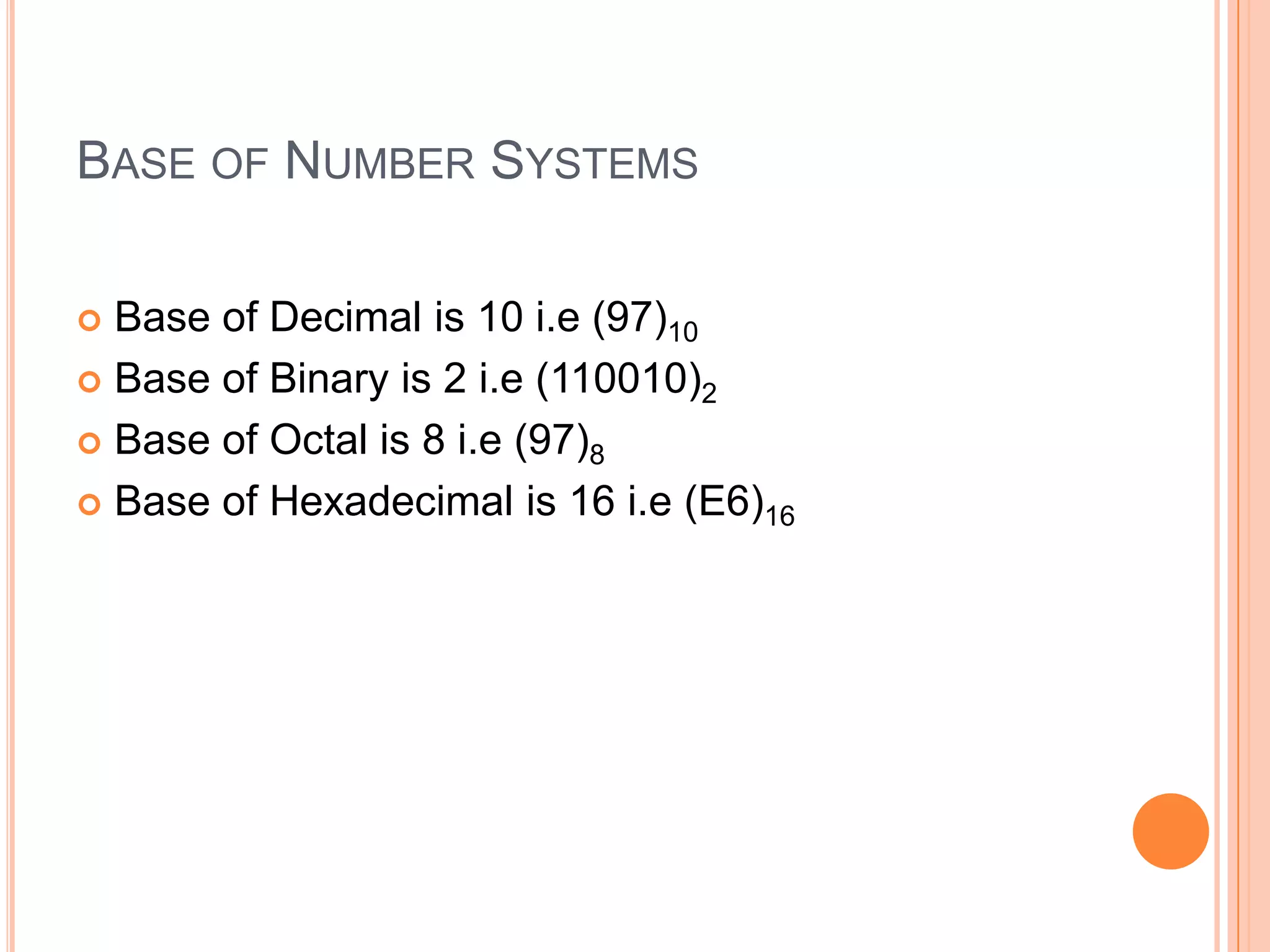
This document provides an overview of digital logic design (DLD). It defines DLD as a system that uses simple number values like 0s and 1s to produce inputs and outputs. The objectives are to understand number systems, Boolean algebra, combinational logic circuits, latches, flip flops and counters. Digital logic is based on binary code and facilitates circuits with logic gates for AND, OR and NOT operations. Computers are digital because they use discrete 0s and 1s rather than continuous values, and all data must be encoded digitally. Examples of digital devices given are digital watches and scoreboards, while analog examples include speedometers, clocks and thermometers.