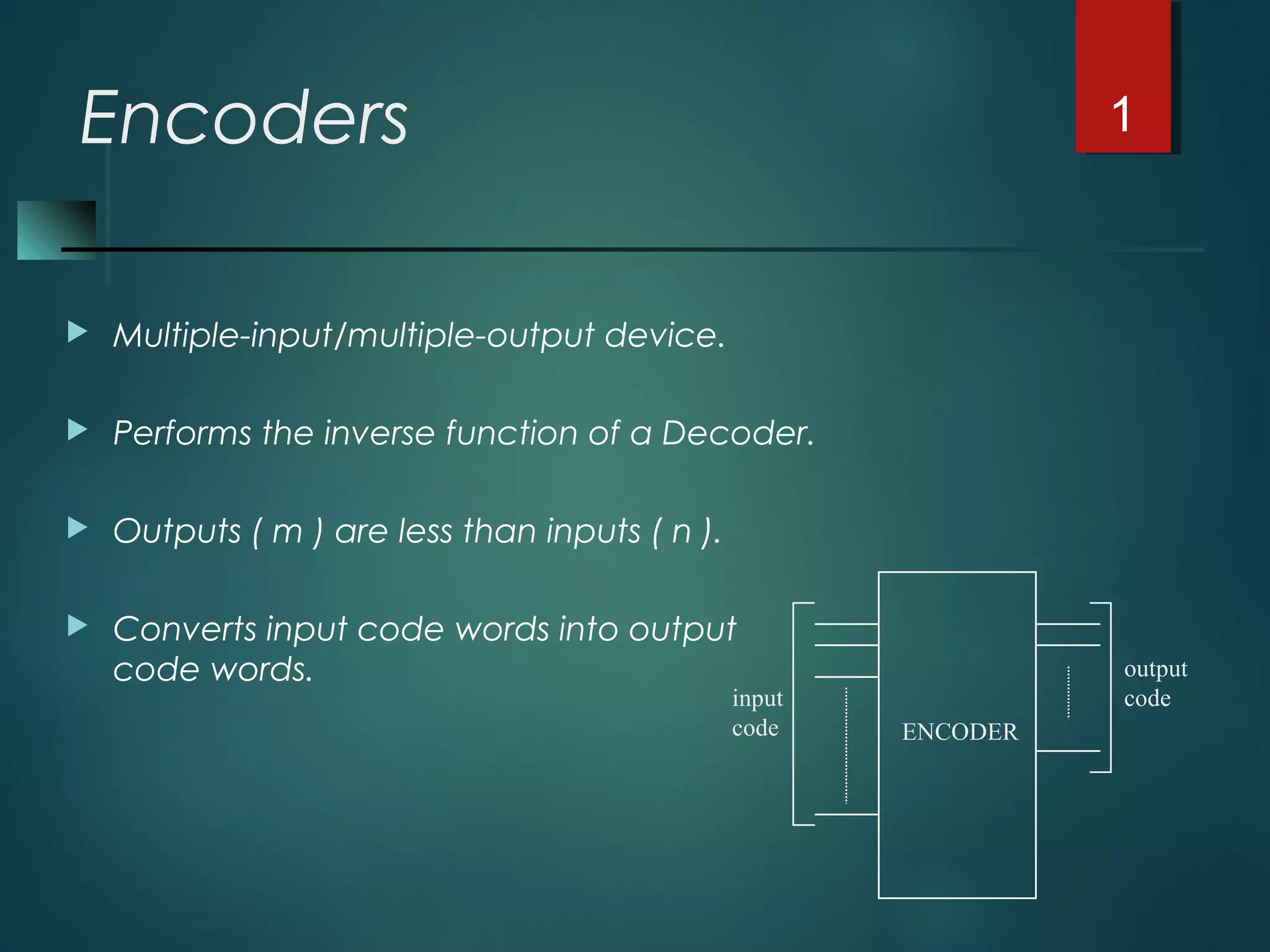
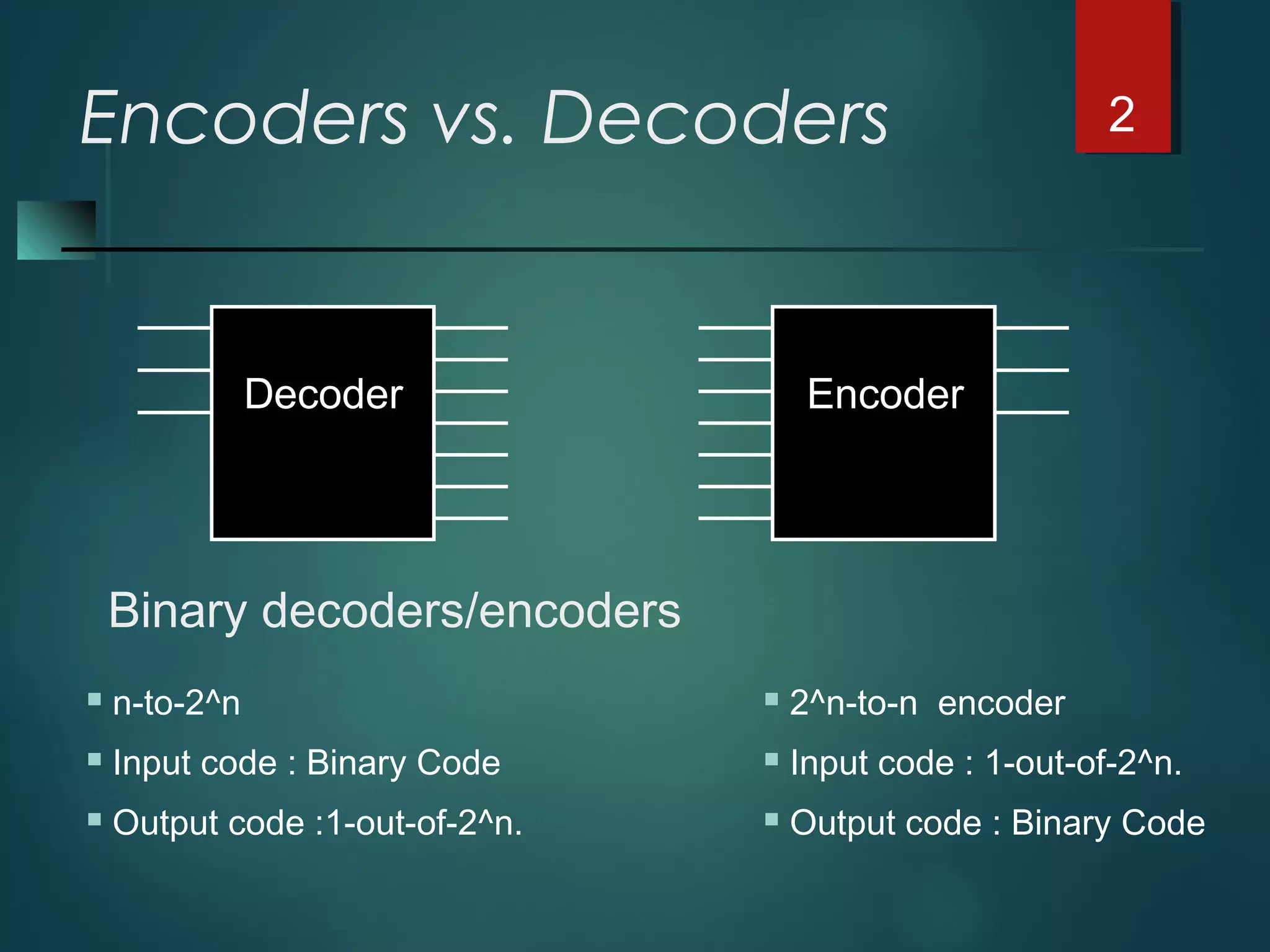
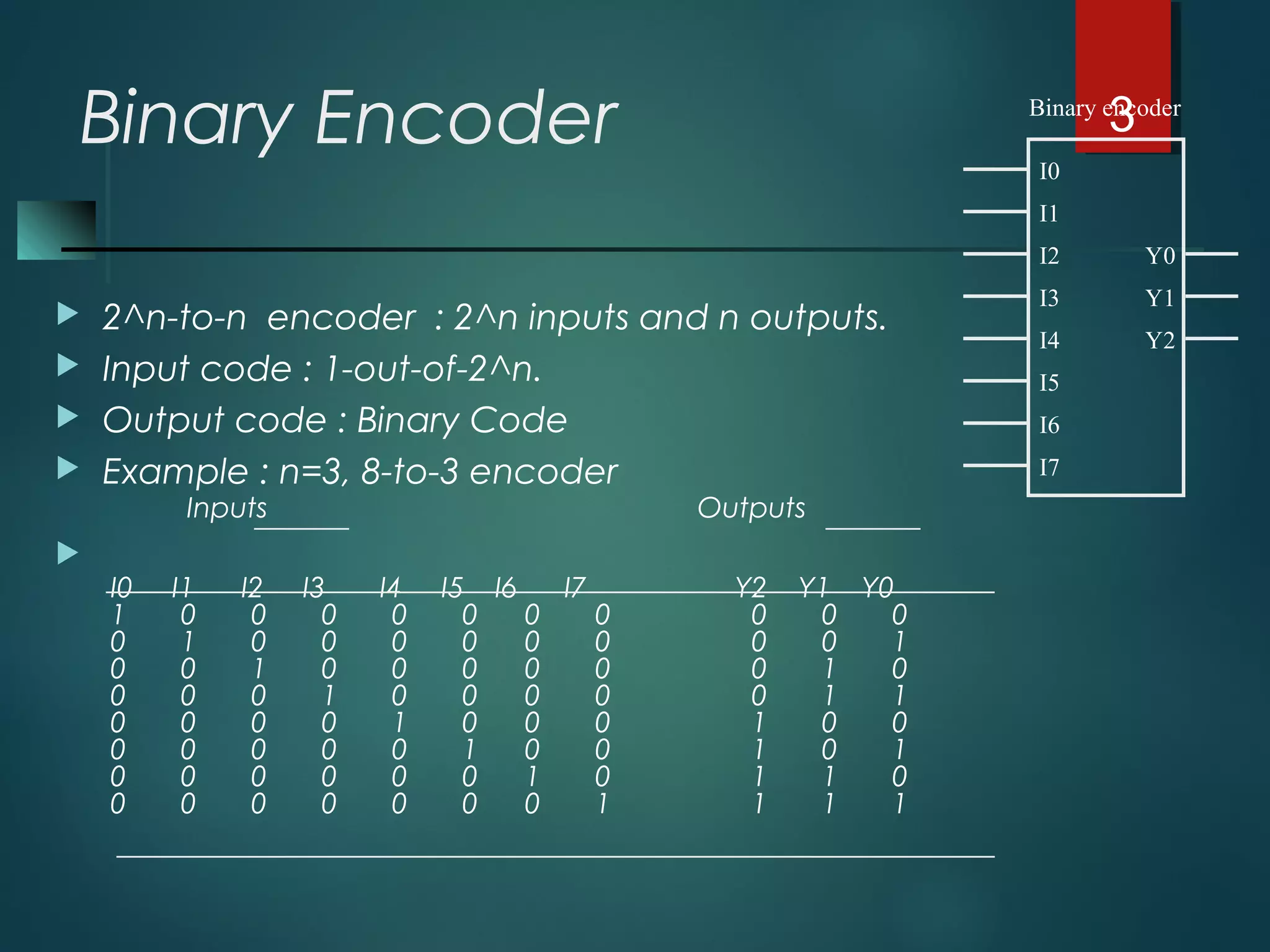
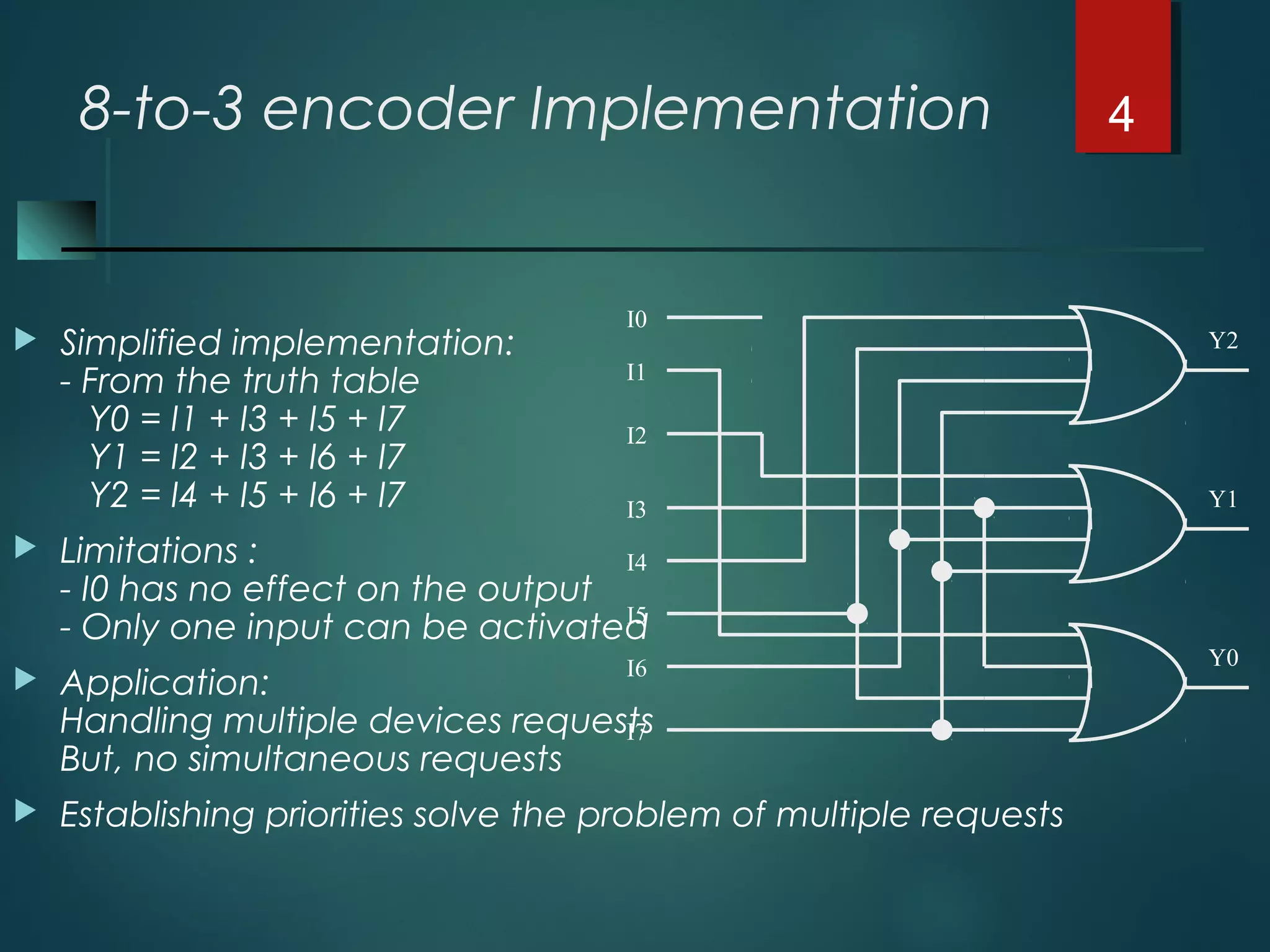
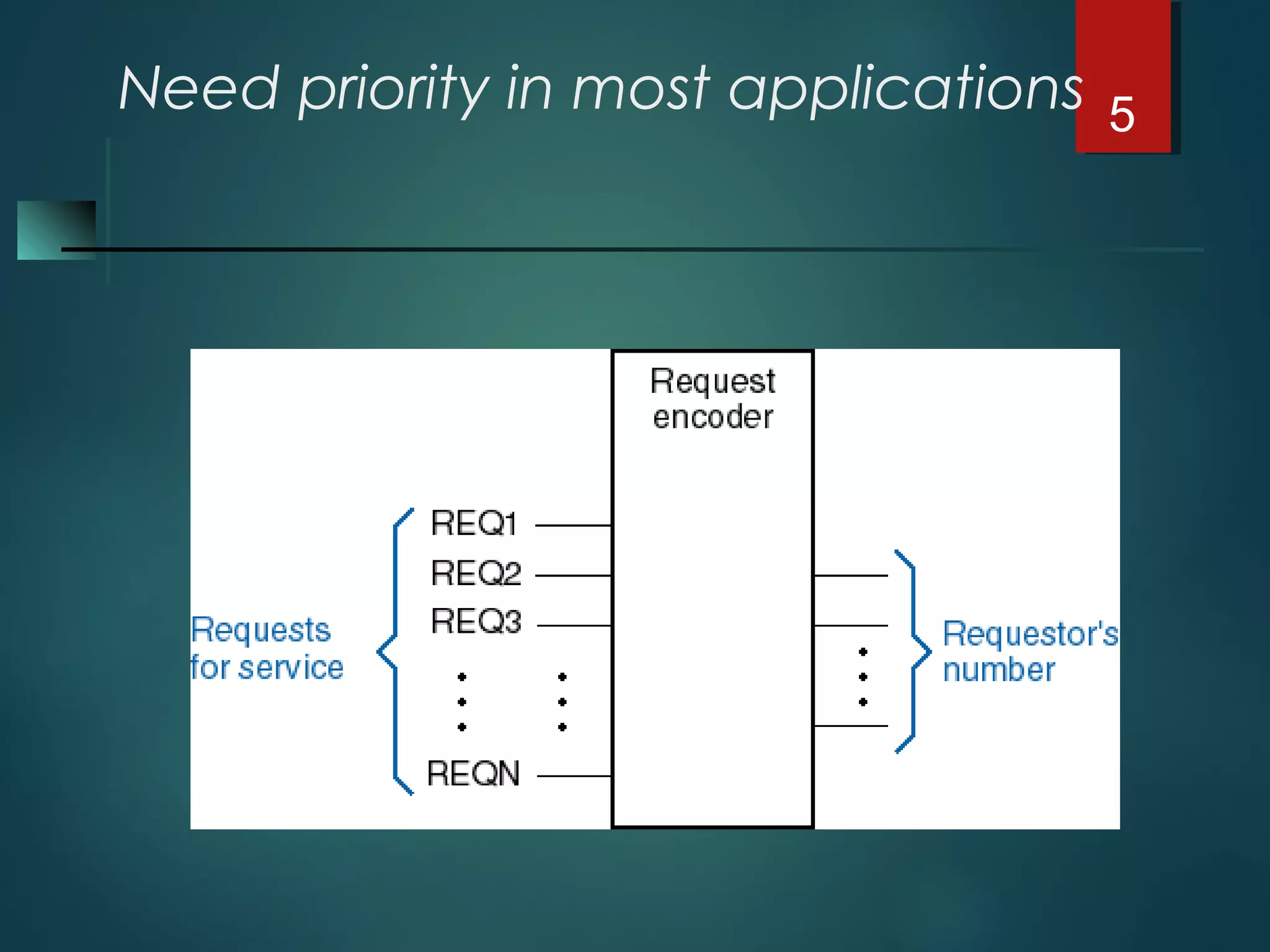
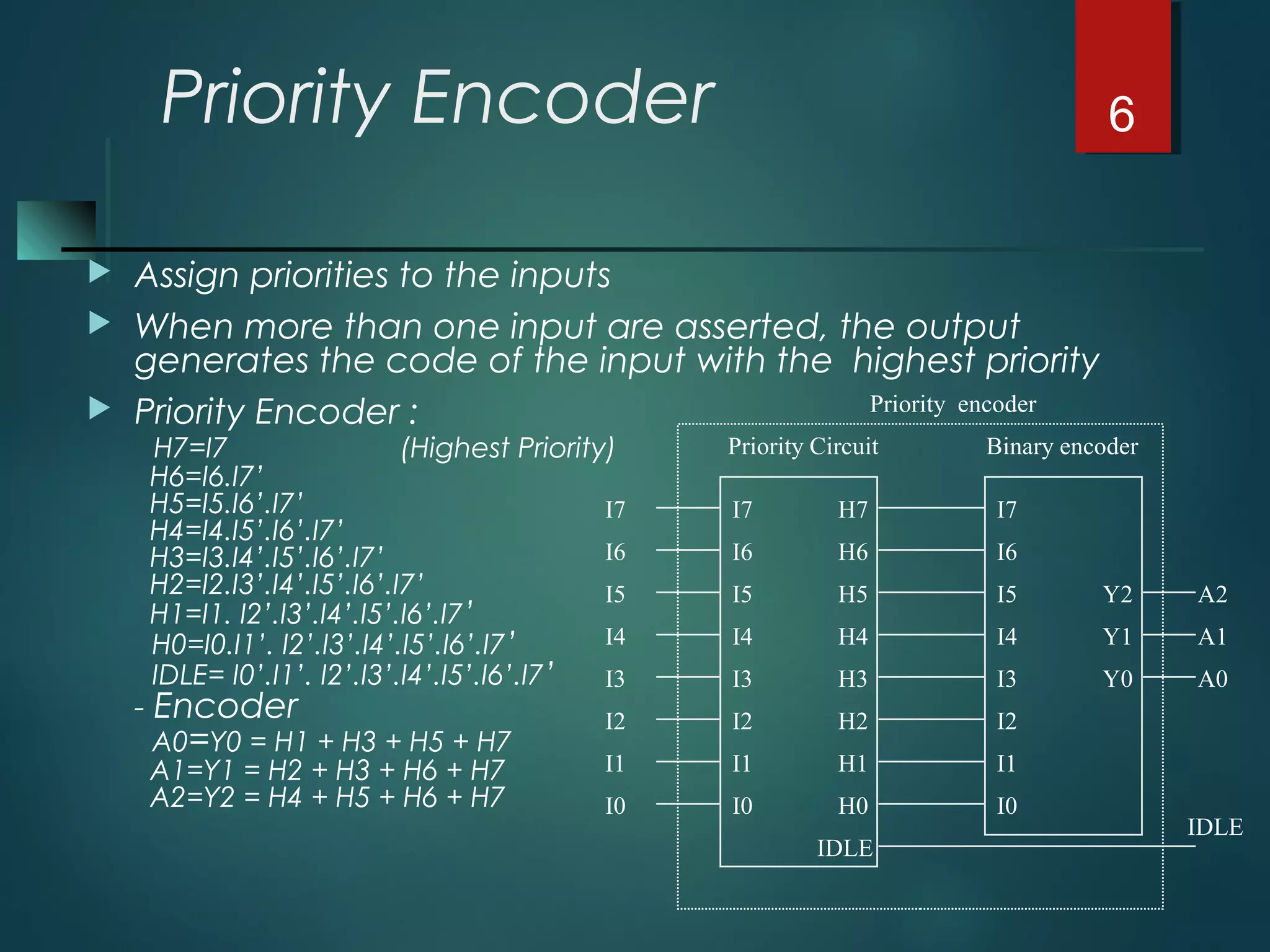
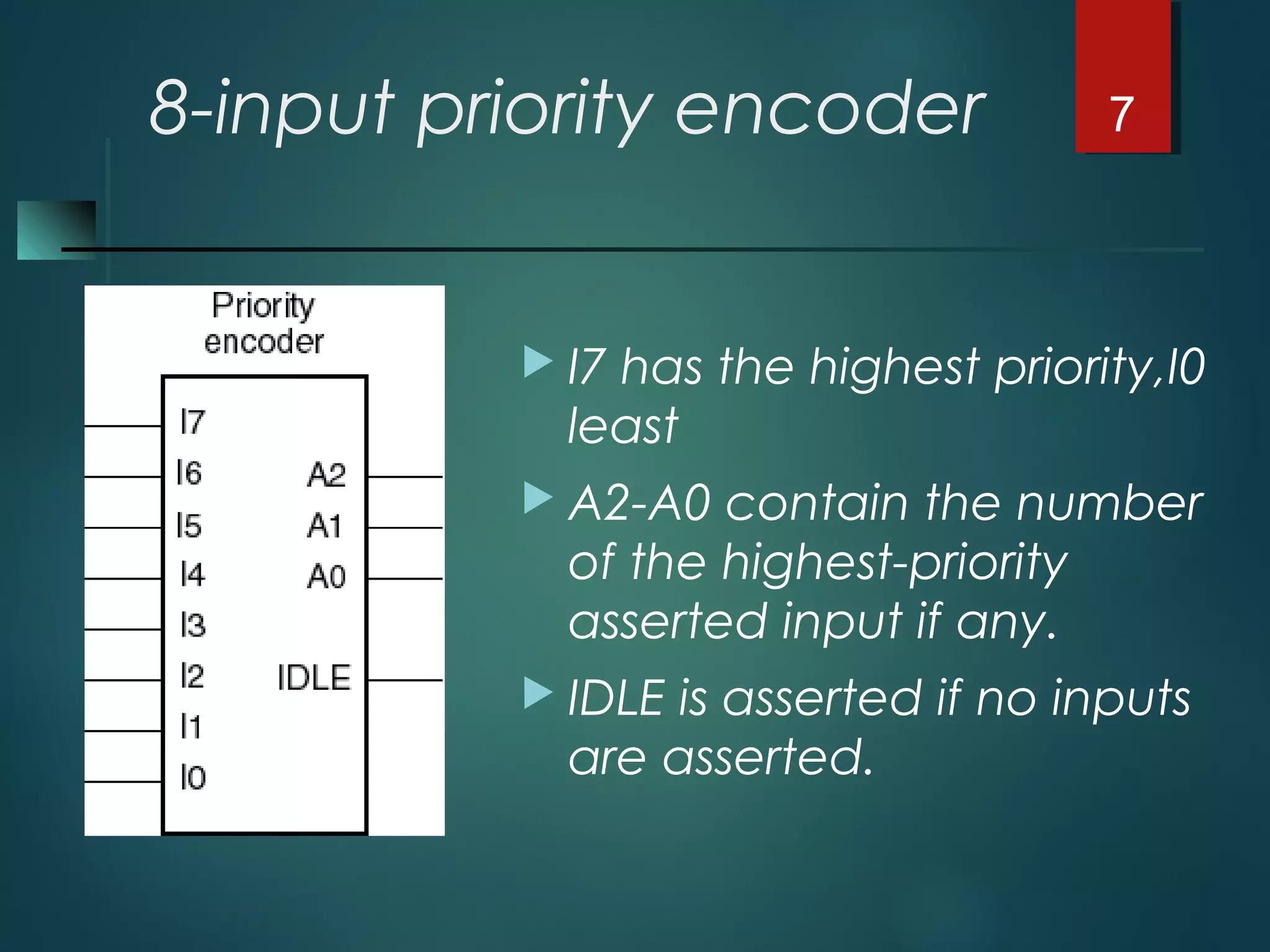
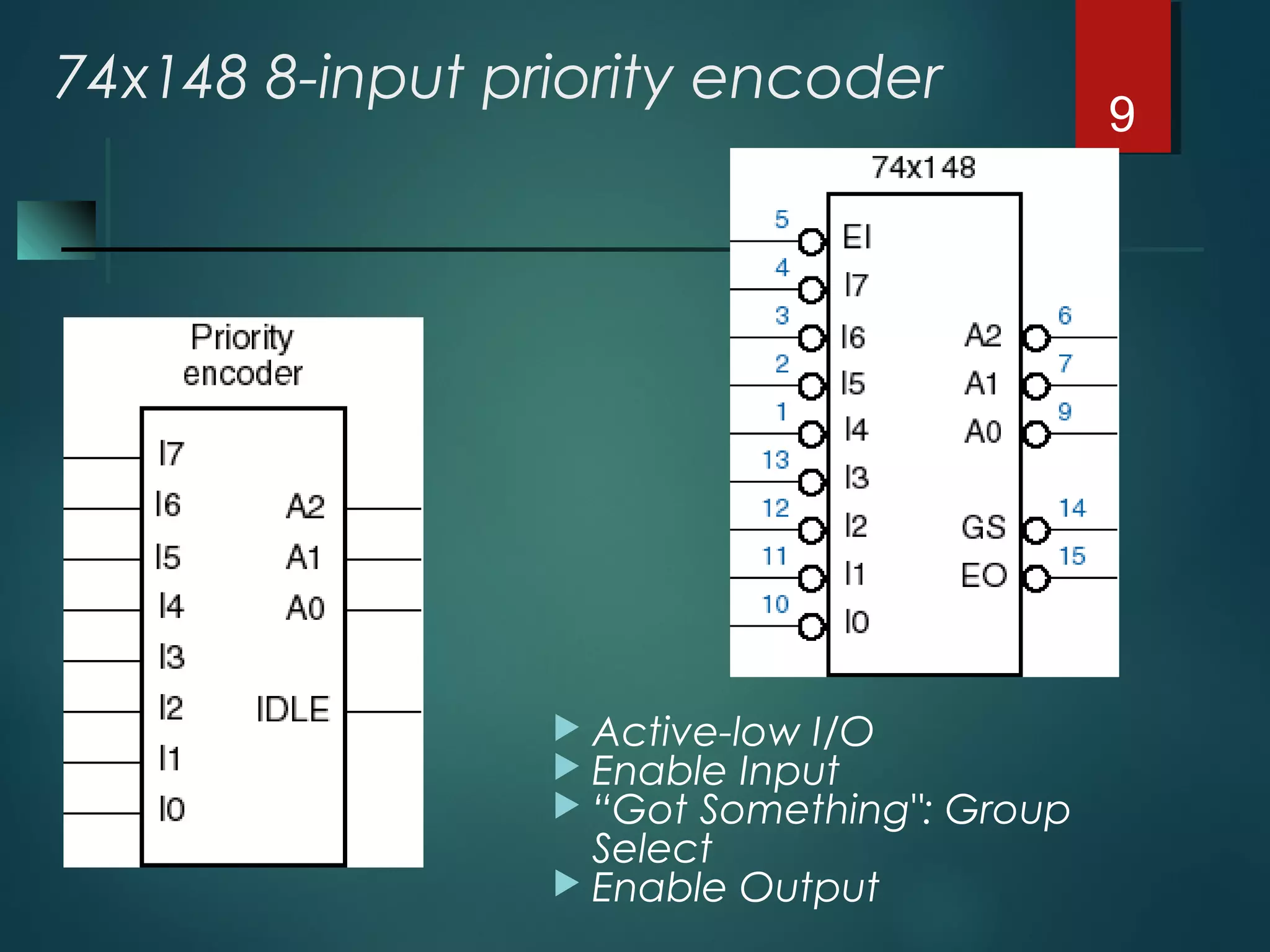
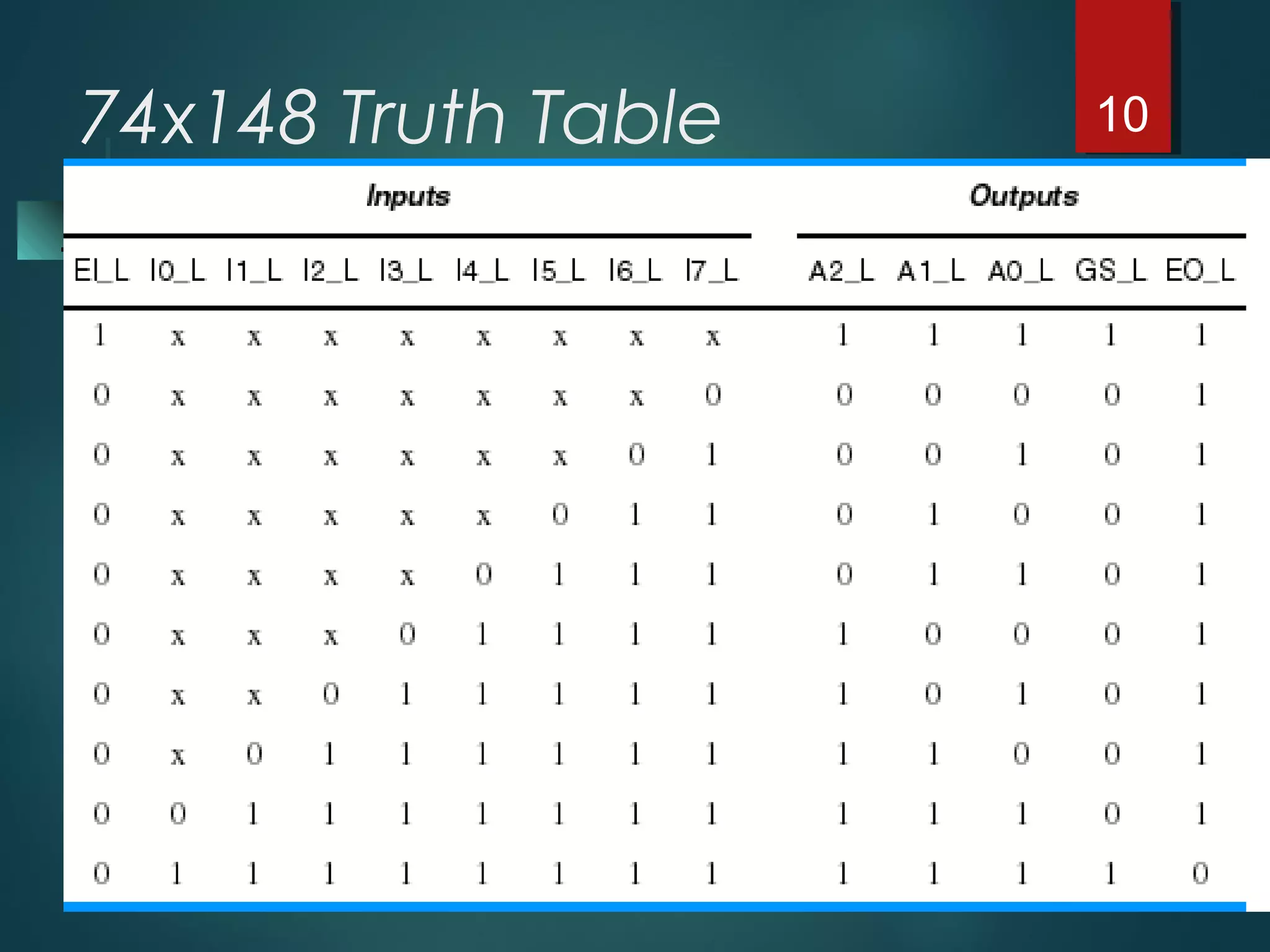
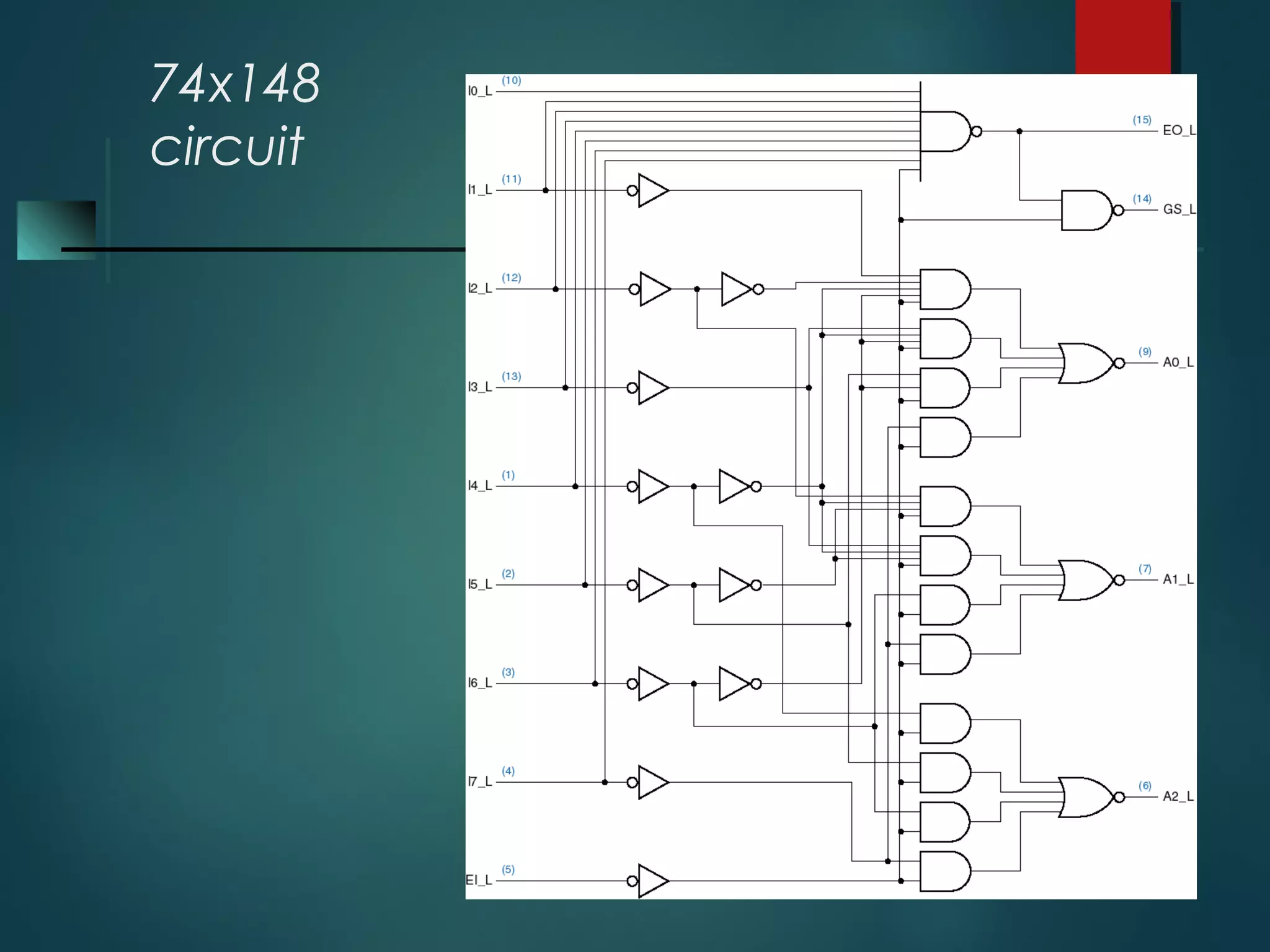
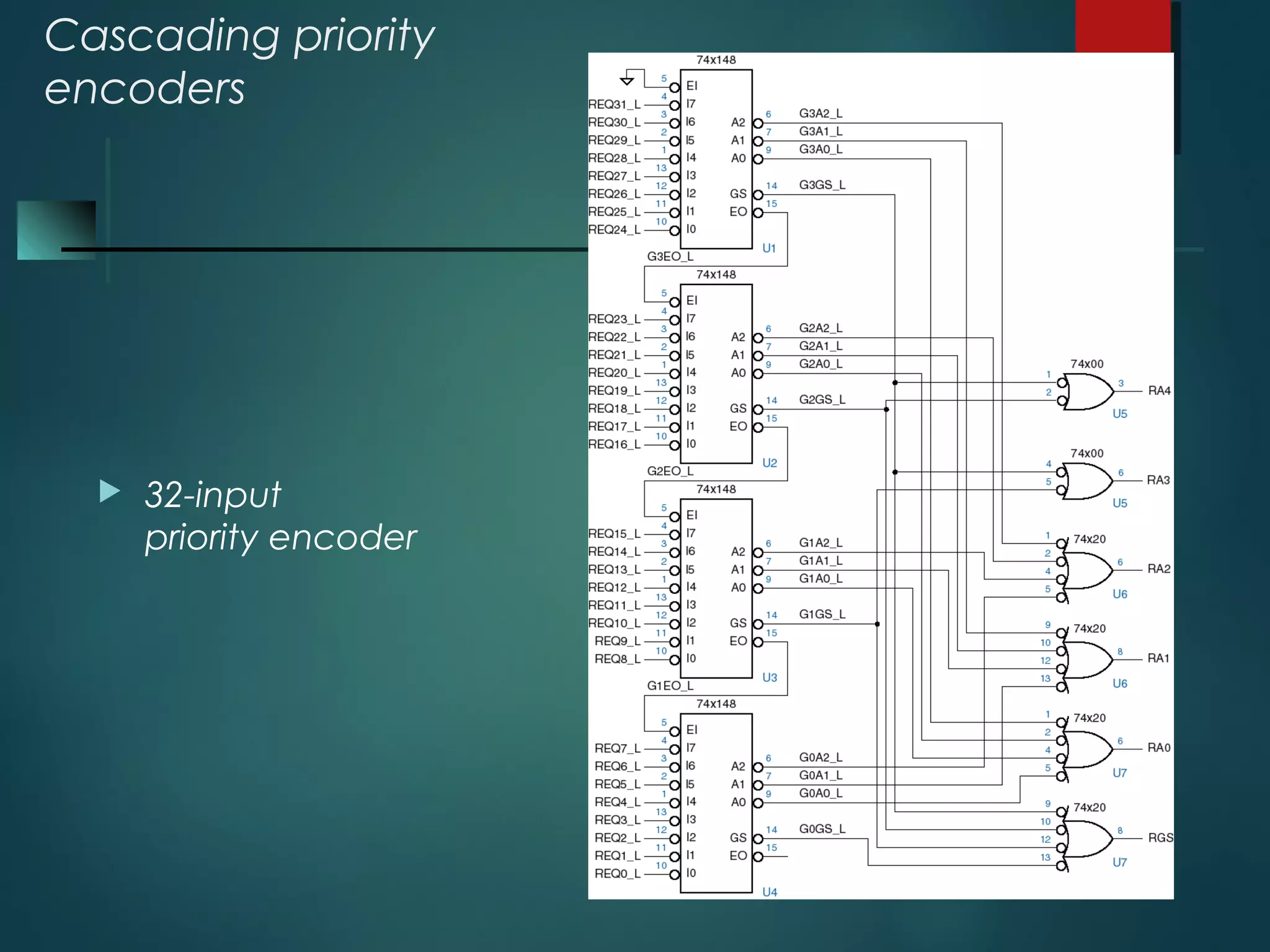
An encoder is a multiple-input, multiple-output device that converts input code words into output code words where the number of outputs is less than the number of inputs. It performs the inverse function of a decoder. A priority encoder assigns priorities to its inputs and outputs the code of the highest priority asserted input when multiple inputs are activated simultaneously. An 8-to-3 priority encoder uses logic gates to implement the priority encoding function with one input having the highest priority and one having the lowest priority.