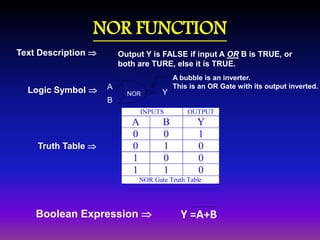
This document provides an overview of Boolean algebra and logic gates. It introduces Boolean logic operations like AND, OR, and NOT. It covers Boolean algebra laws and De Morgan's theorems. It also discusses logic gate types like AND, OR, NOT, NAND, NOR, XOR and XNOR. Karnaugh maps are introduced as a method to simplify Boolean expressions.







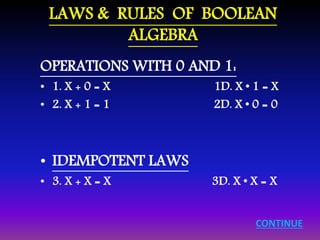

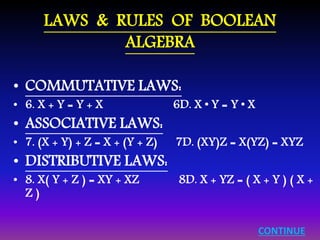
![LAWS & RULES OF BOOLEAN
ALGEBRA
• SIMPLIFICATION THEOREMS:
• 9. X Y + X Y' = X 9D. ( X + Y ) ( X + Y' ) = X
• 10. X + XY = X 10D. X ( X + Y ) = X
• 11. ( X + Y' ) Y = XY 11D. XY' + Y = X + Y
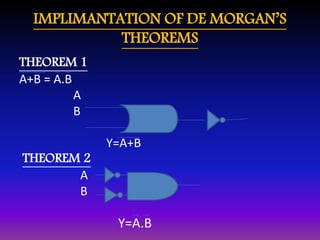
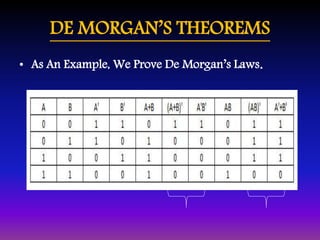
• DEMORGAN’S LAWS:
• 12. ( X + Y + Z + … )' = X'Y'Z'… 12D. (X Y Z …)' = X' + Y' + Z' + …
• 13. [ f ( X1, X2, … XN, 0, 1, +, • ) ]' = f ( X1', X2', … XN', 1, 0, •, + )
CONTINUE](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/idealeyesbusinesscollegebooleanalgebra-141105032520-conversion-gate01/85/BOOLEAN-ALGEBRA-LOGIC-GATE-13-320.jpg)