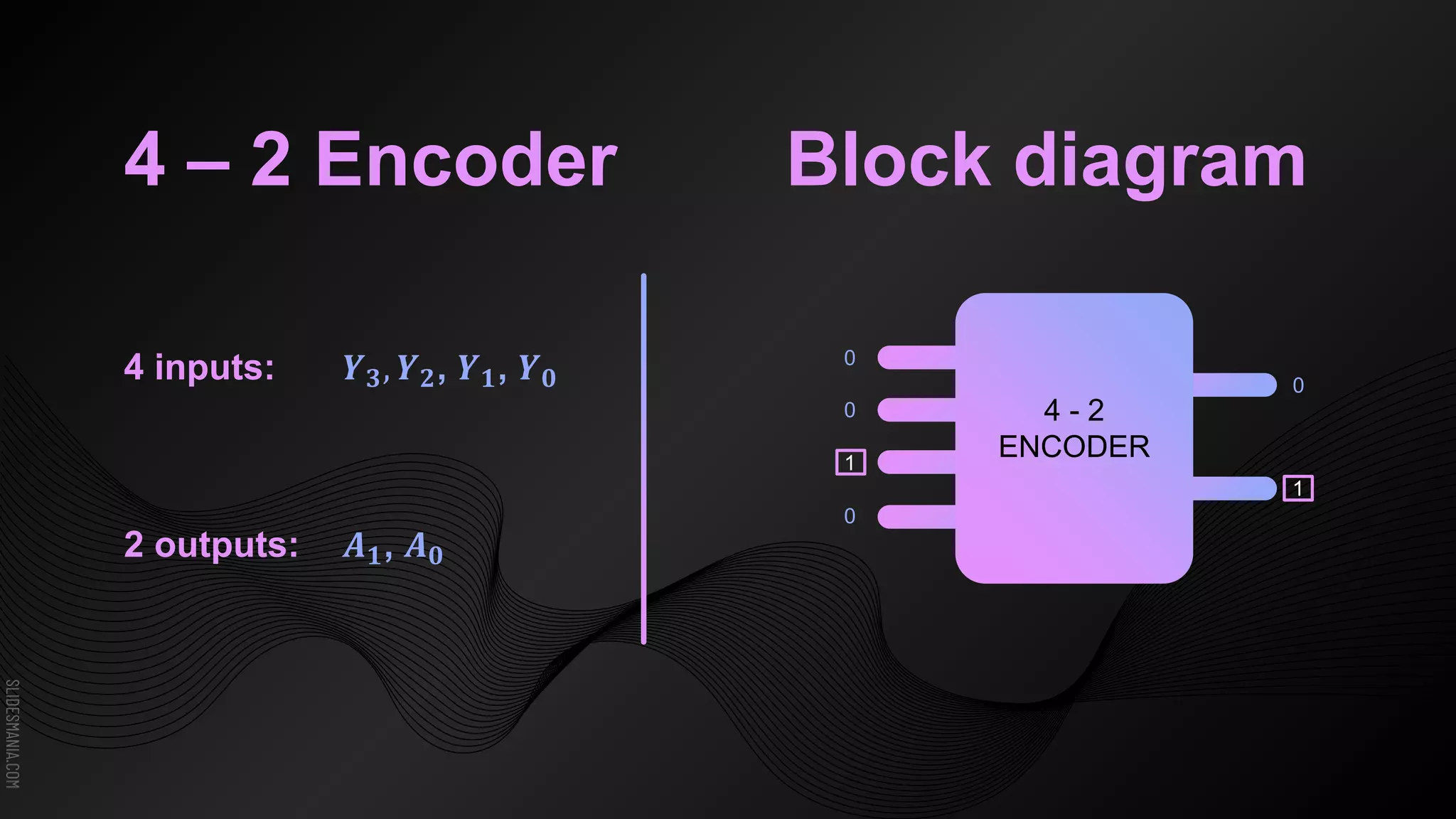
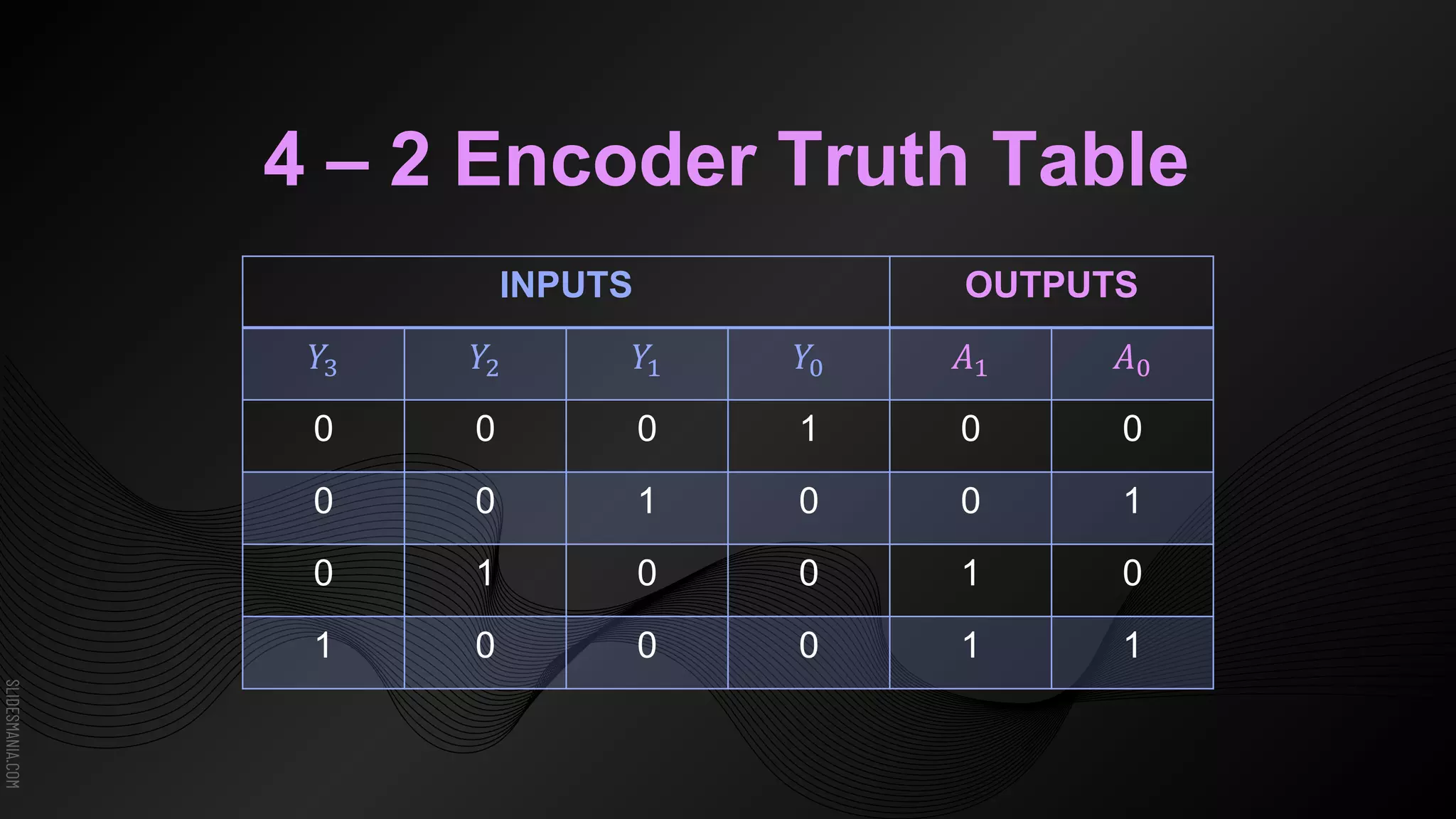
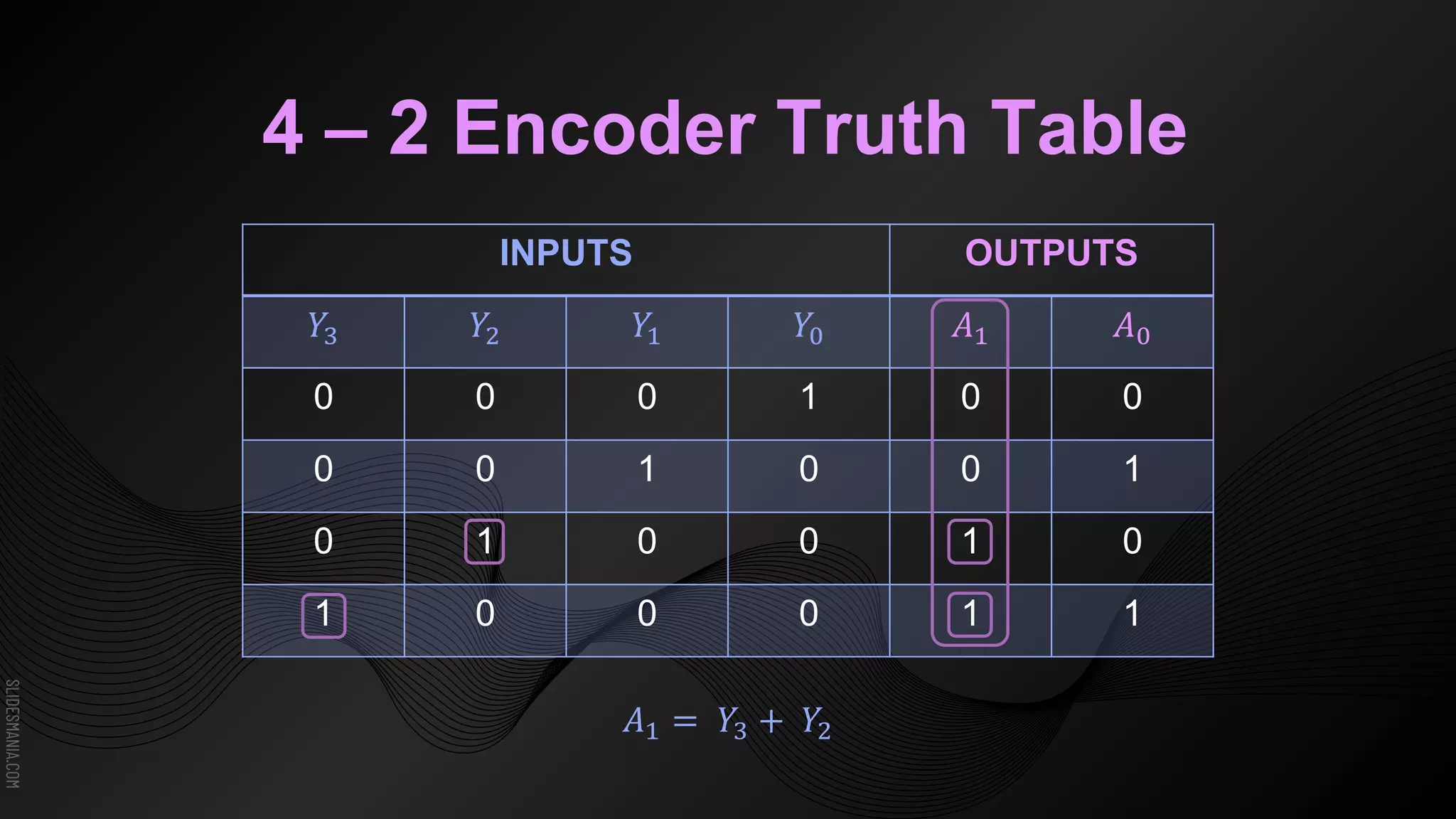
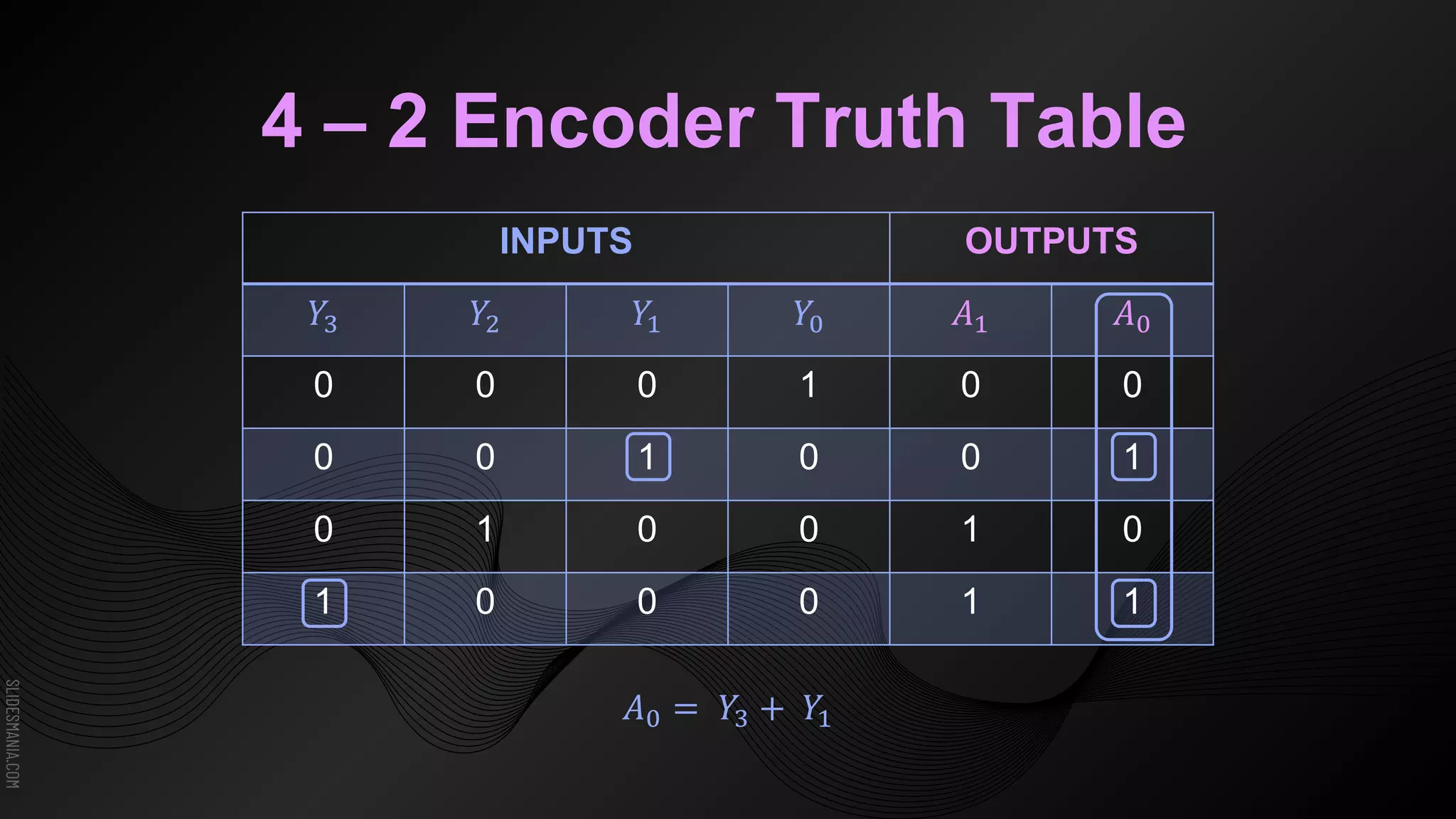
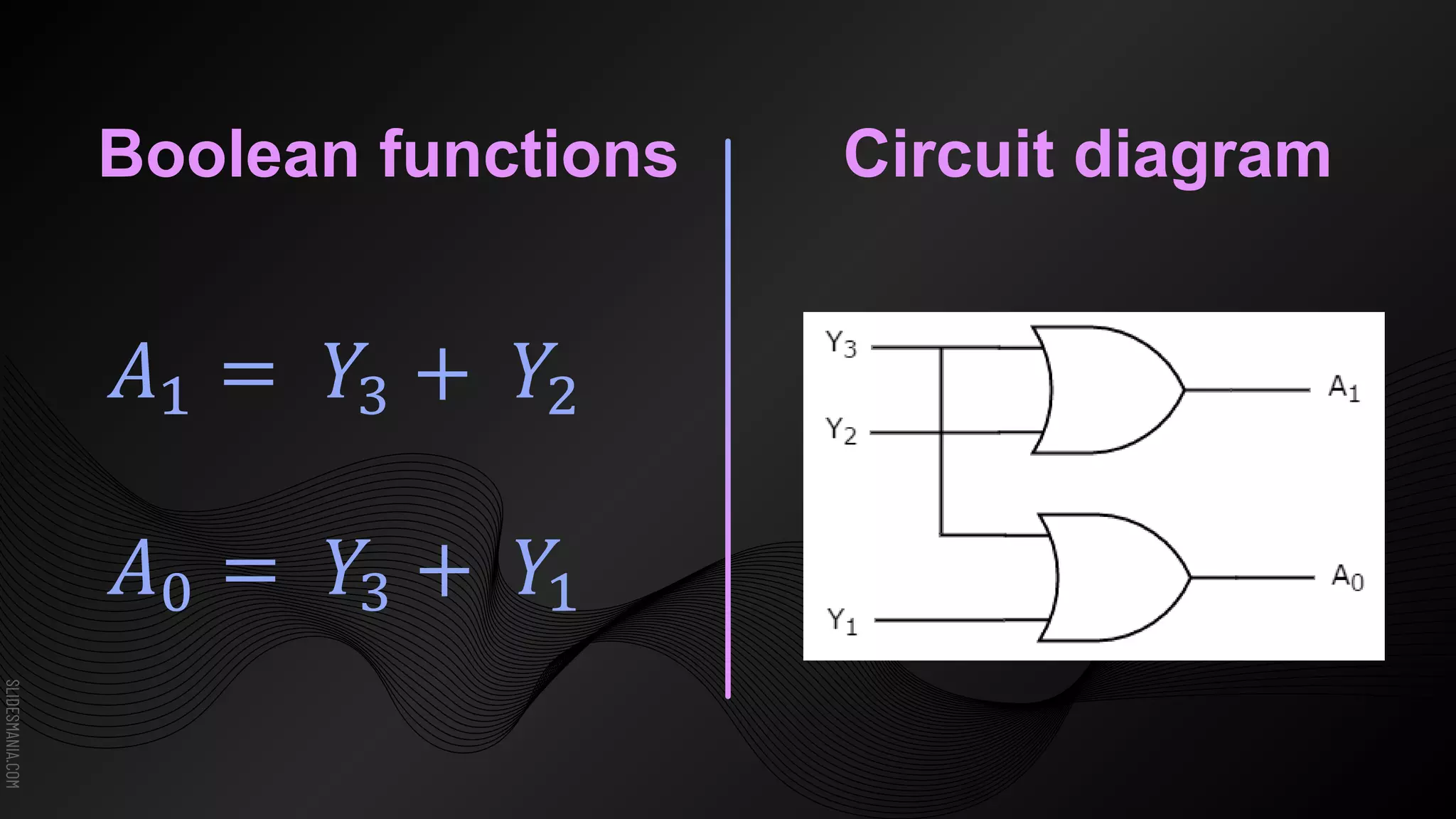
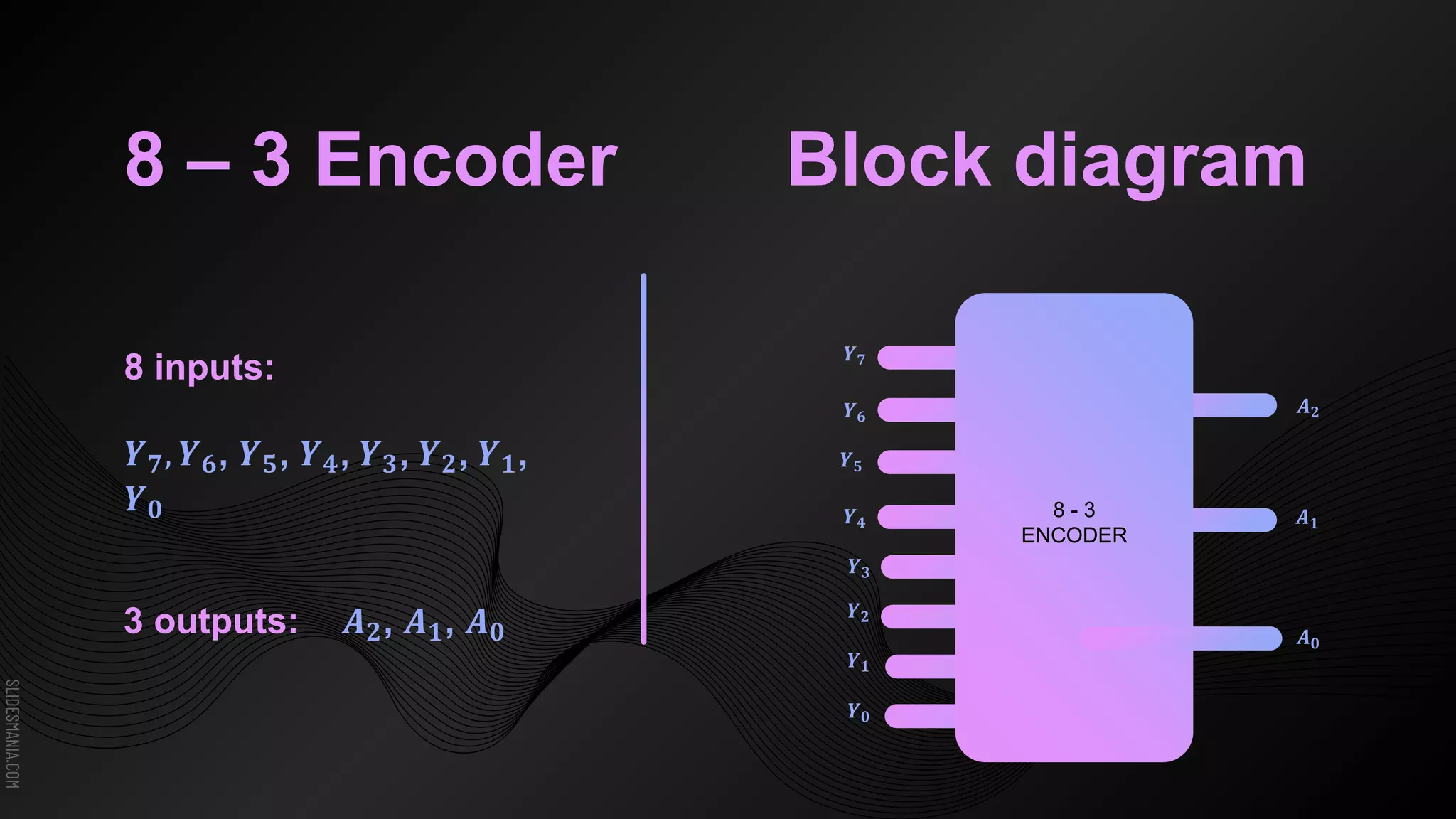
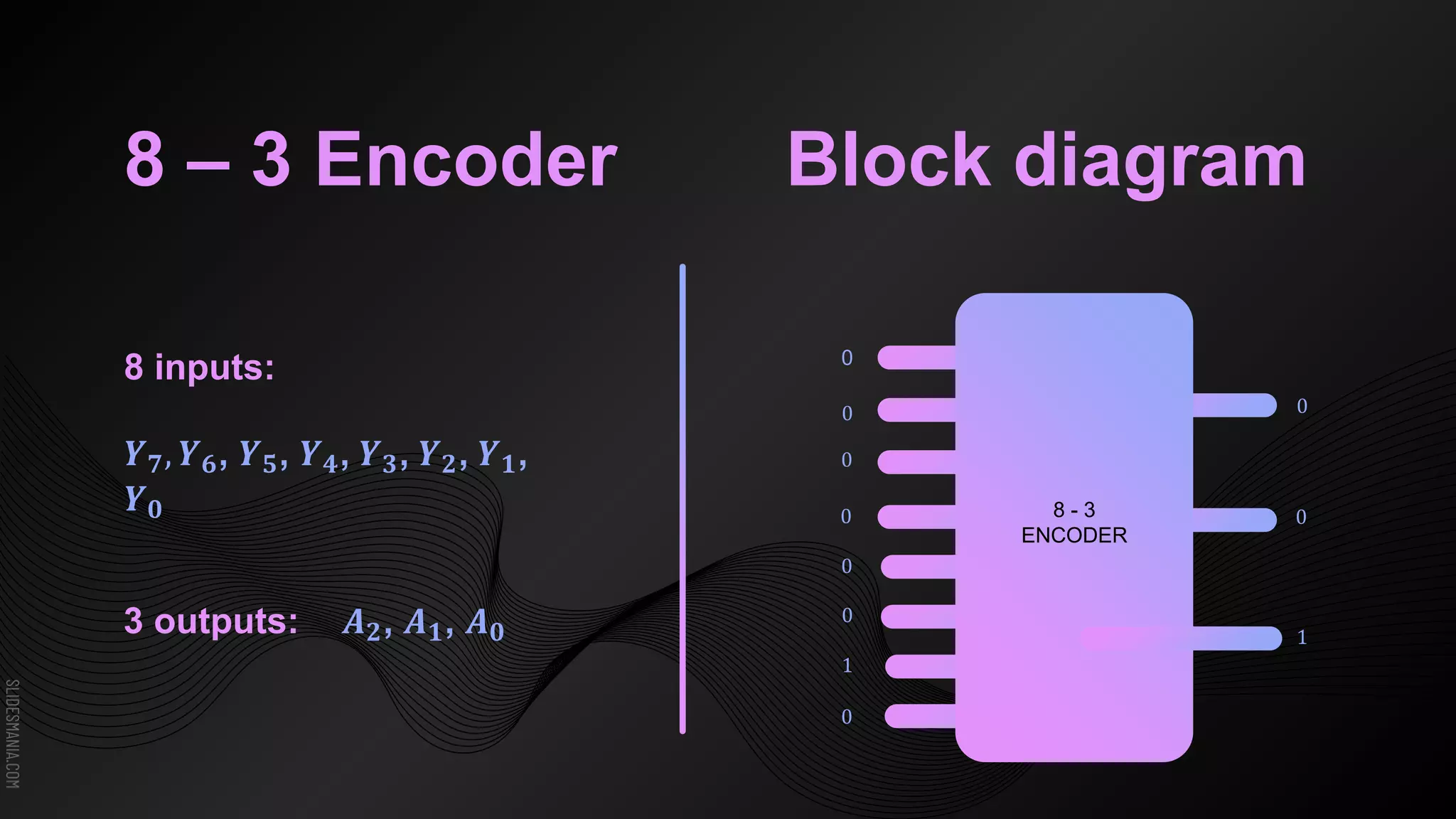
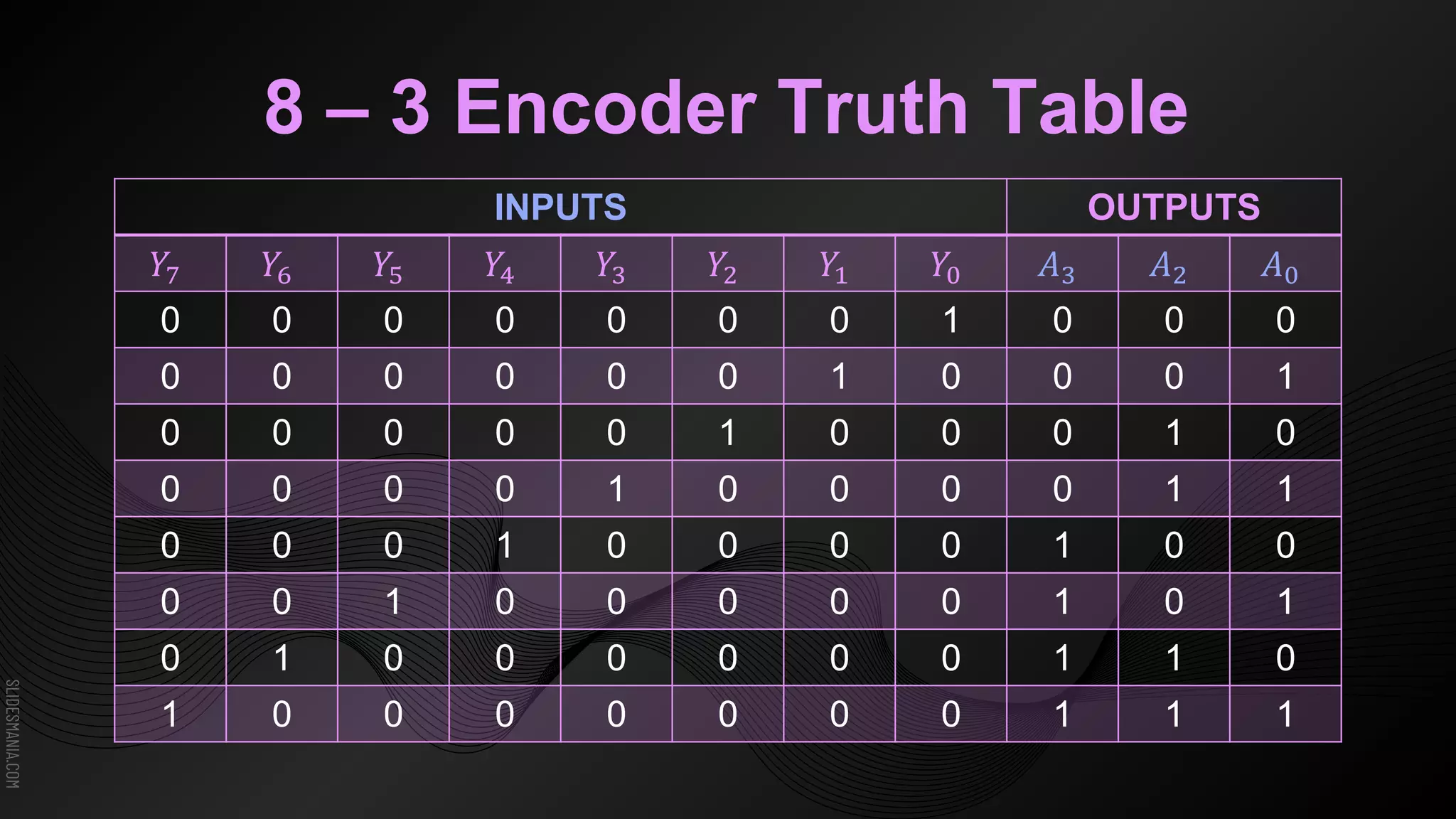
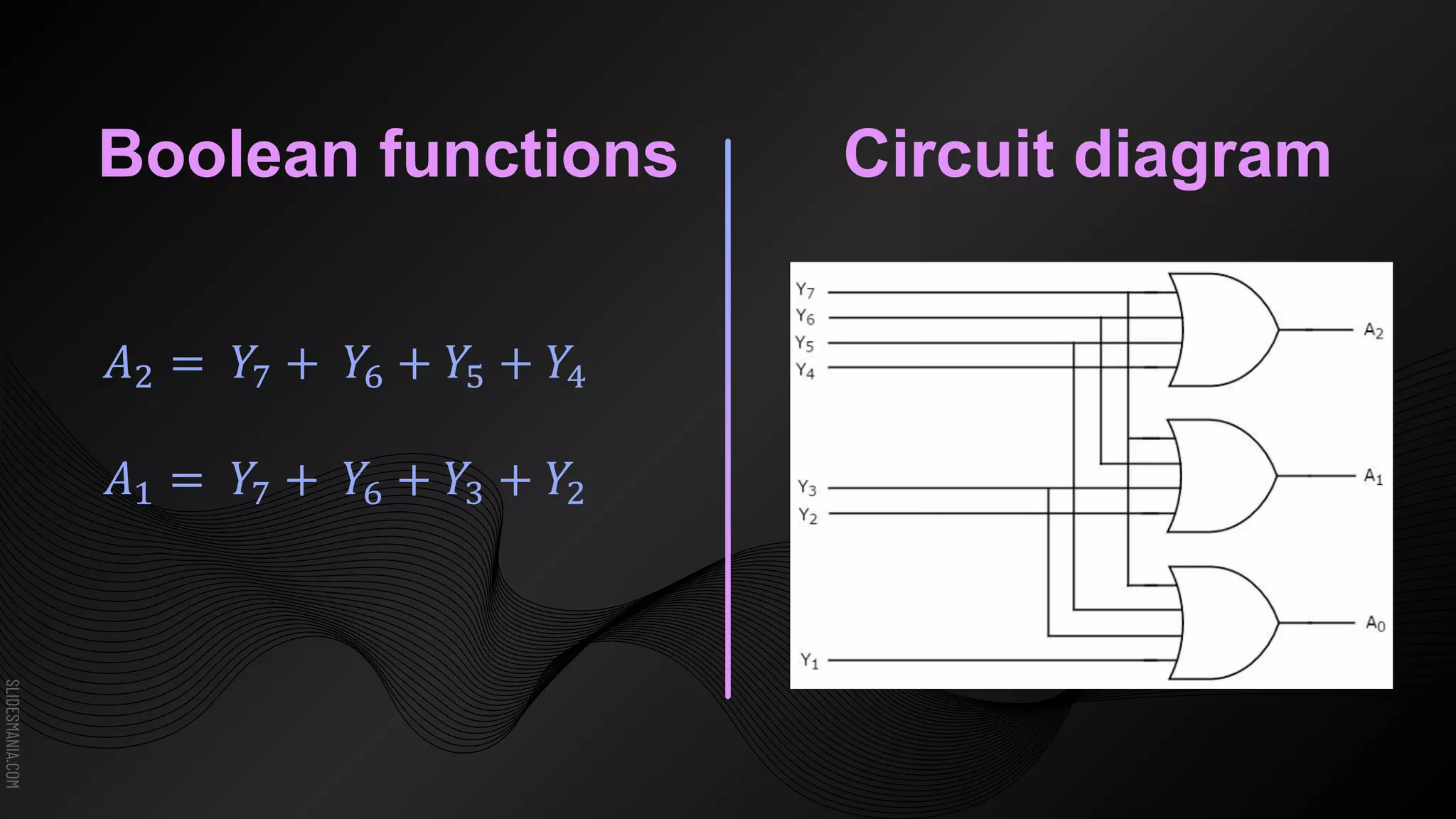
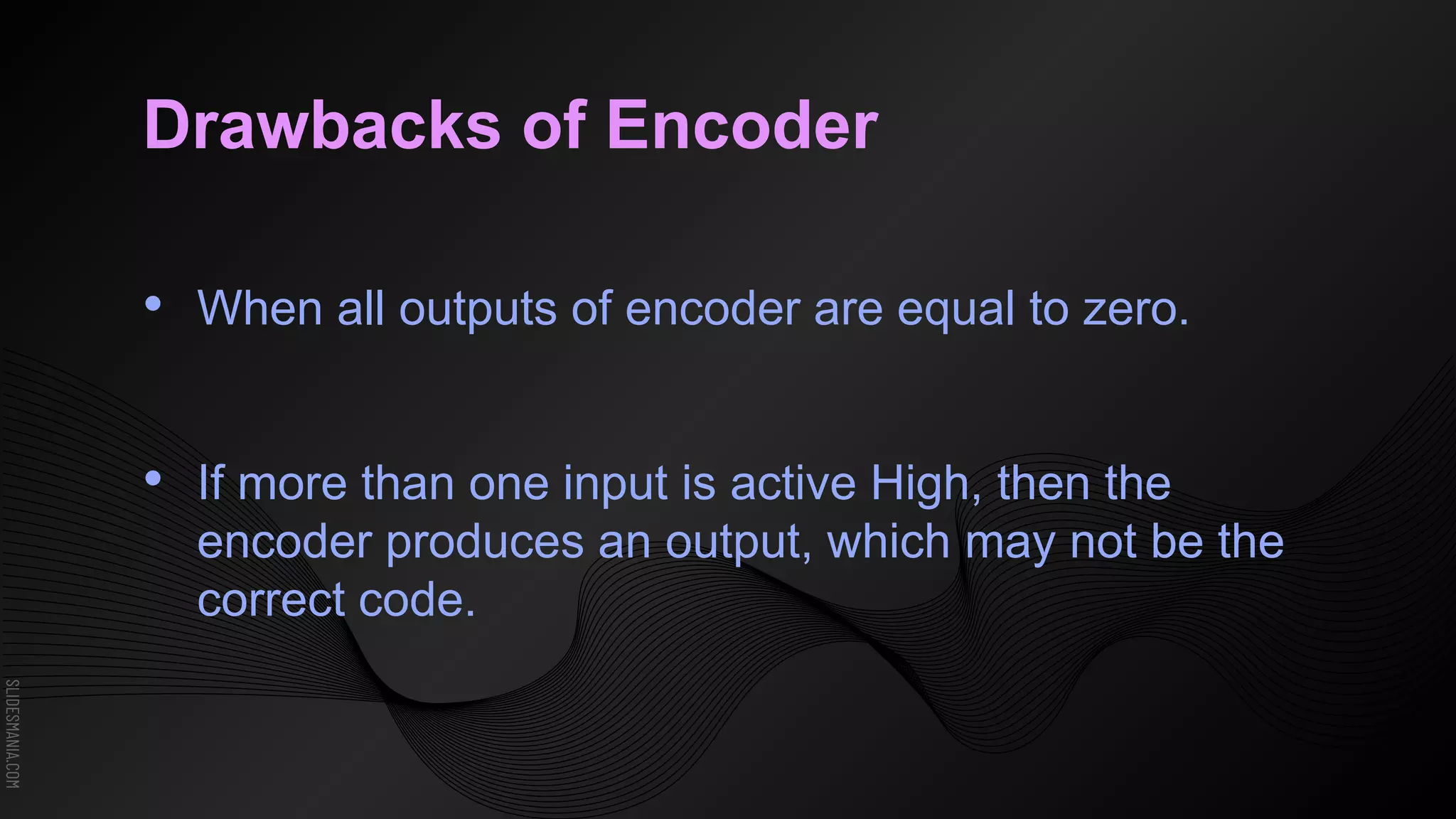
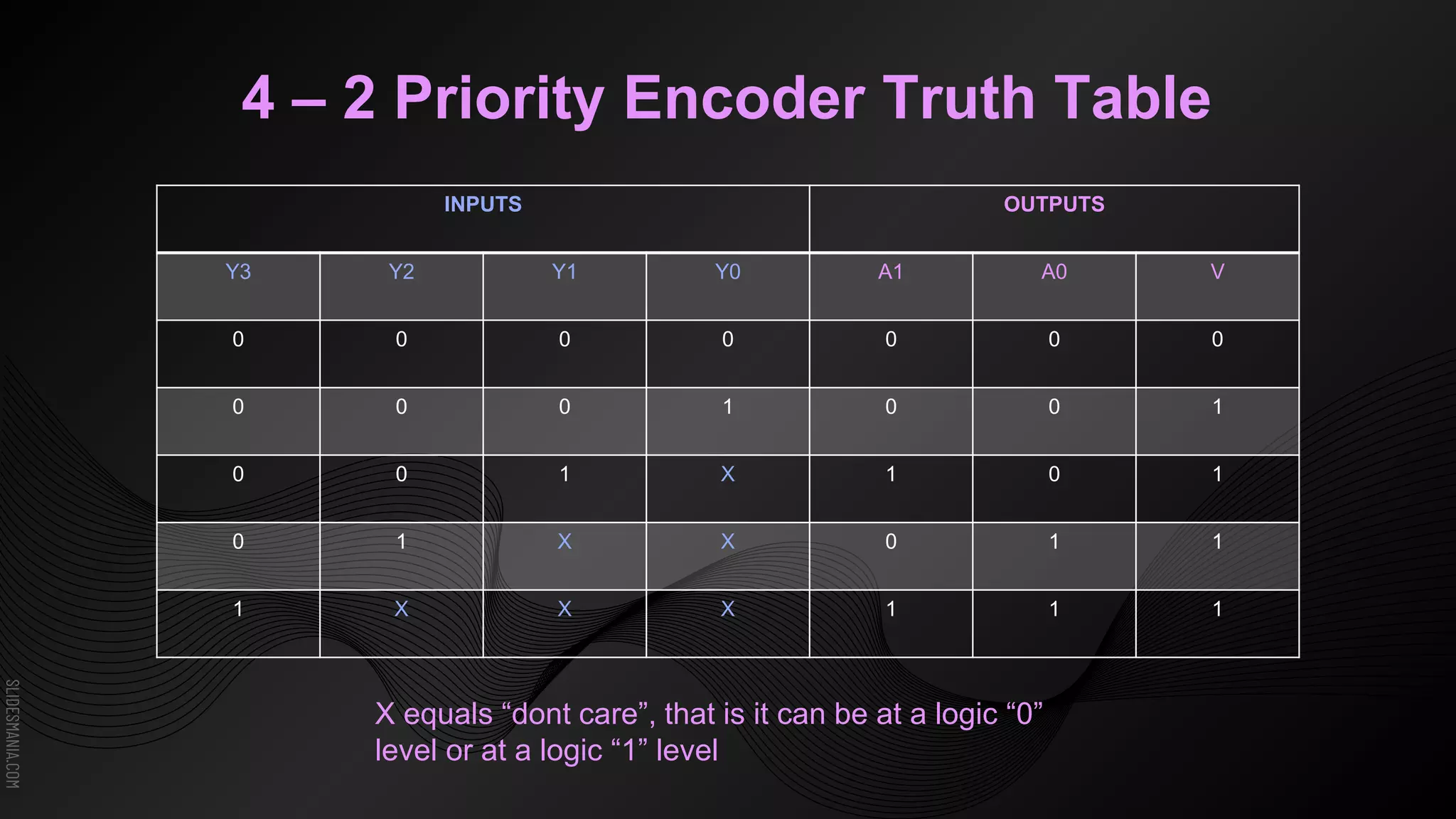
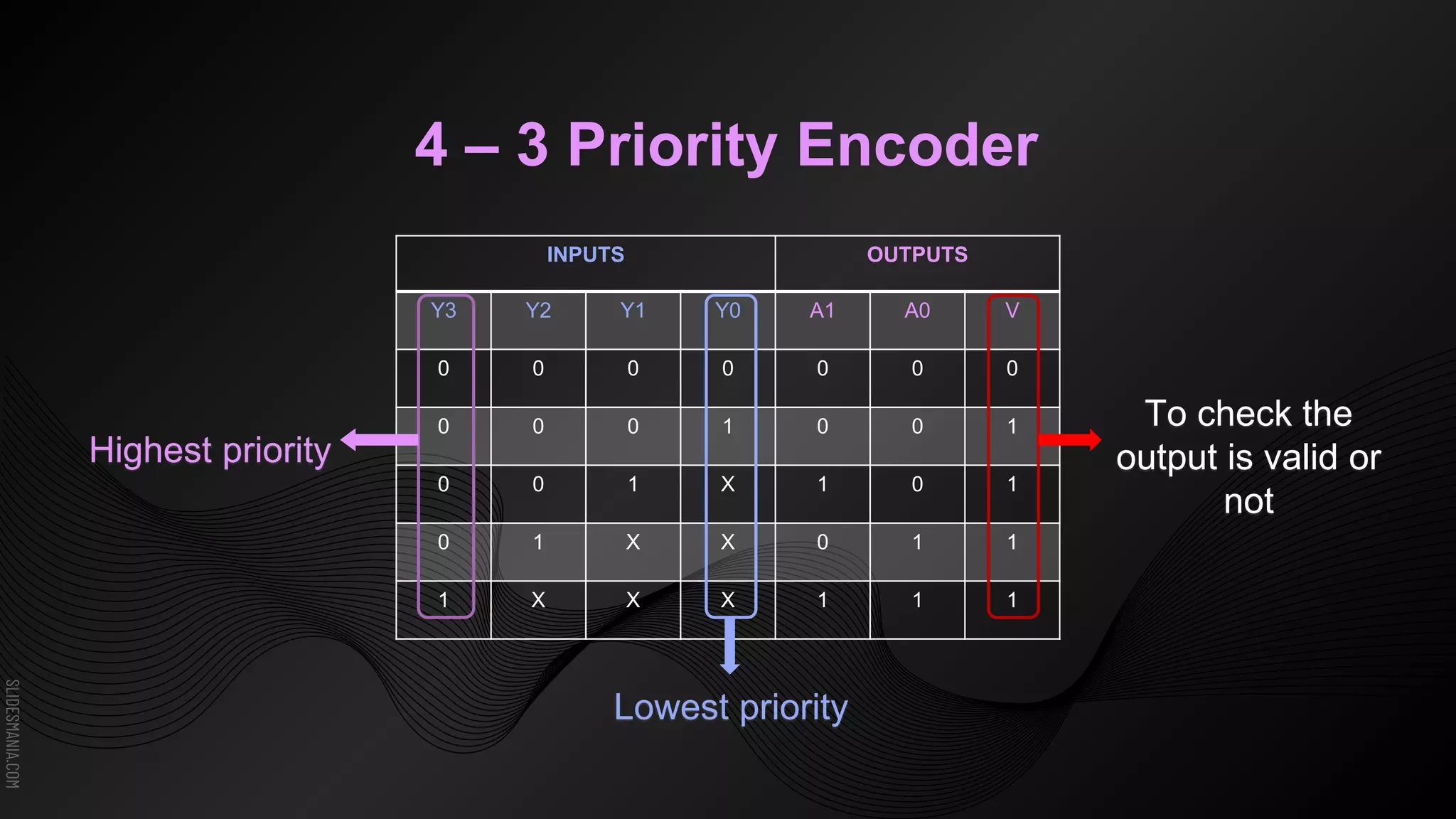
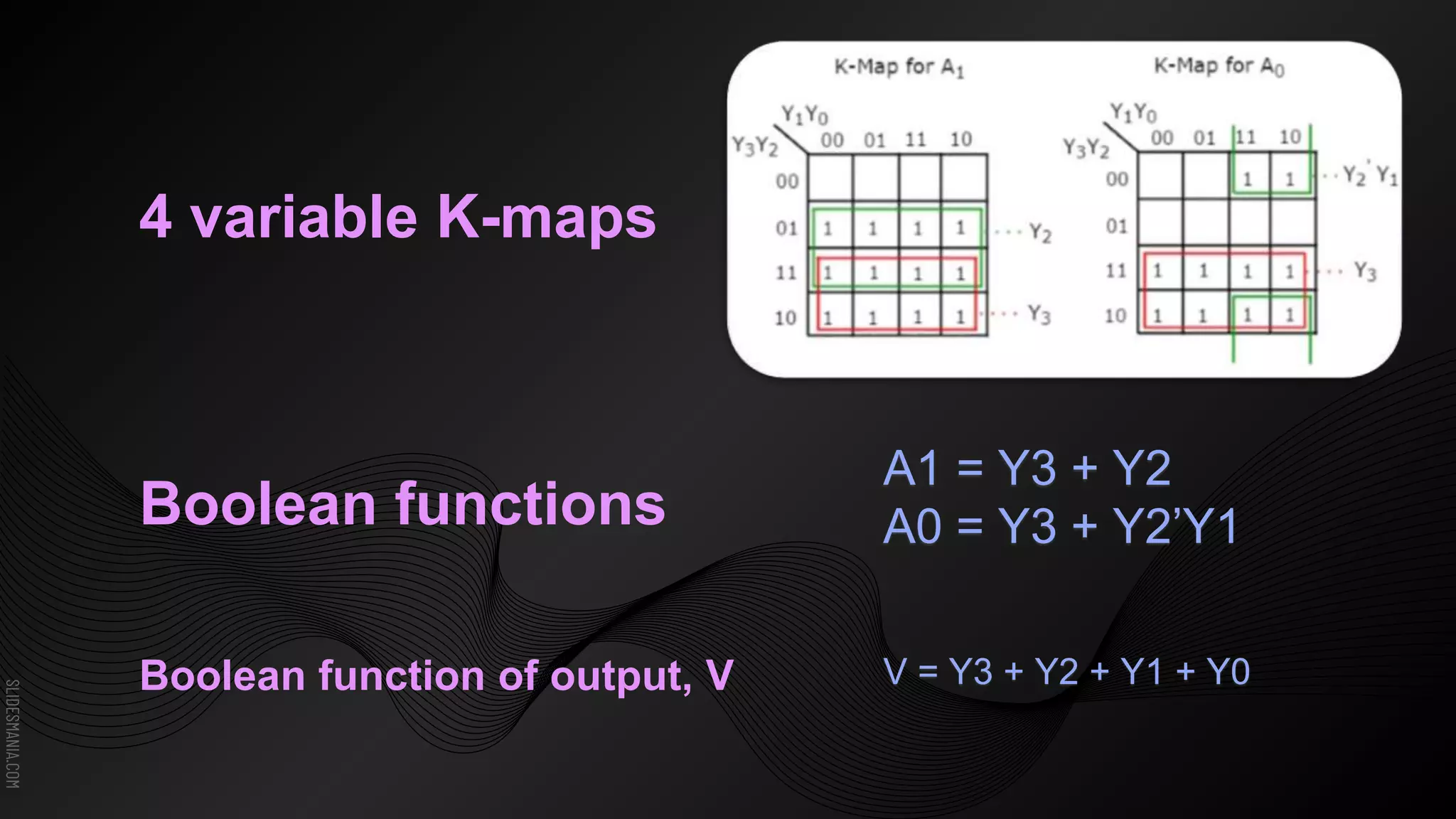
The document discusses encoders, which are combinational logic circuits that convert binary coded input into a binary coded output. An encoder performs the reverse operation of a decoder. It can have up to 2n input lines and n output lines. The encoder generates an output based on the highest prioritized input. Truth tables and boolean equations are provided for 4-to-2 and 8-to-3 encoders as examples. Priority encoders are also discussed, which ensure only one valid output is produced even if multiple inputs are active.