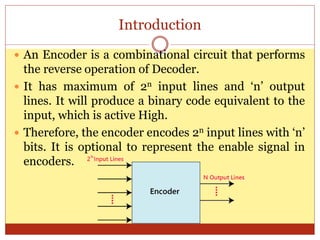
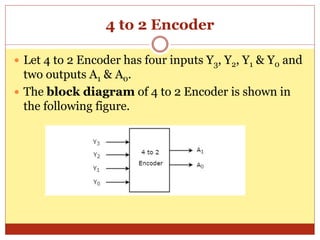
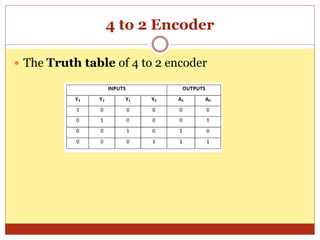
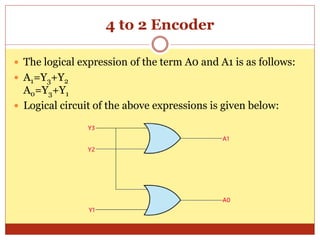
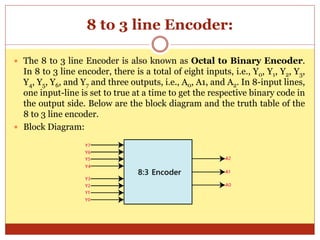
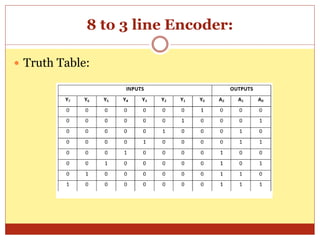
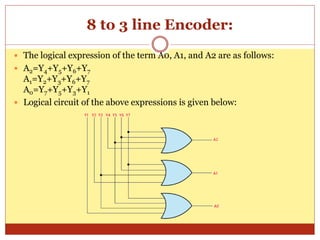
This document discusses encoders and provides examples of 4-to-2 and 8-to-3 line encoders. It defines an encoder as a combinational circuit that performs the reverse operation of a decoder, with a maximum of 2n input lines and n output lines. Truth tables and logic circuits are given for 4-to-2 and 8-to-3 line encoders. Uses of encoders include converting decimal to binary numbers to perform binary operations like addition and subtraction in digital systems.