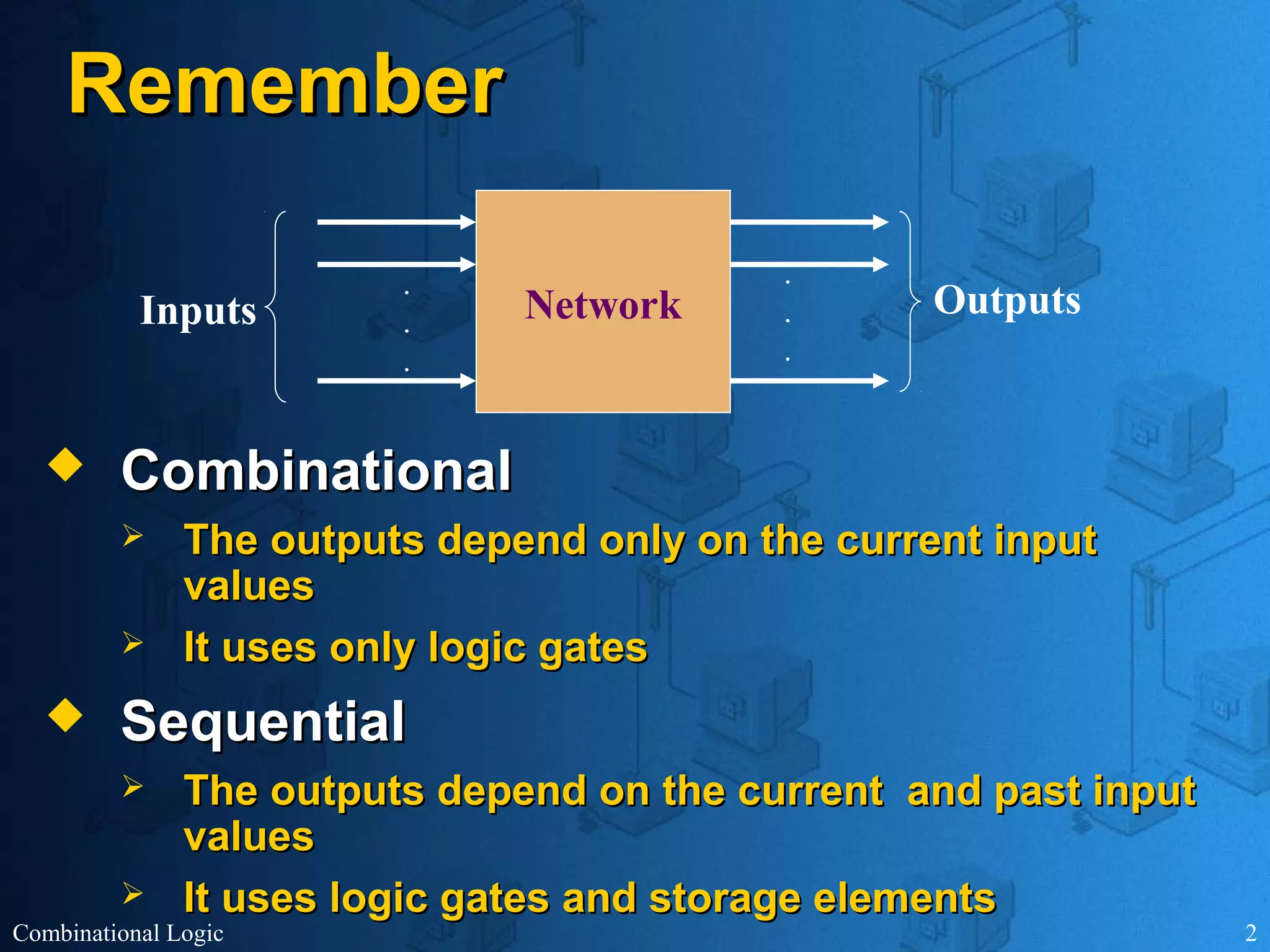
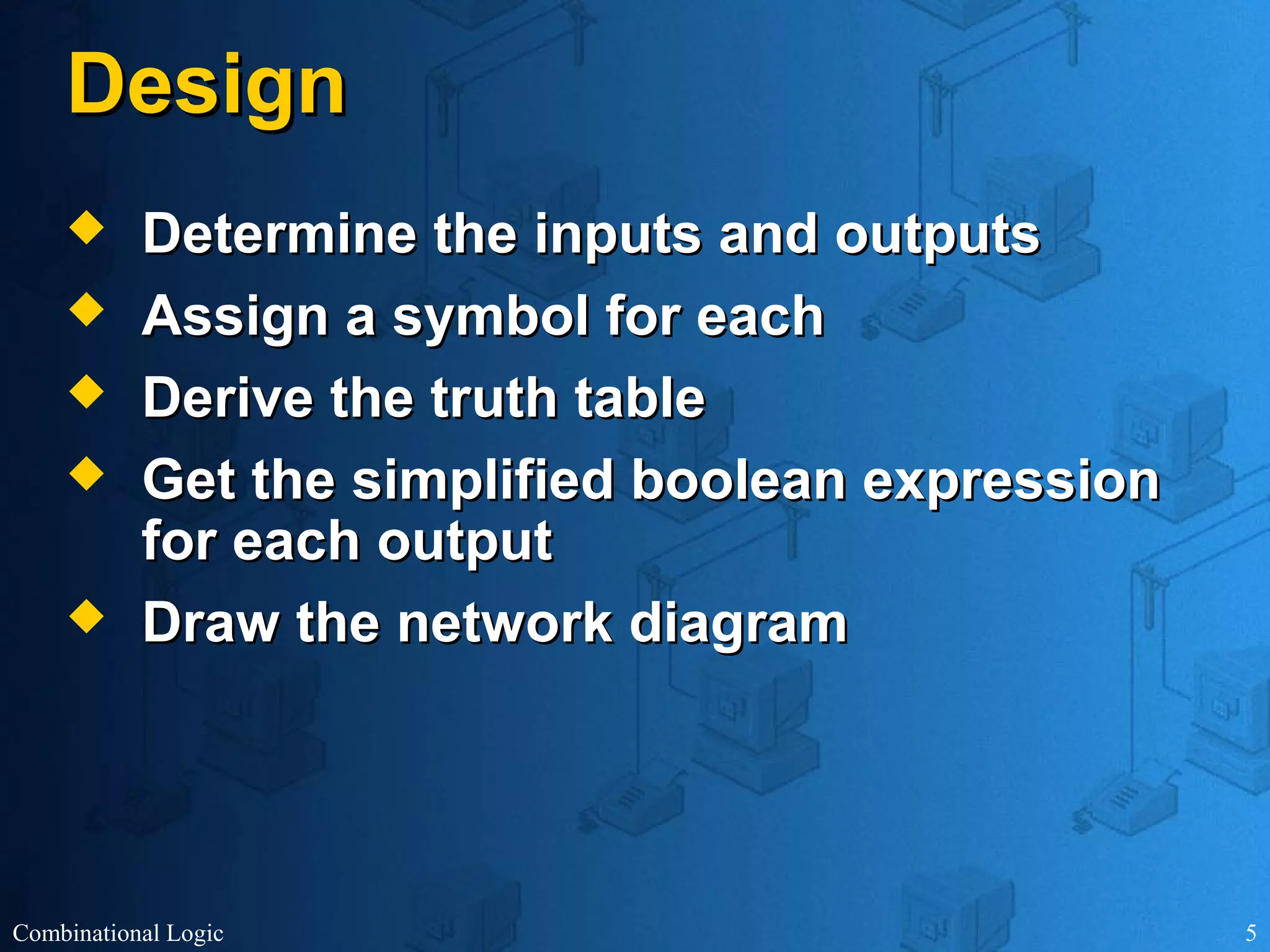
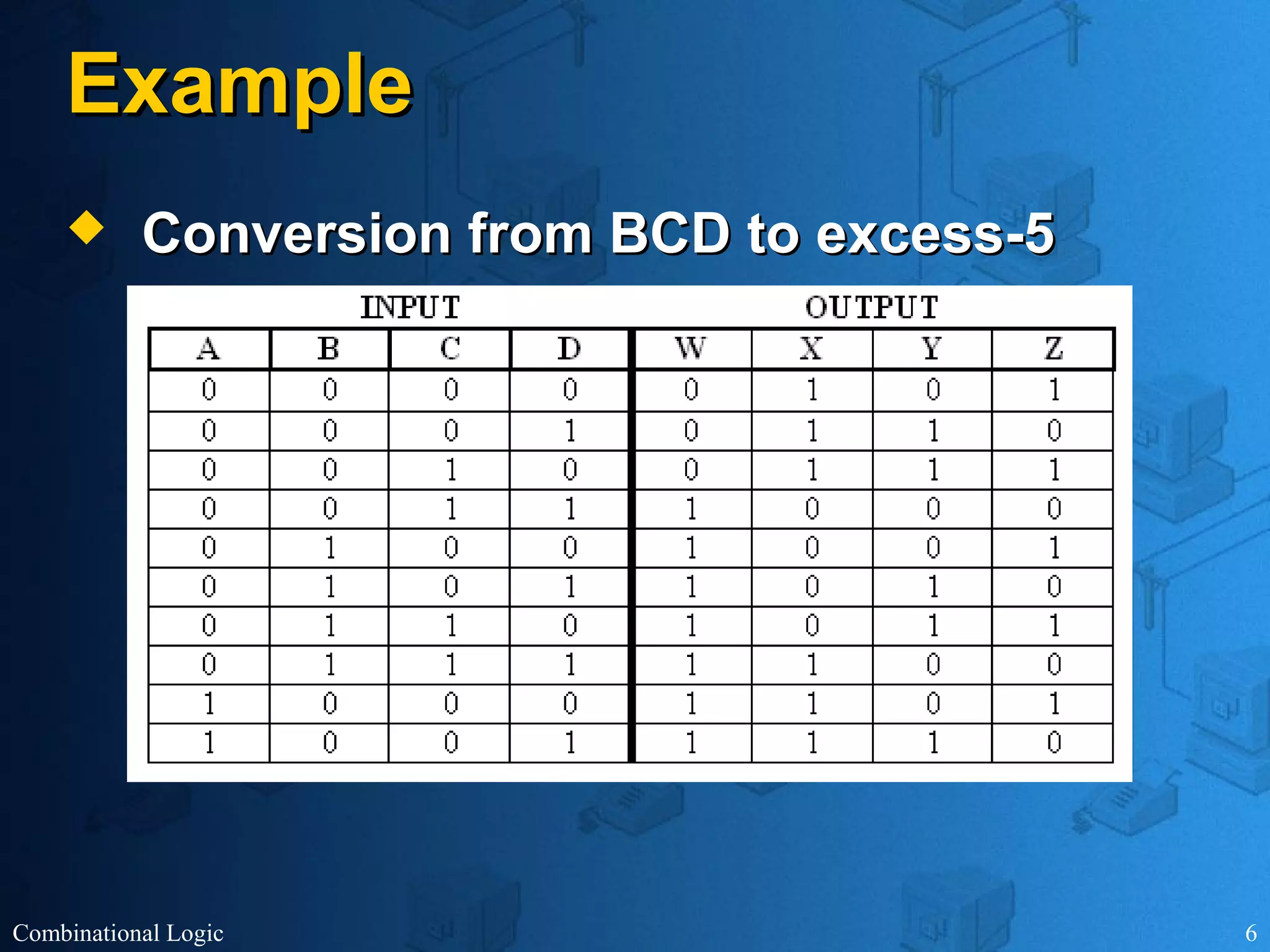
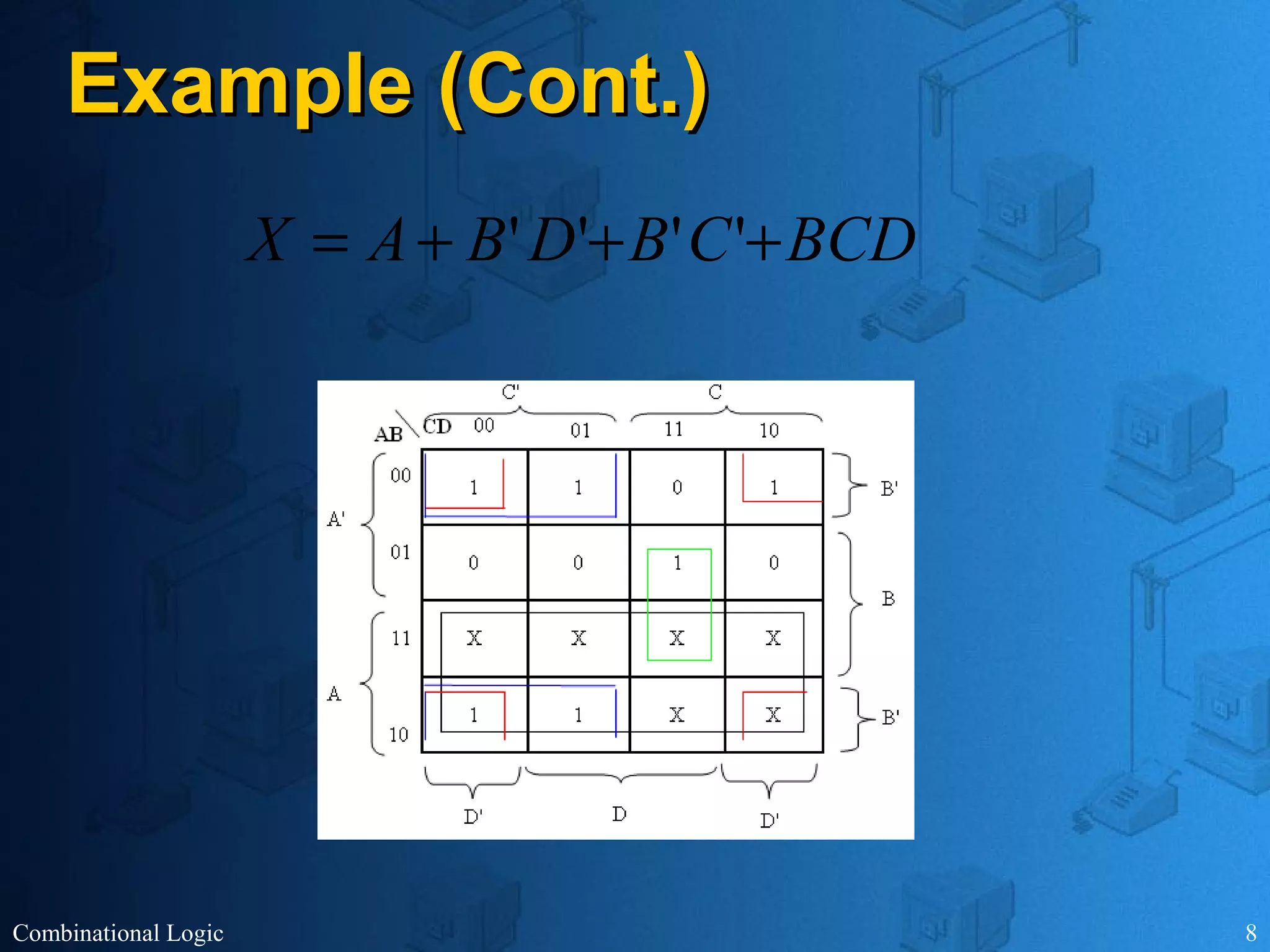
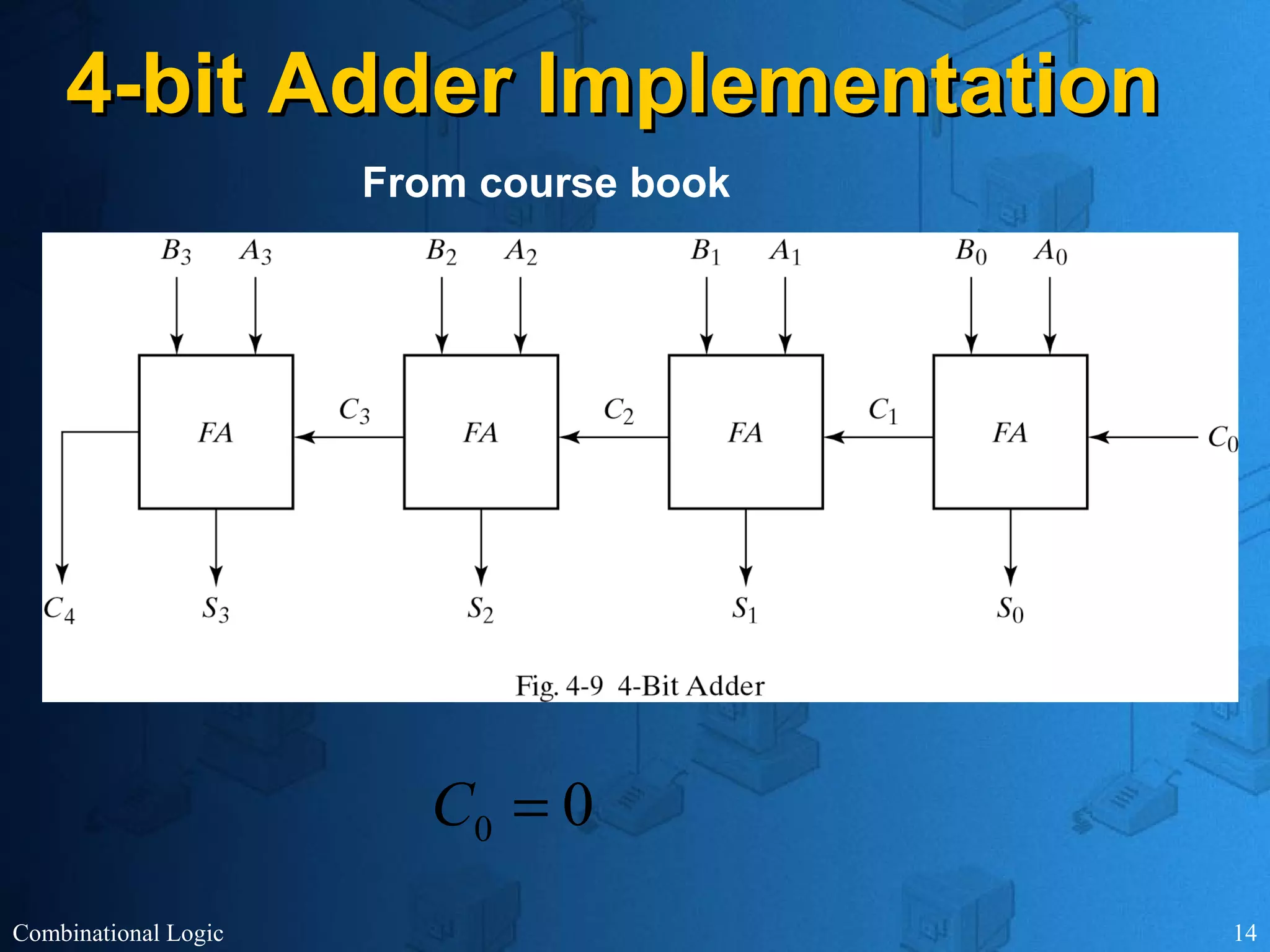
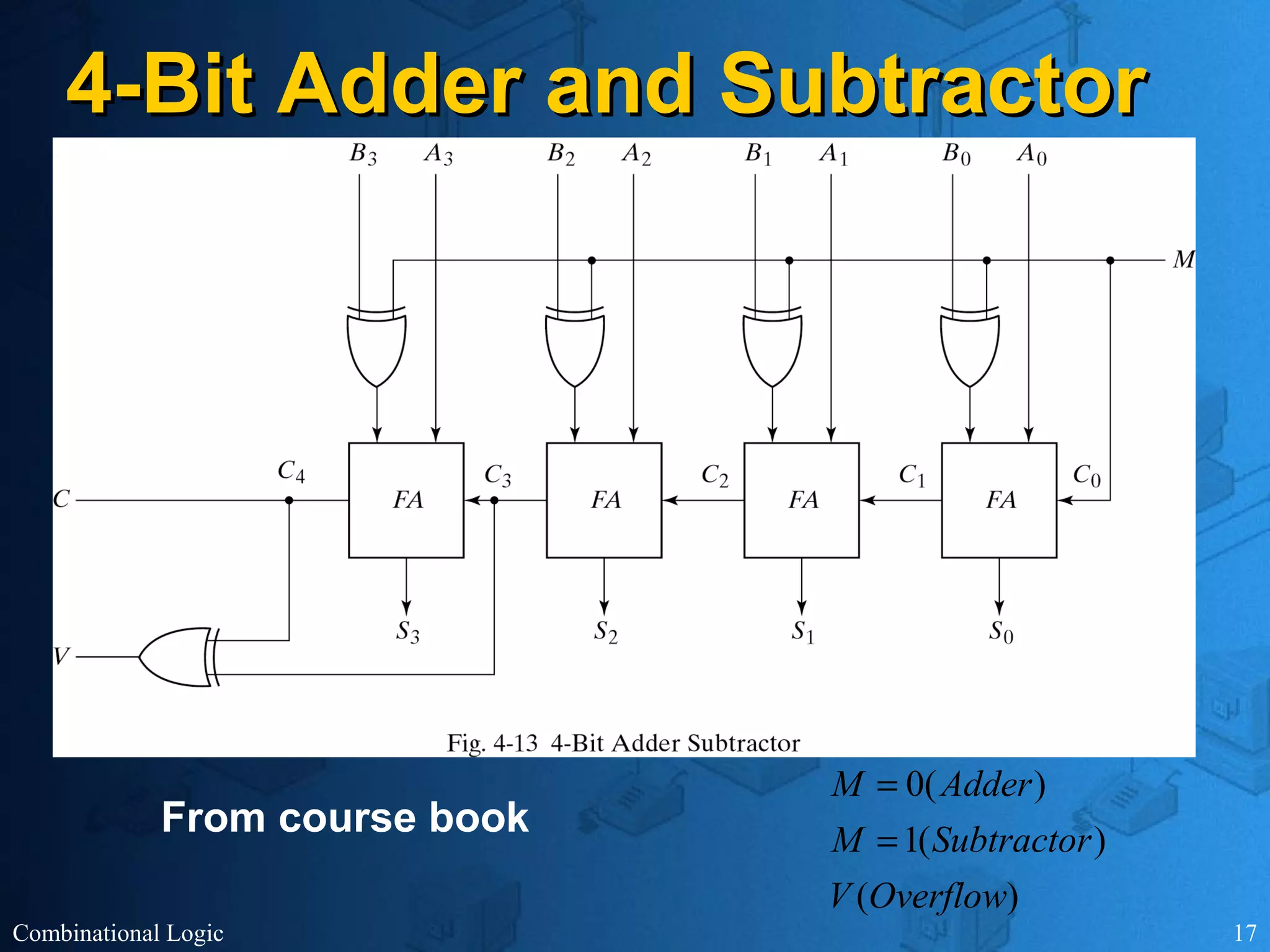
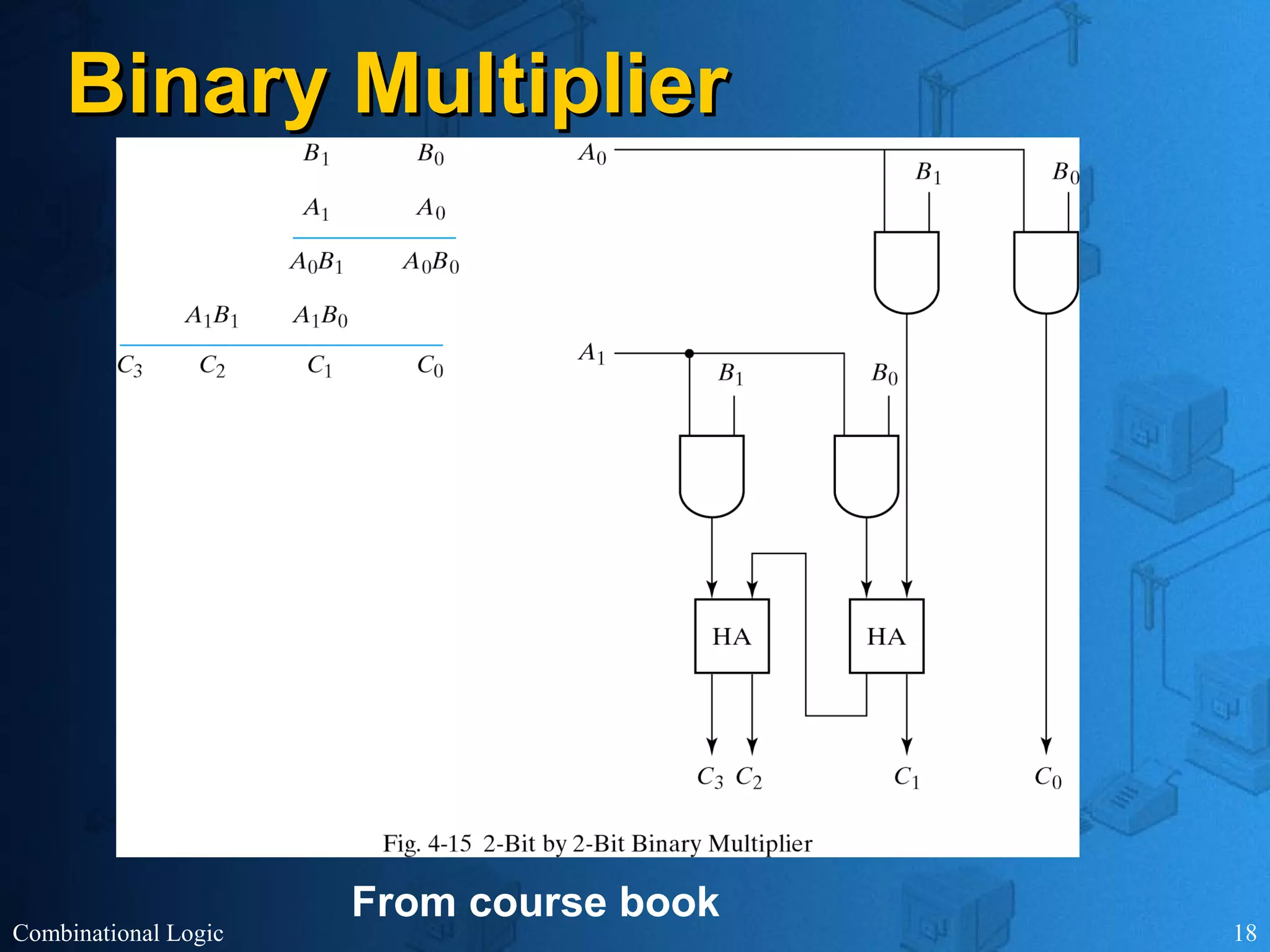
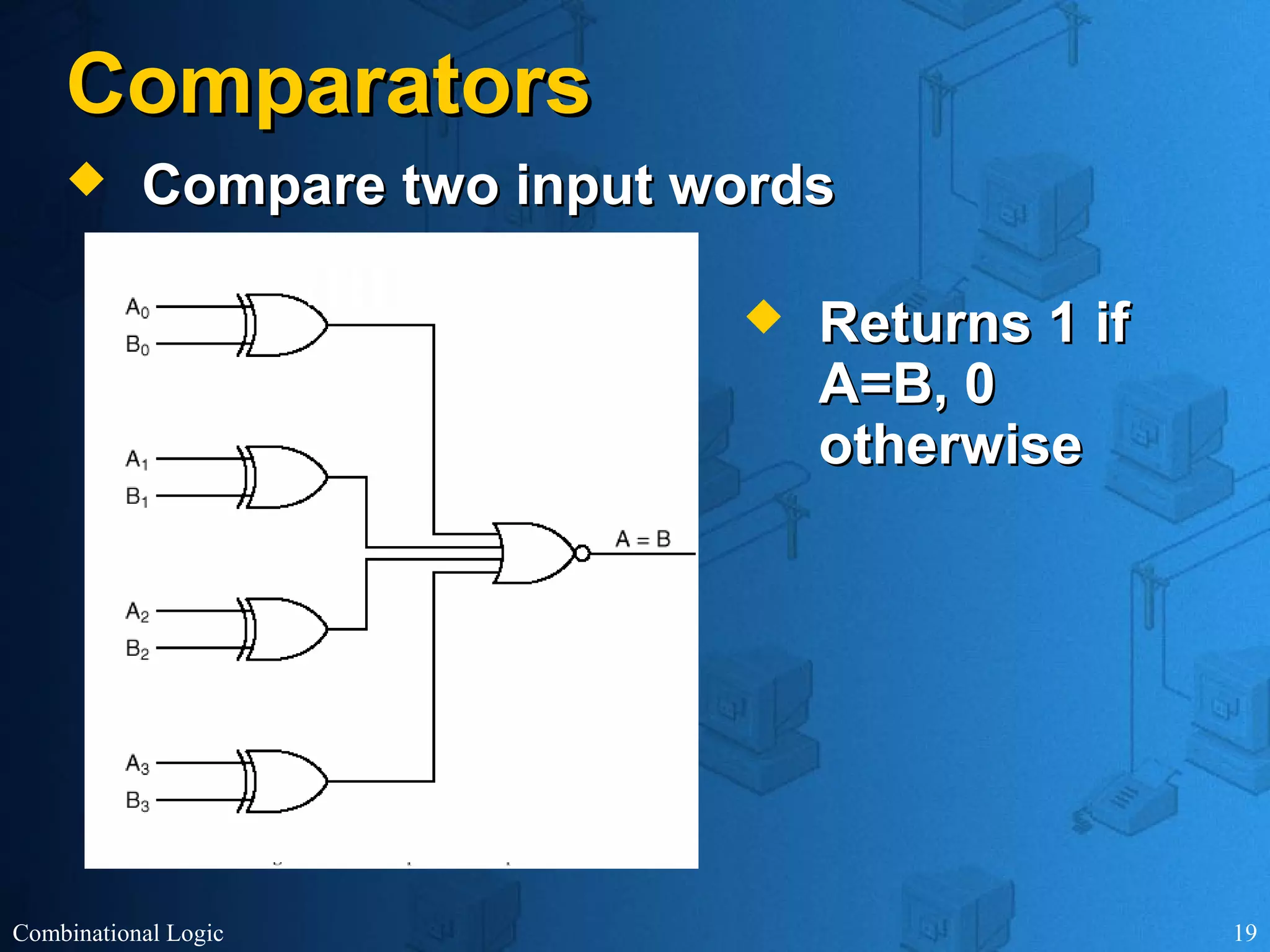
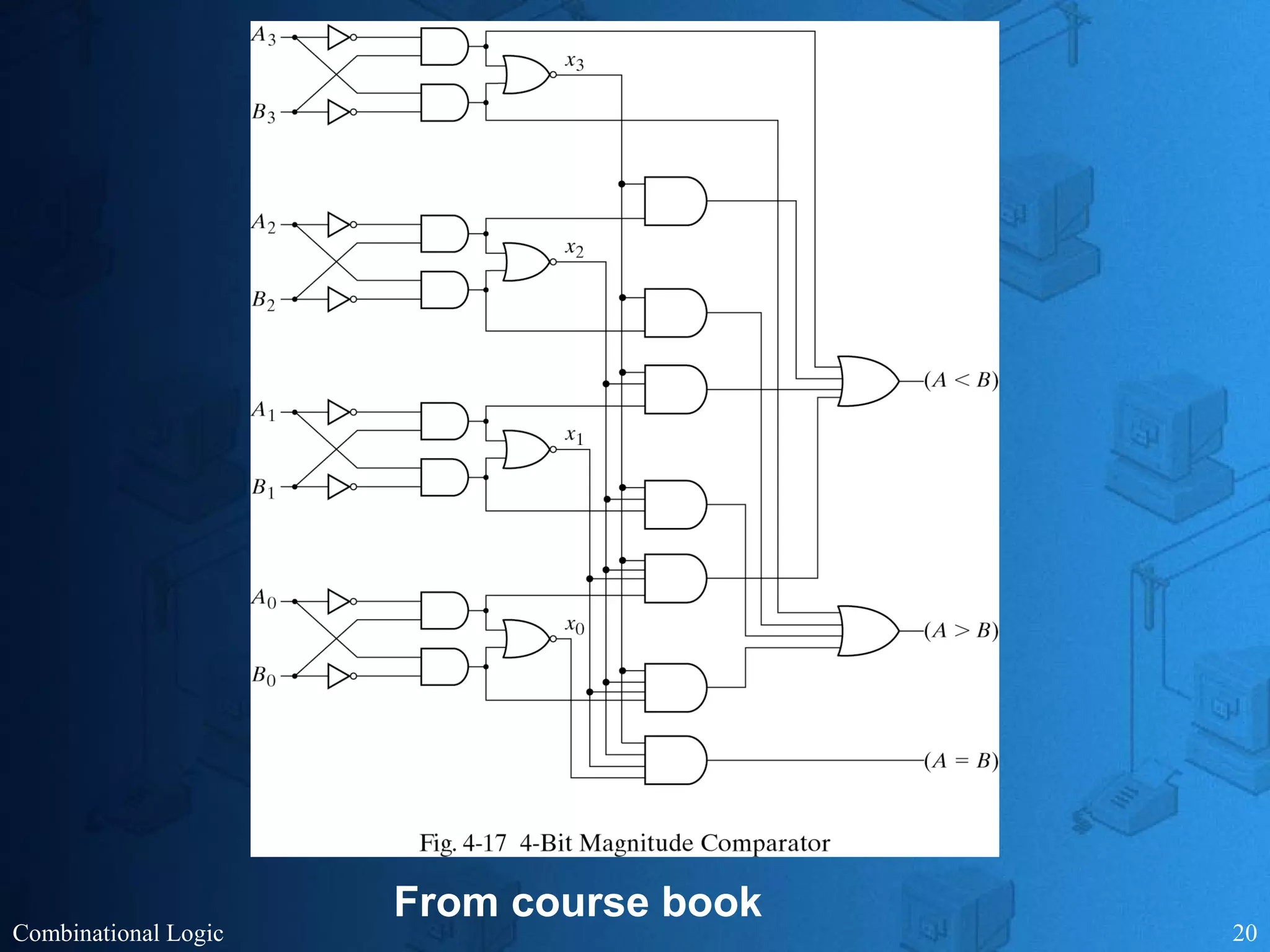
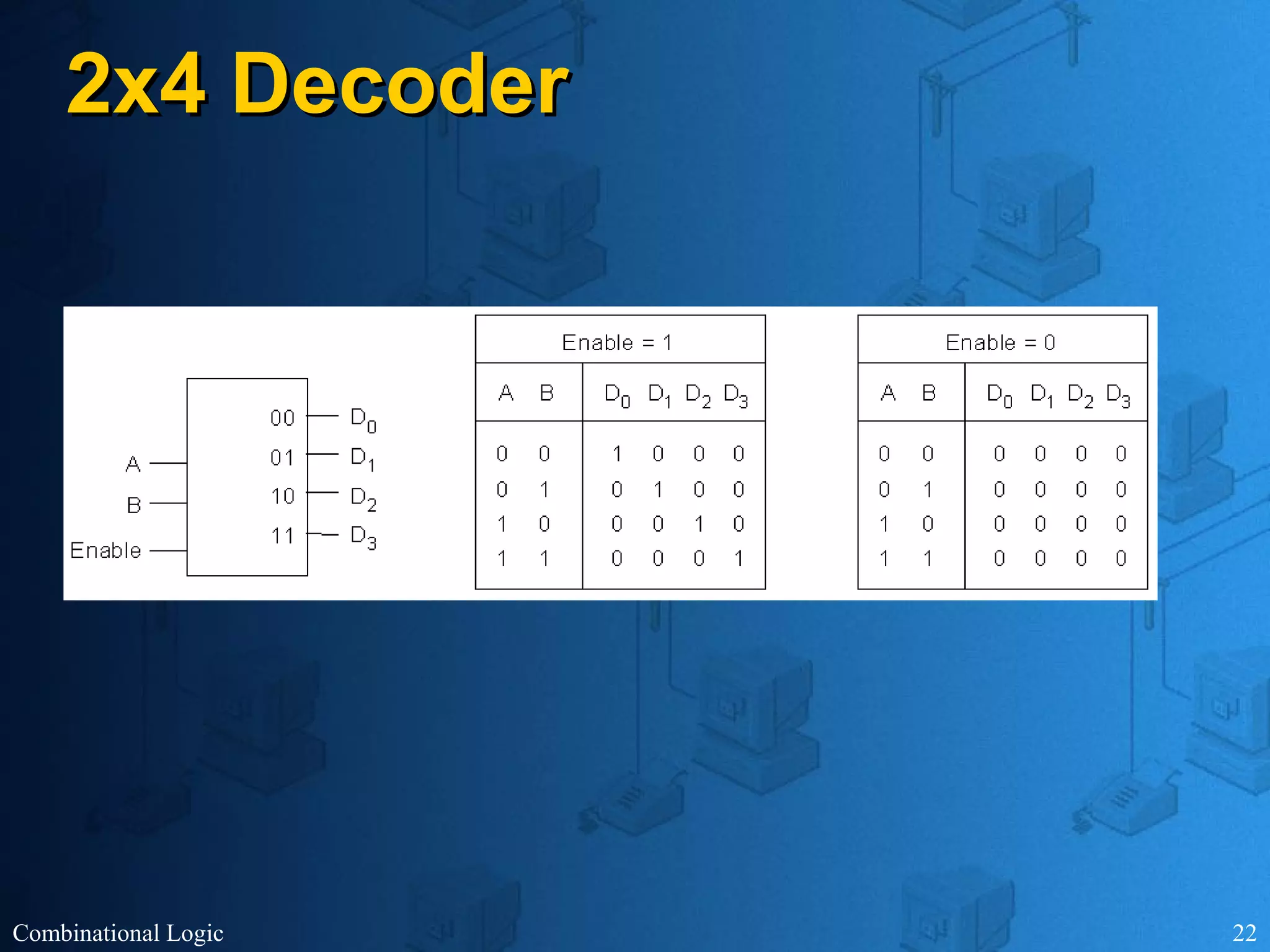
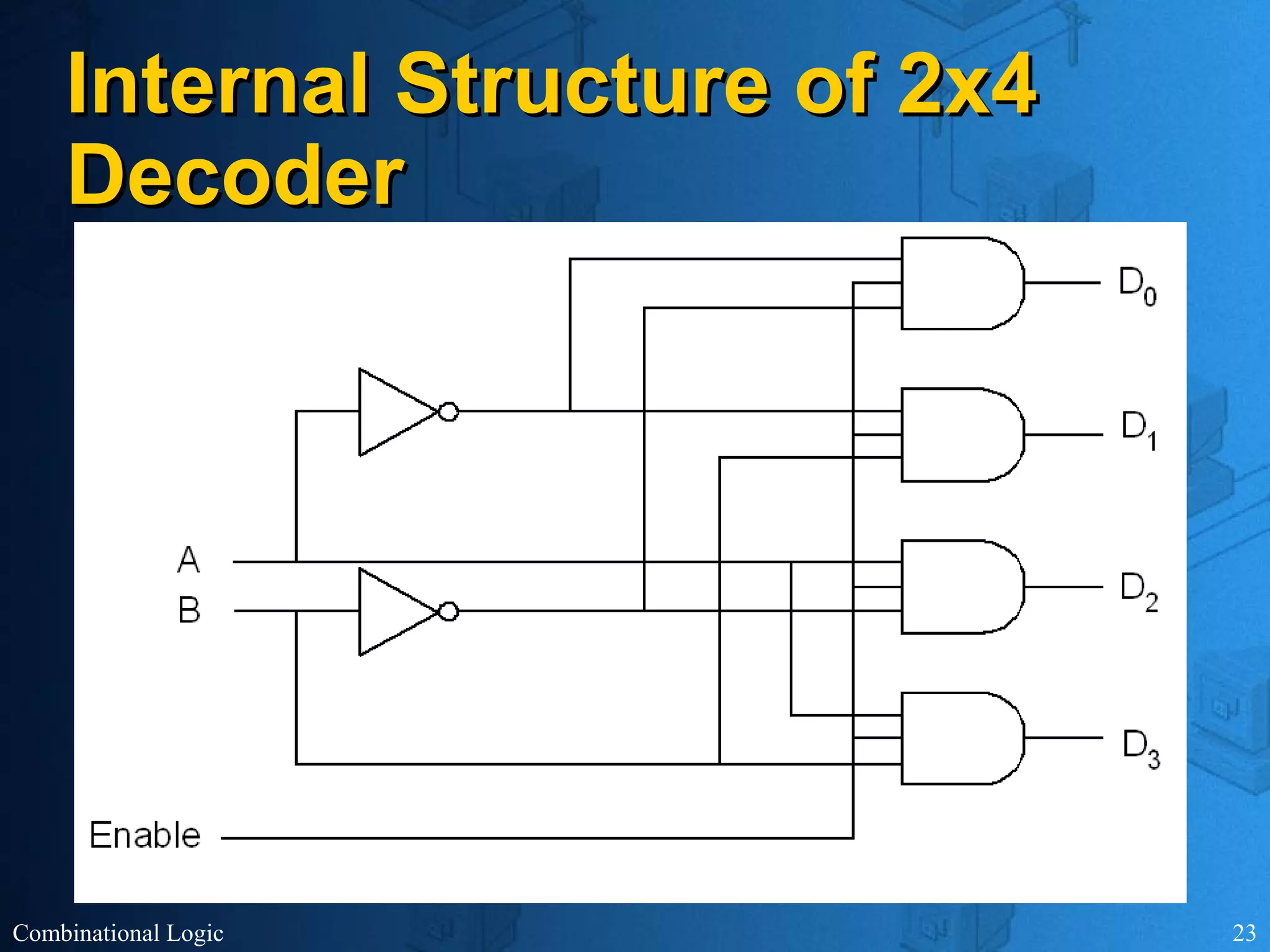
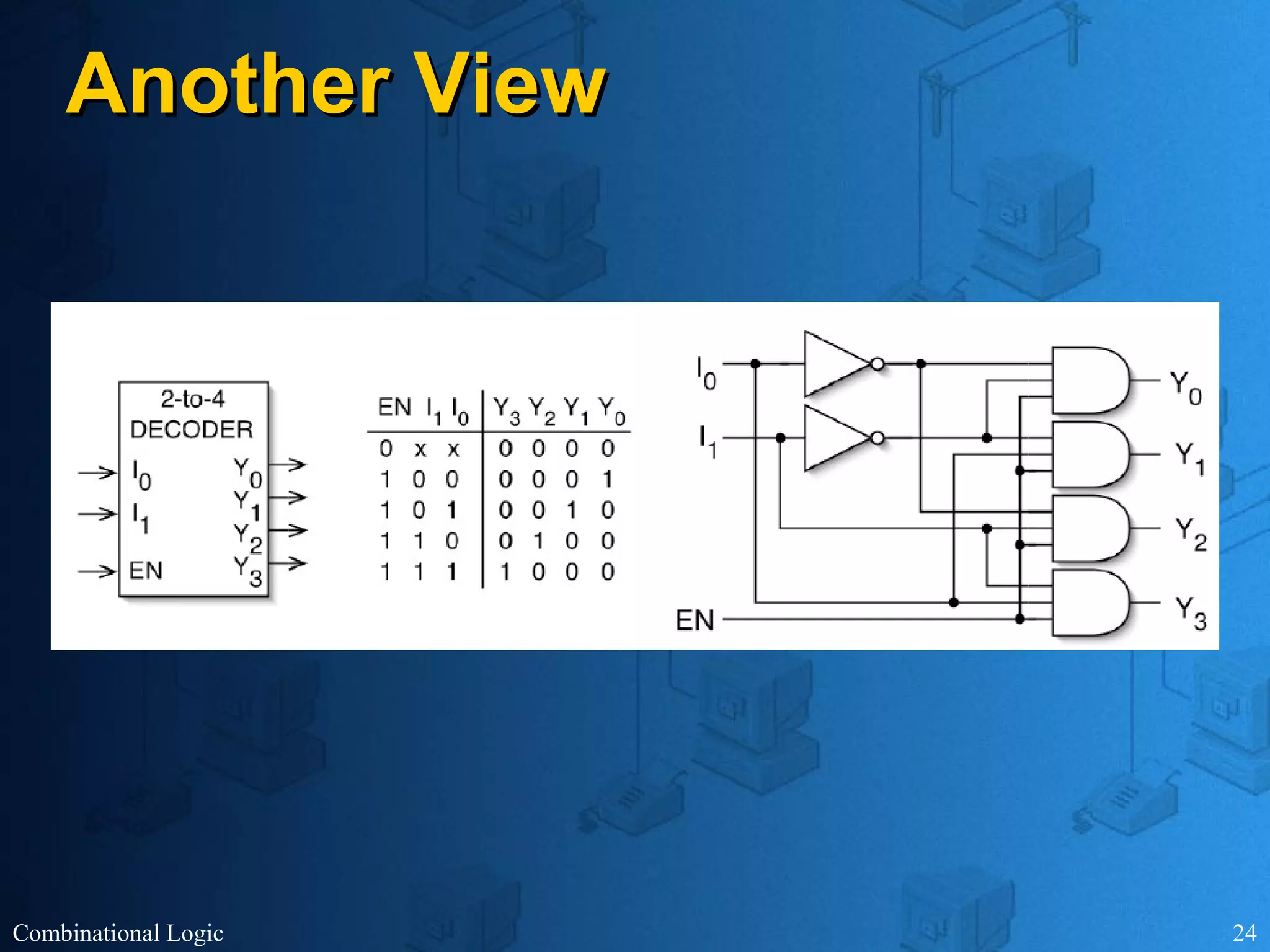
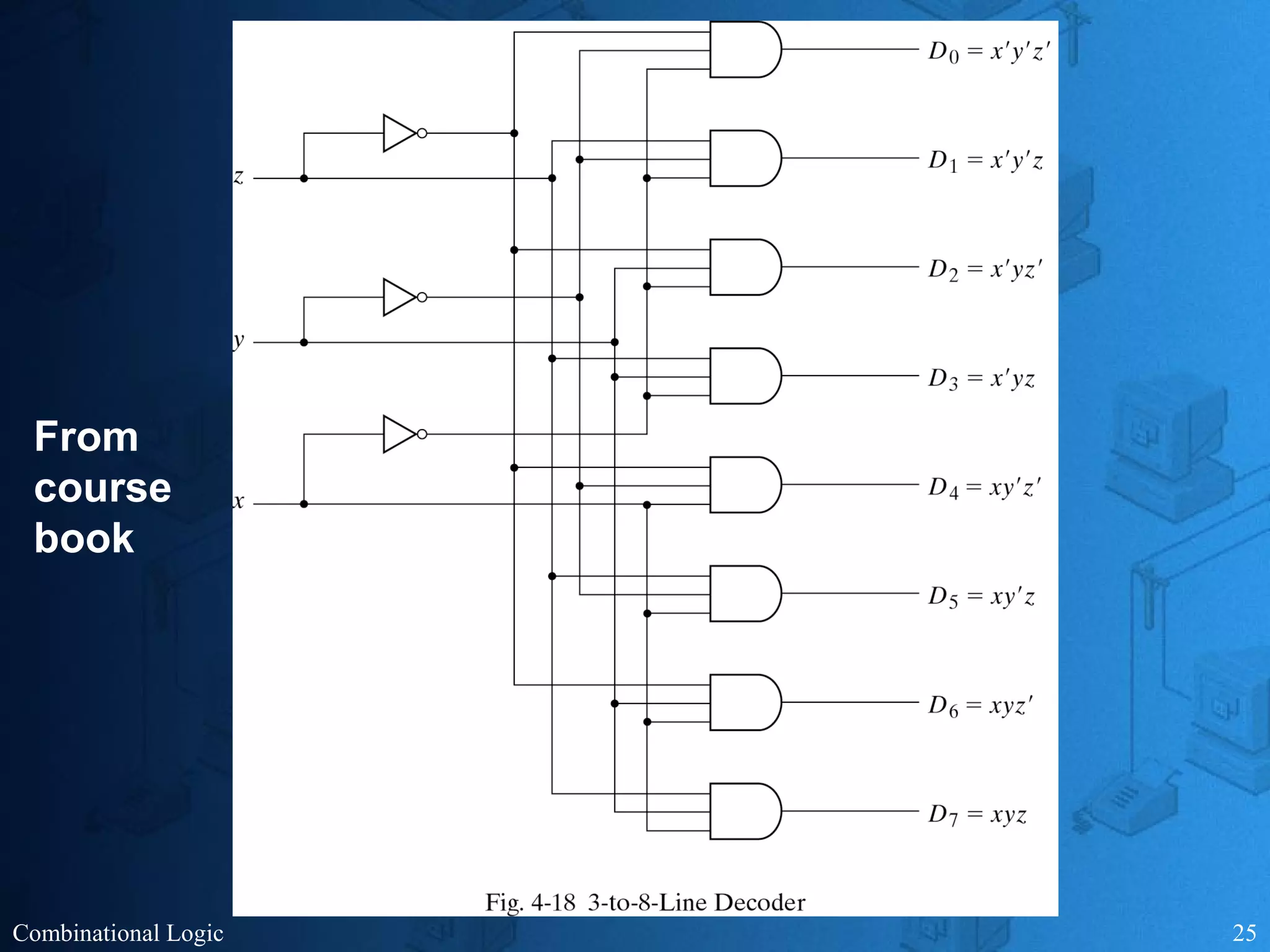
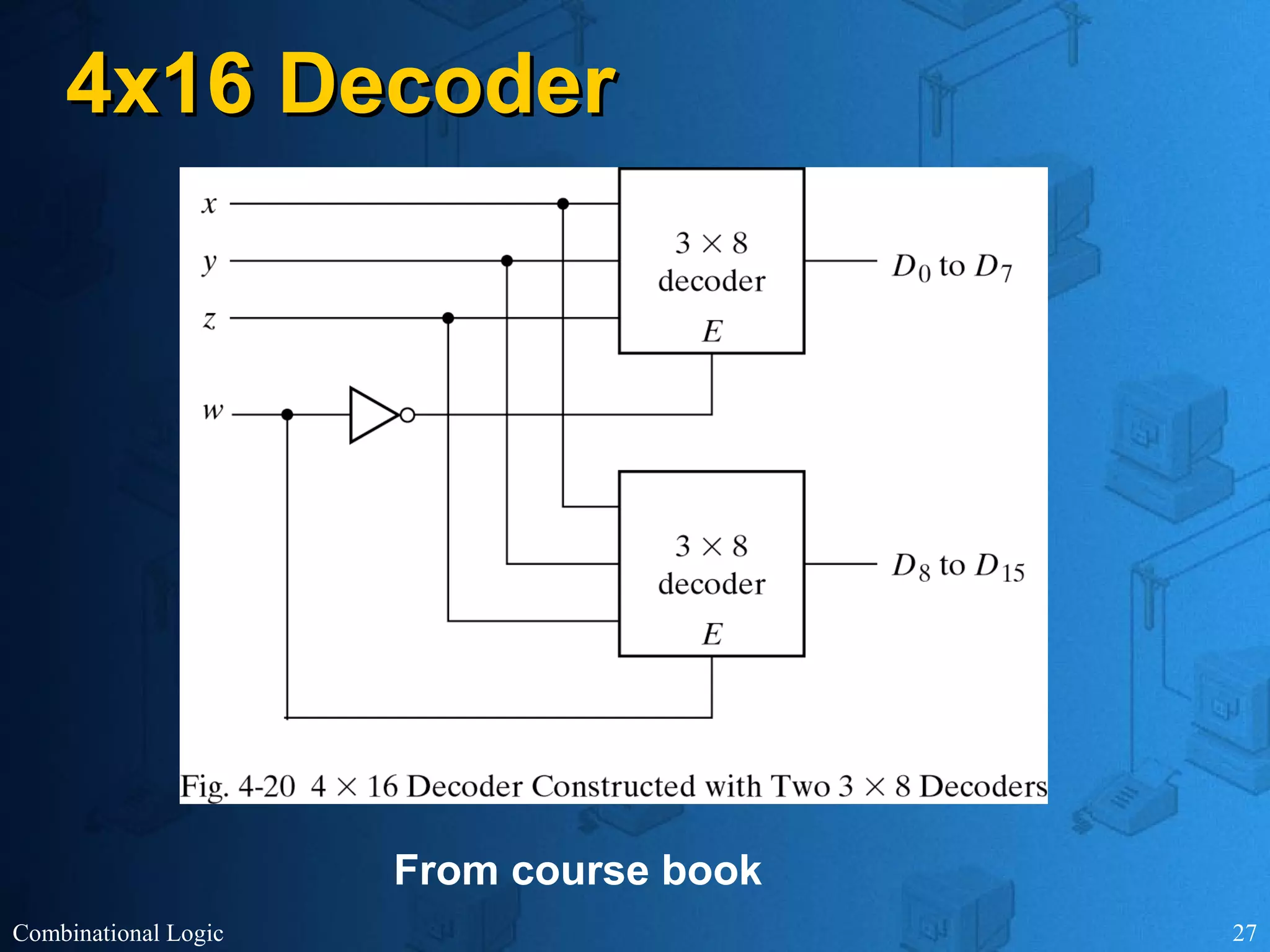
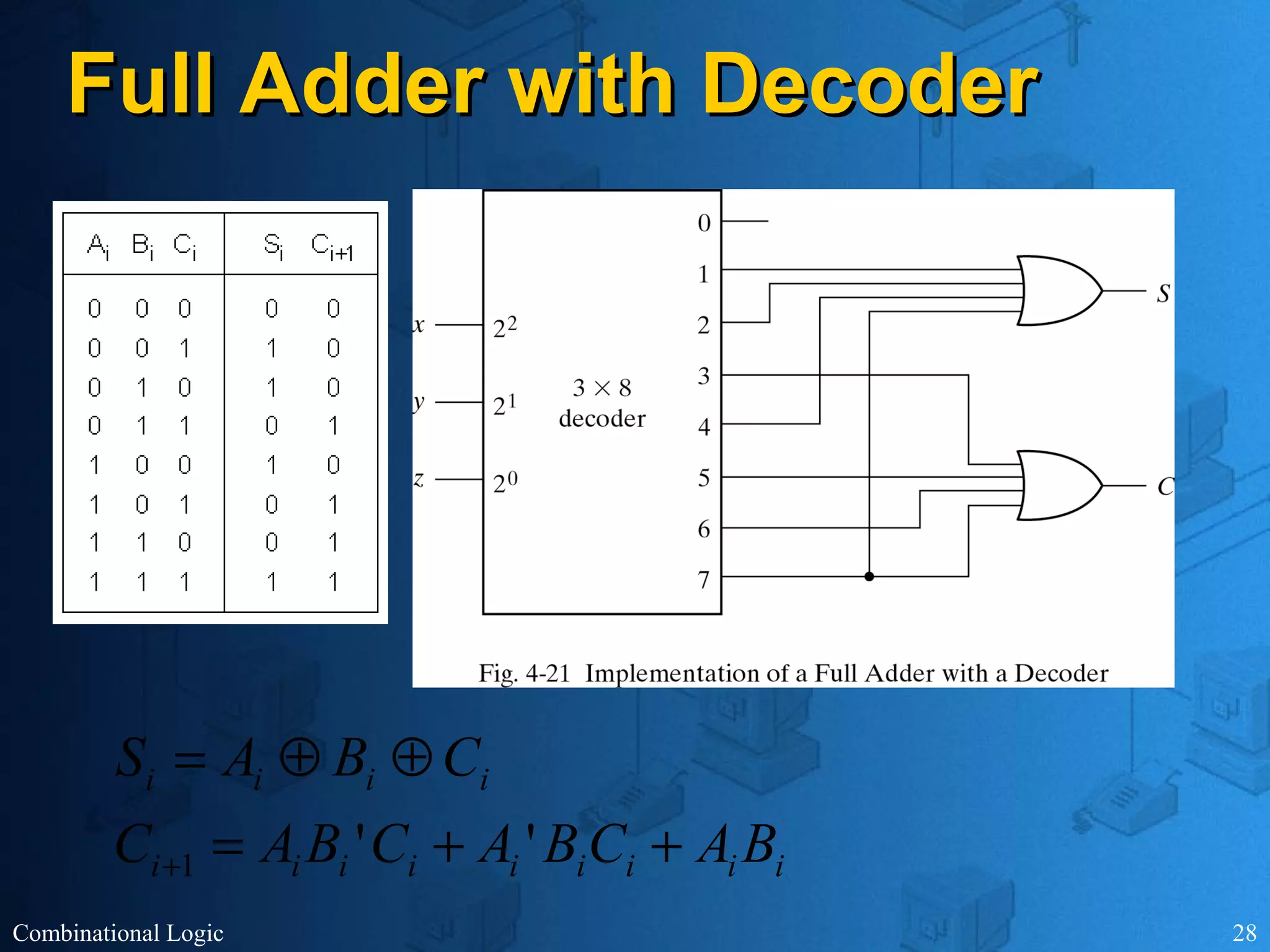
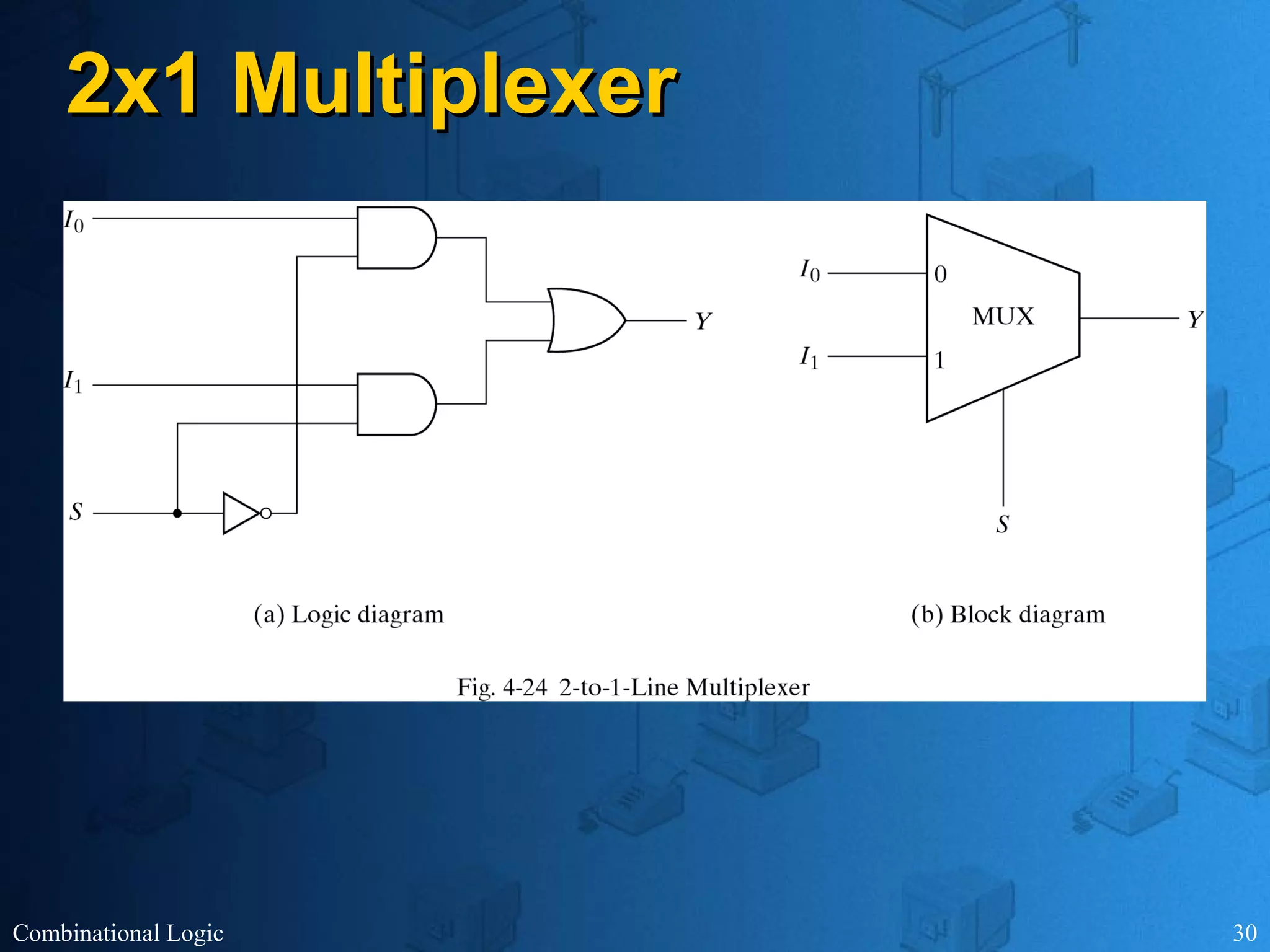
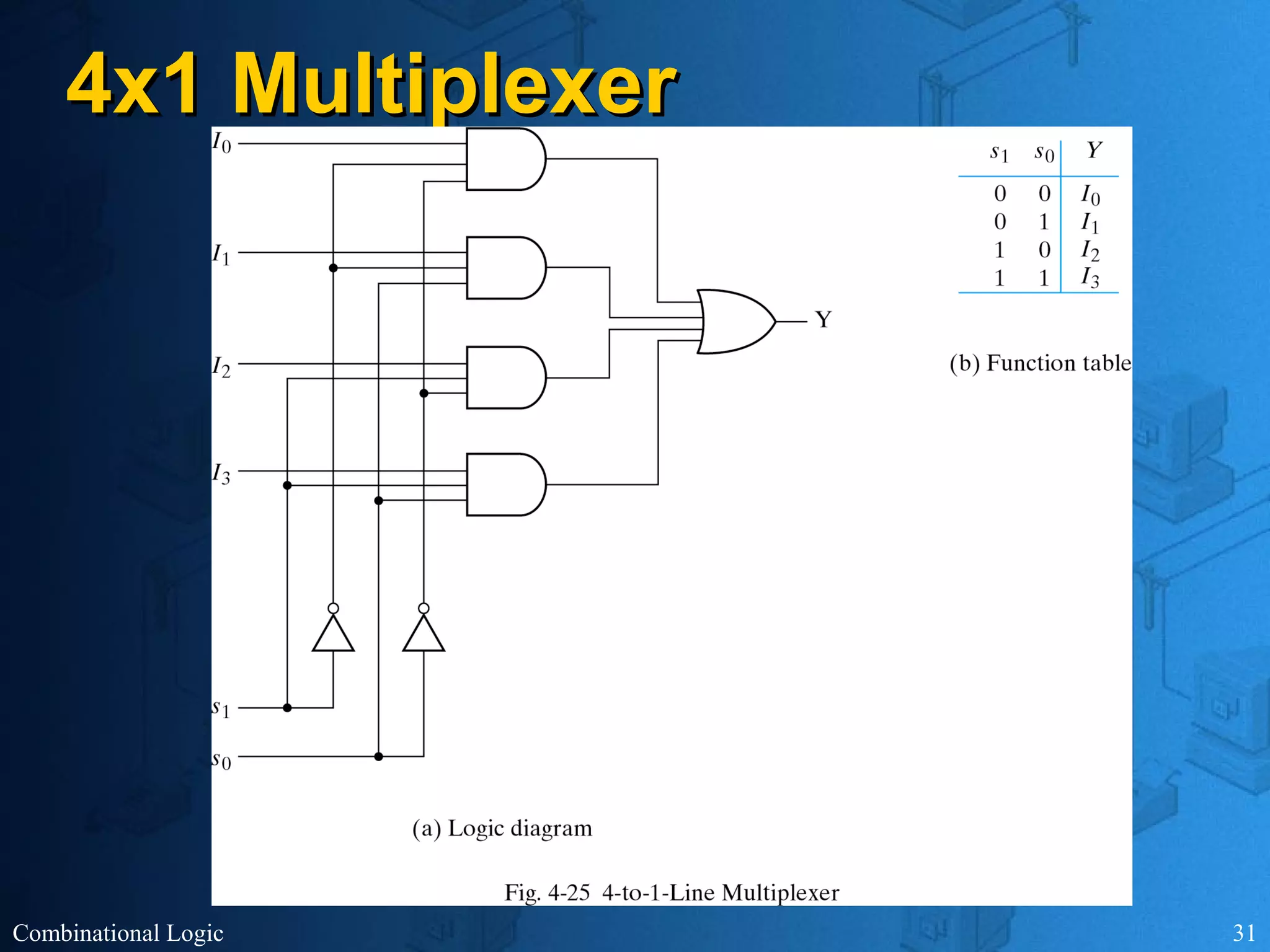
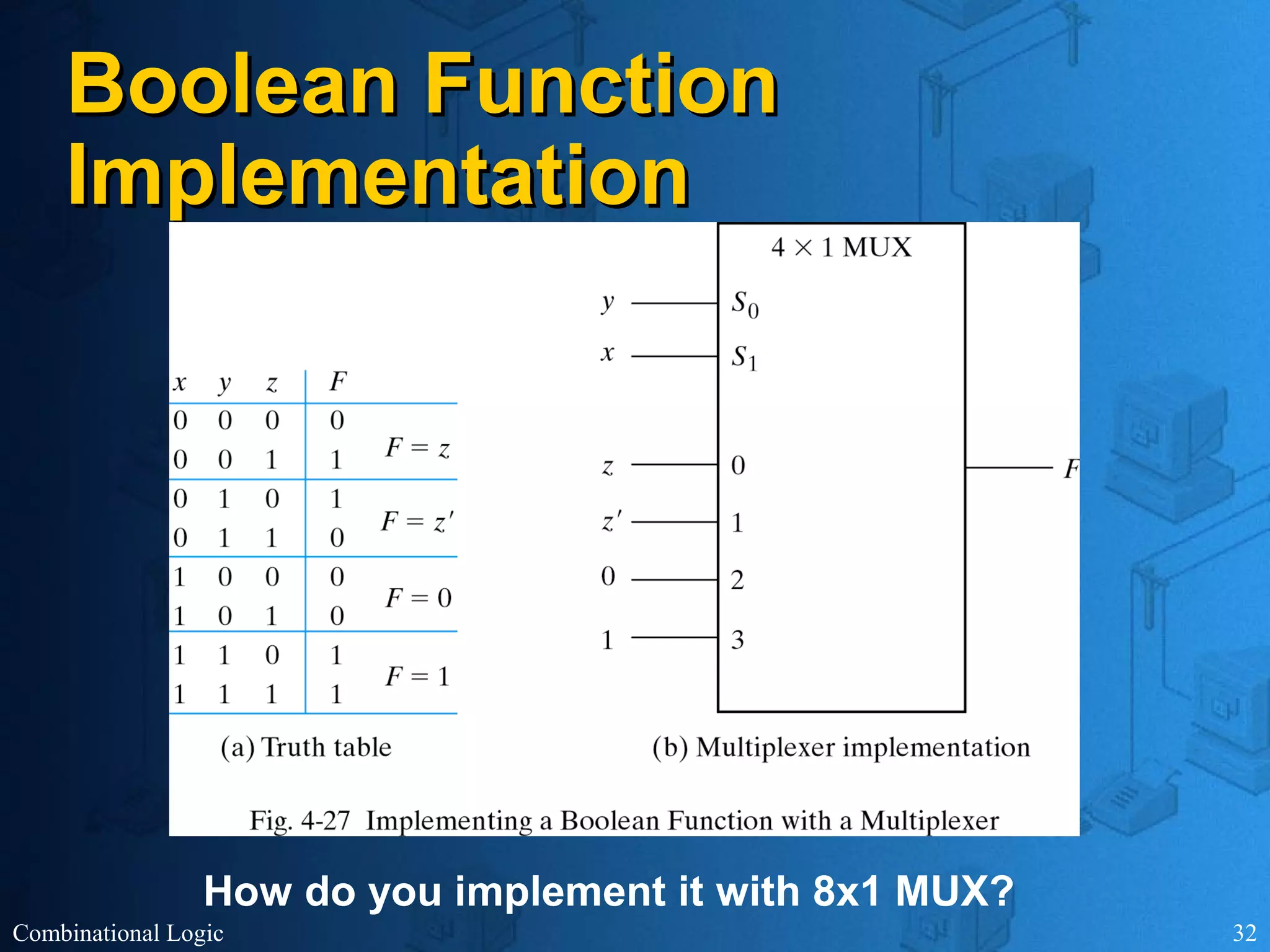
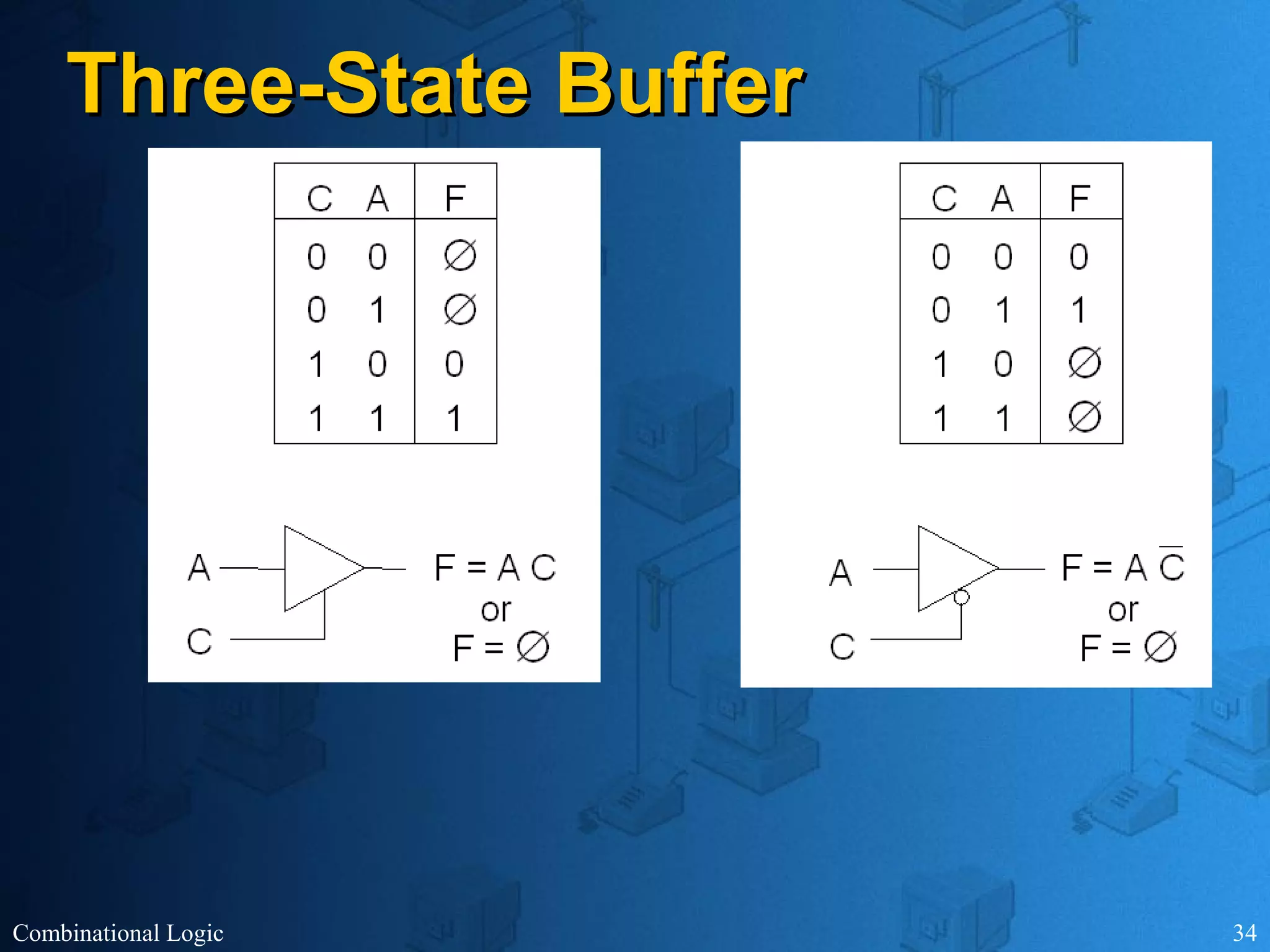
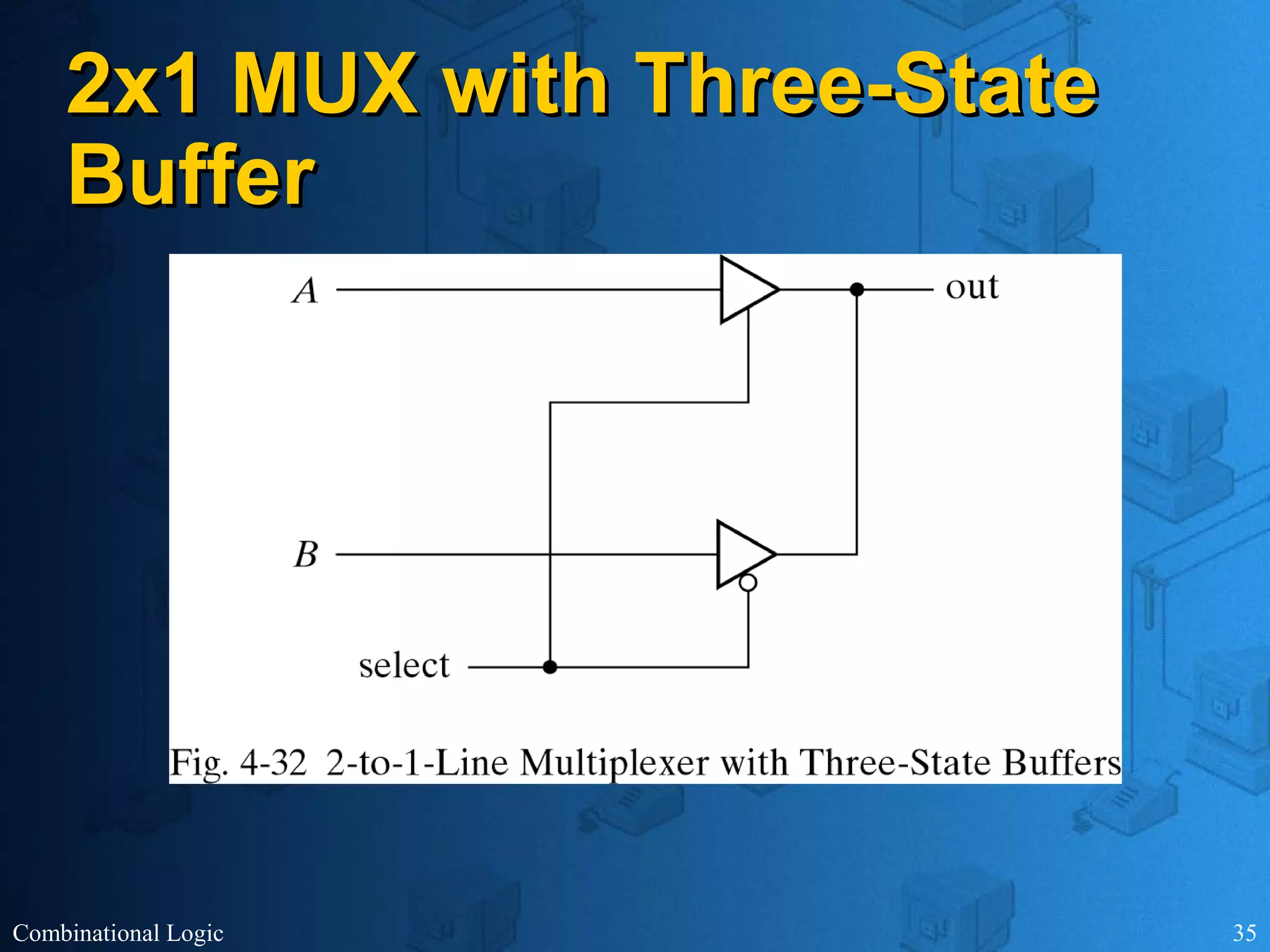
The document presents an overview of digital logic design, focusing on combinational and sequential logic circuits. It covers essential components like adders, multiplexers, and decoders, explaining their functions and the design process involving truth tables and simplified Boolean expressions. Additionally, it includes examples and study problems related to these concepts.