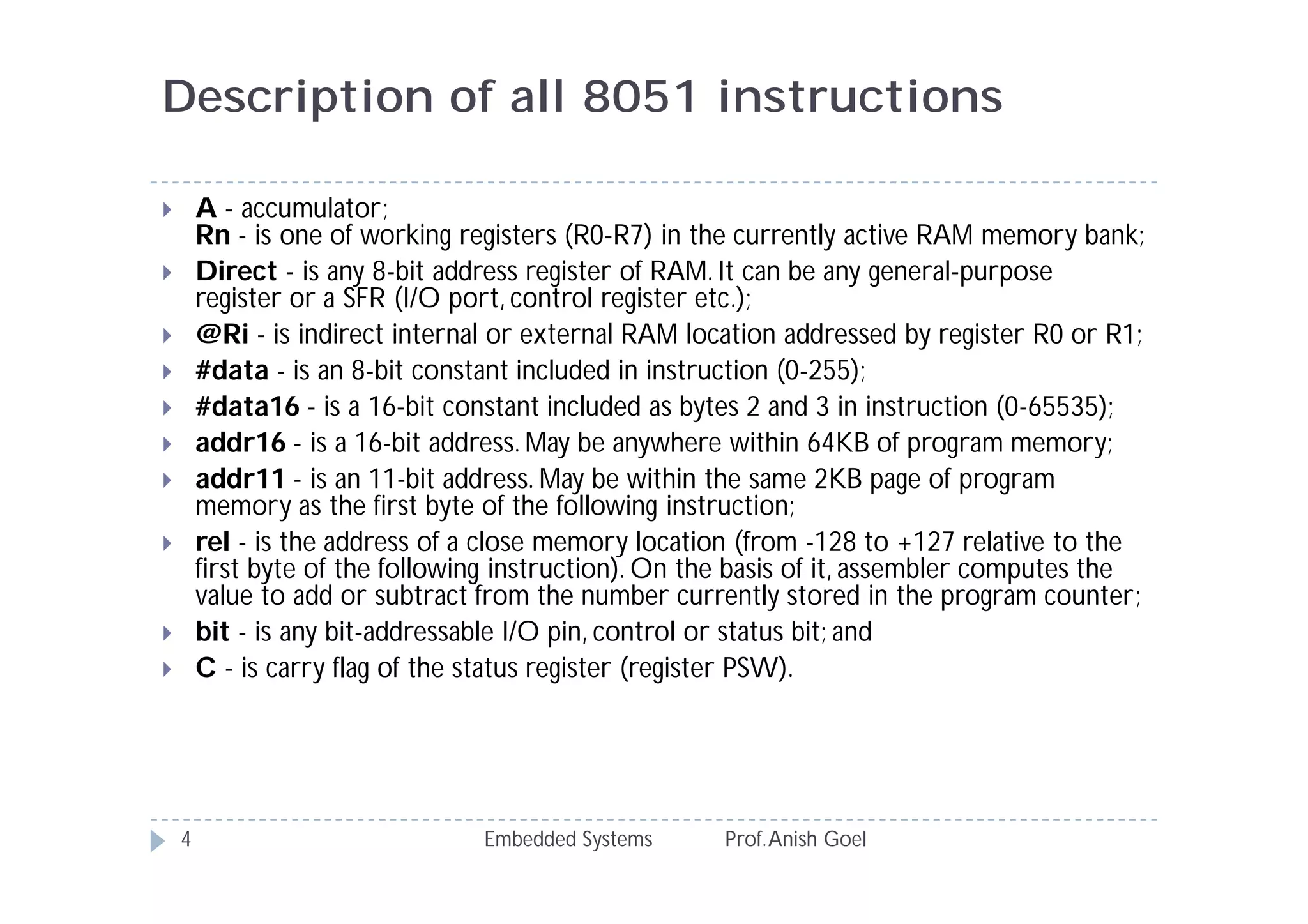
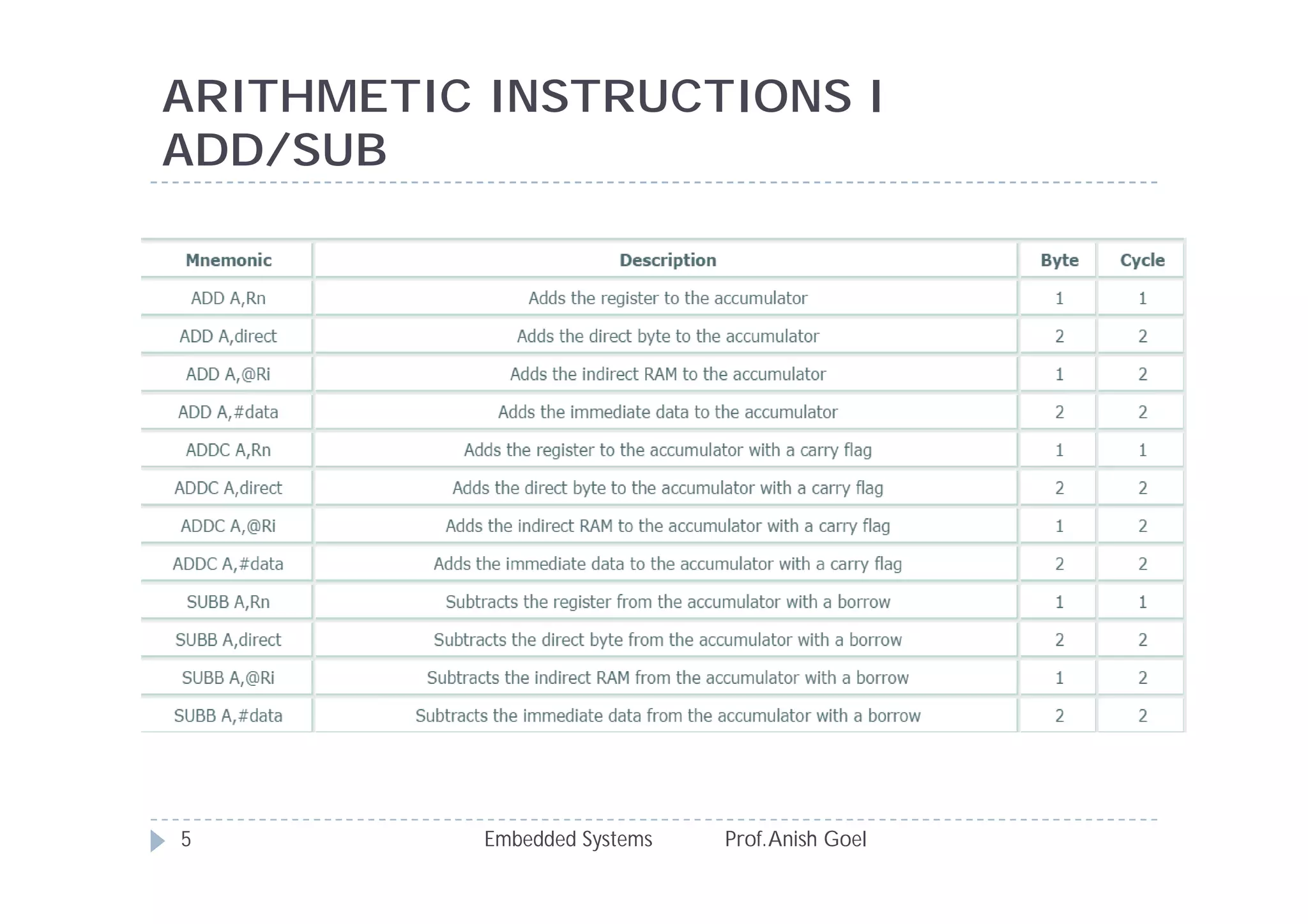
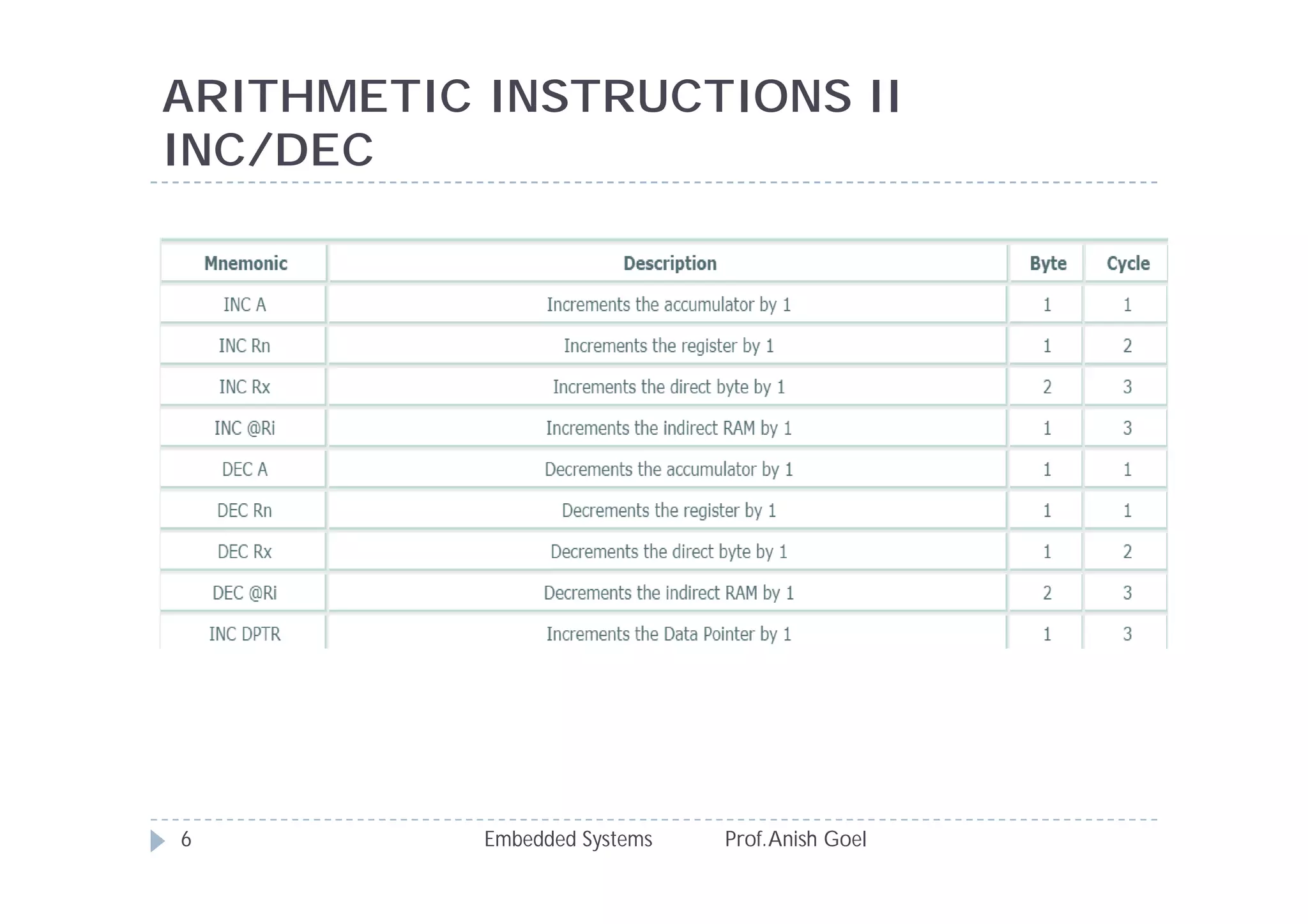
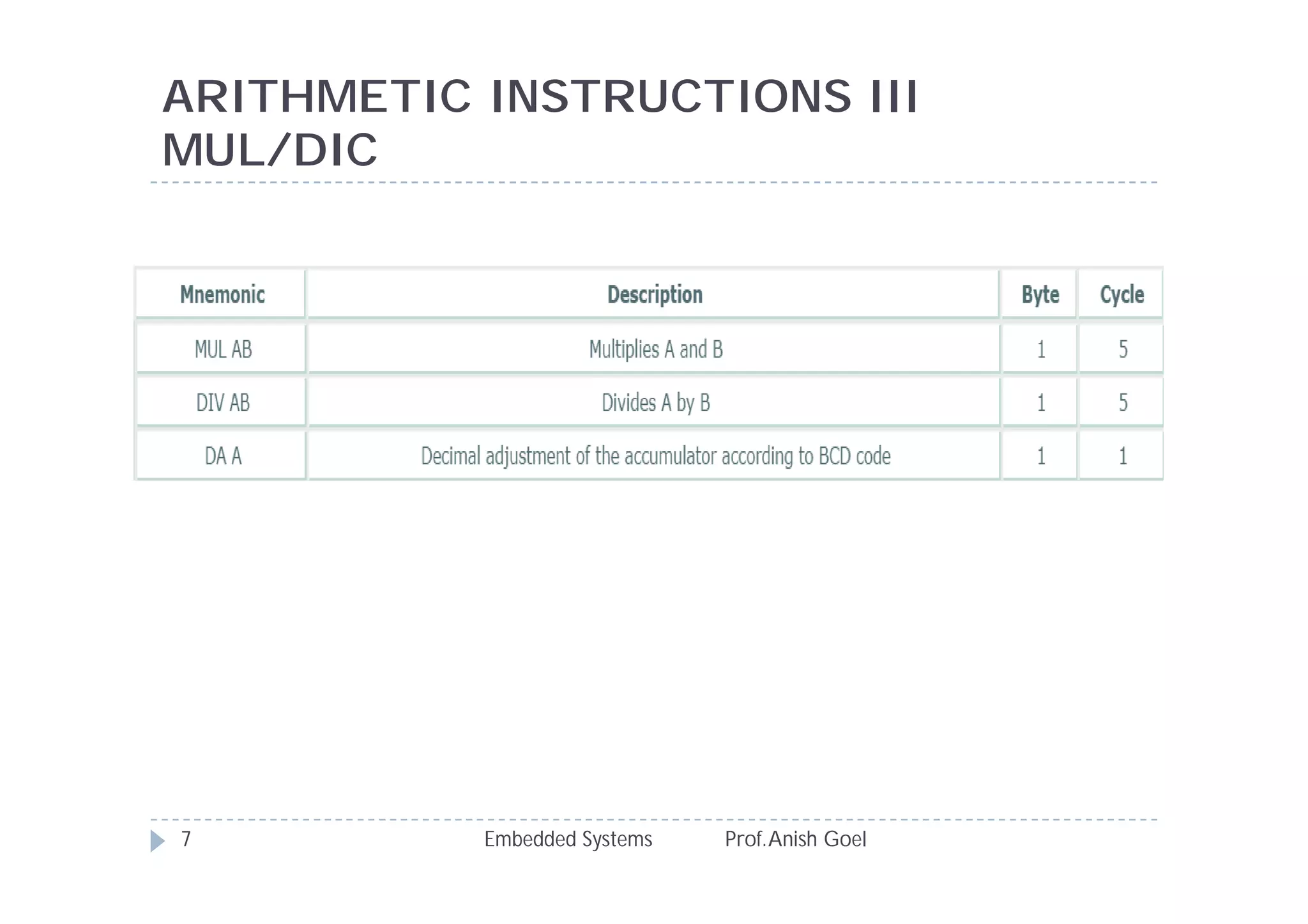
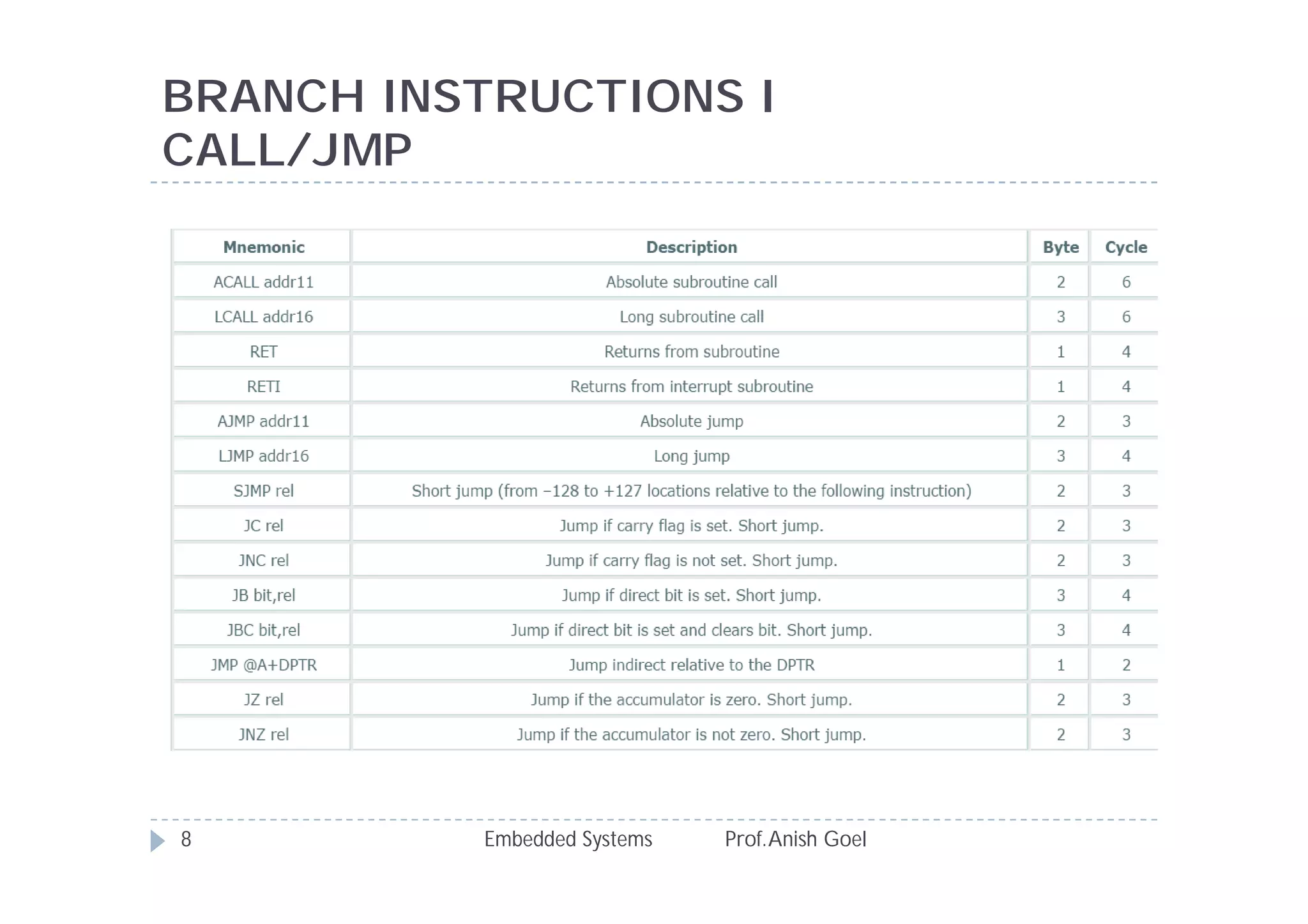
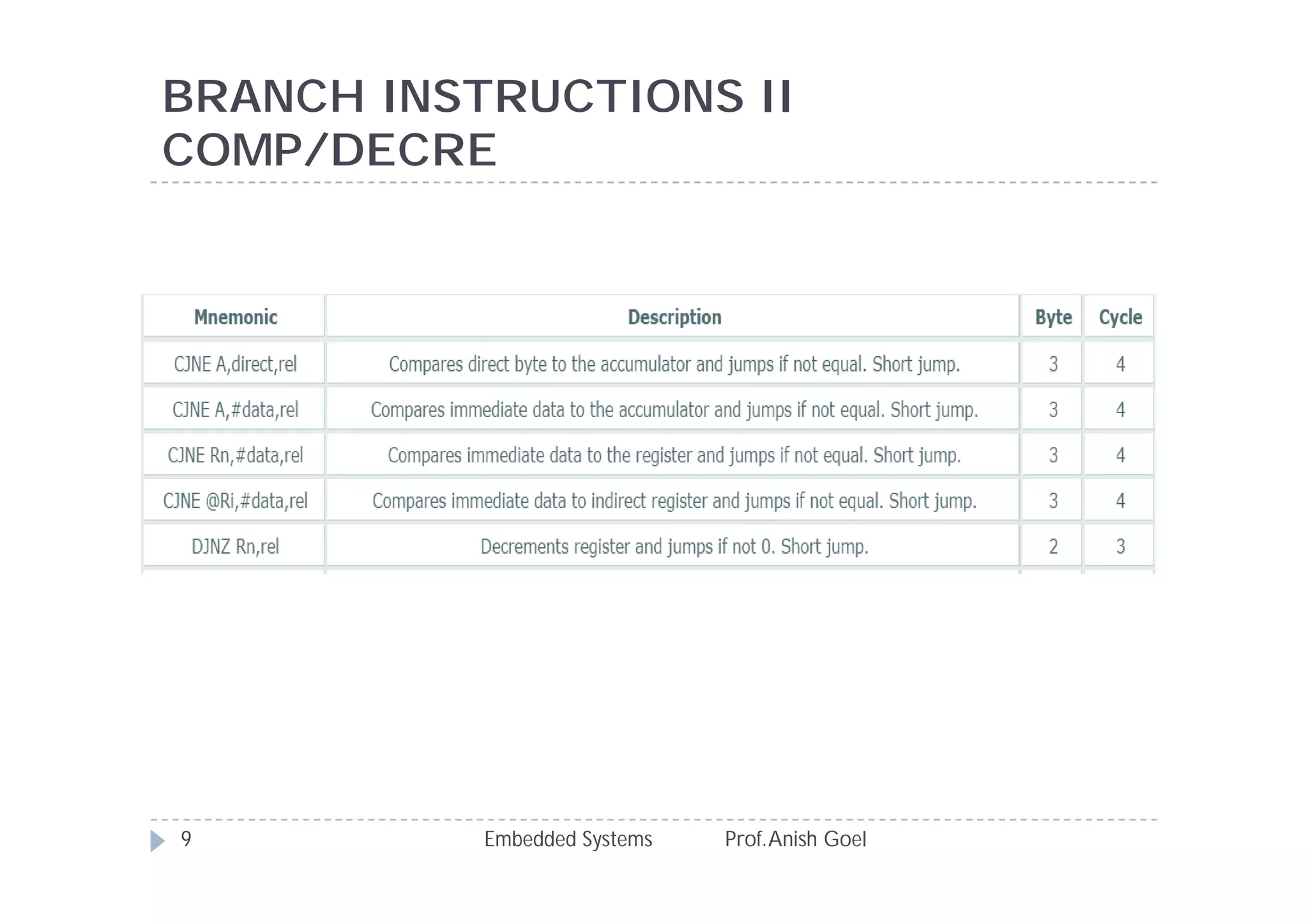
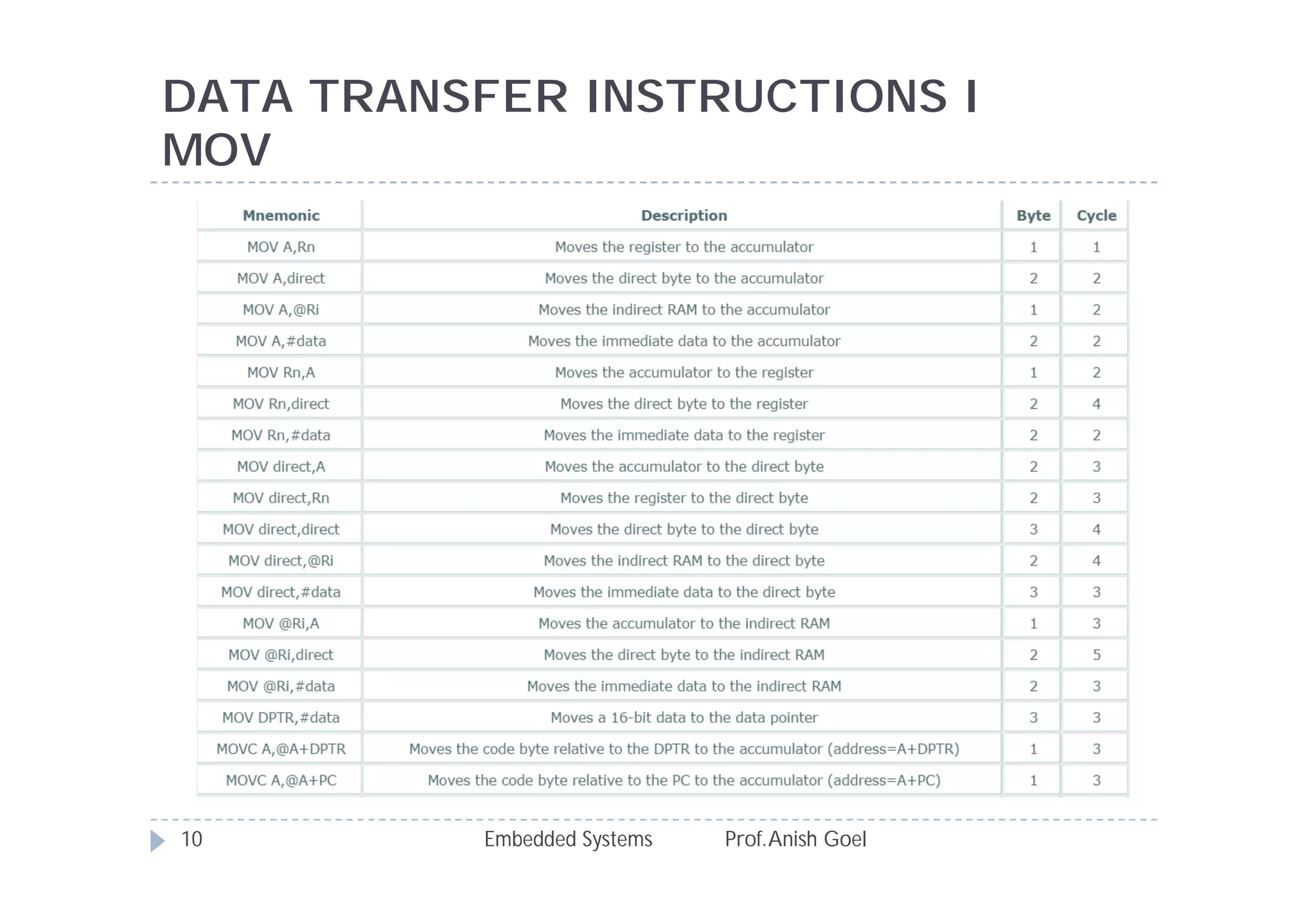
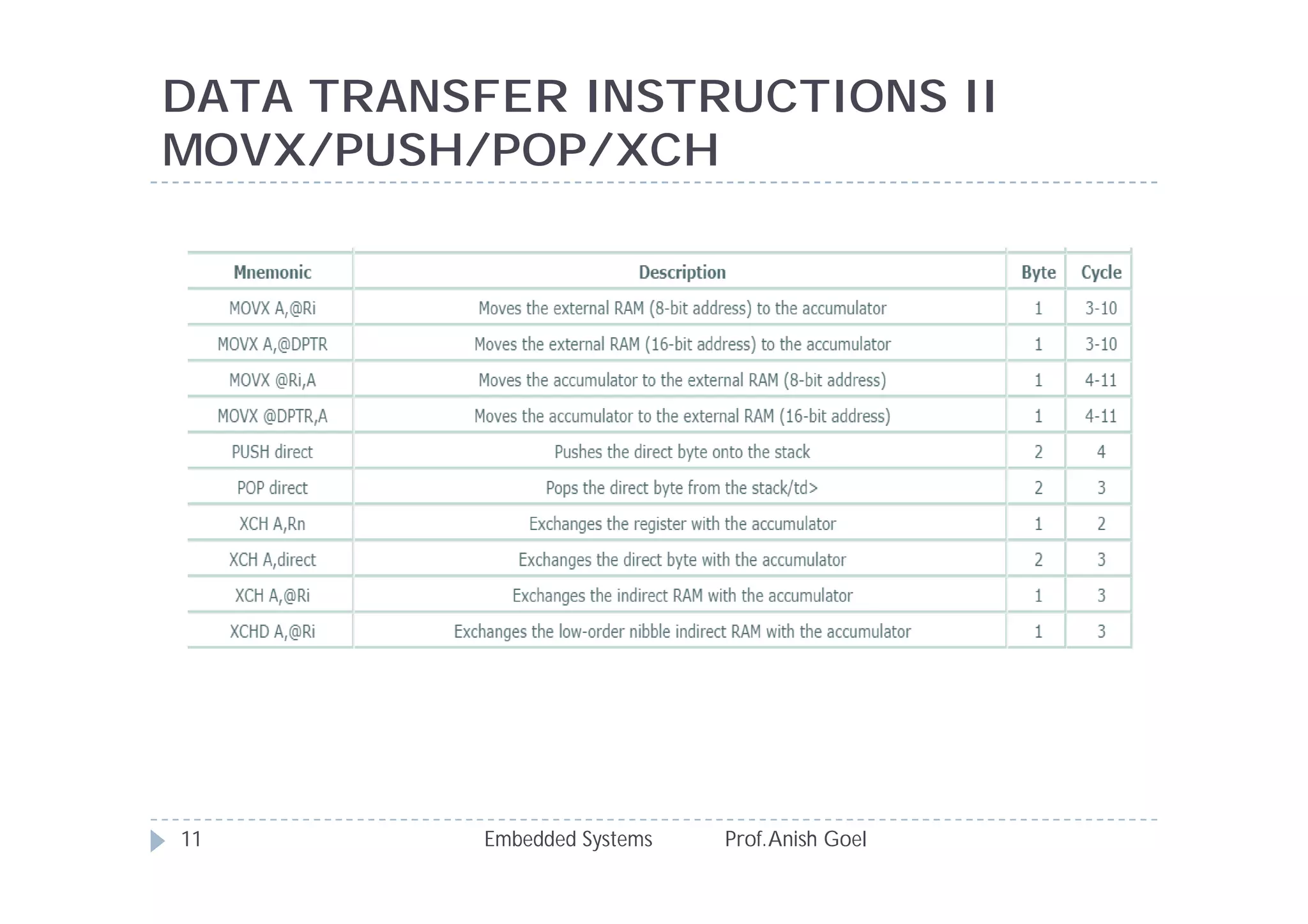
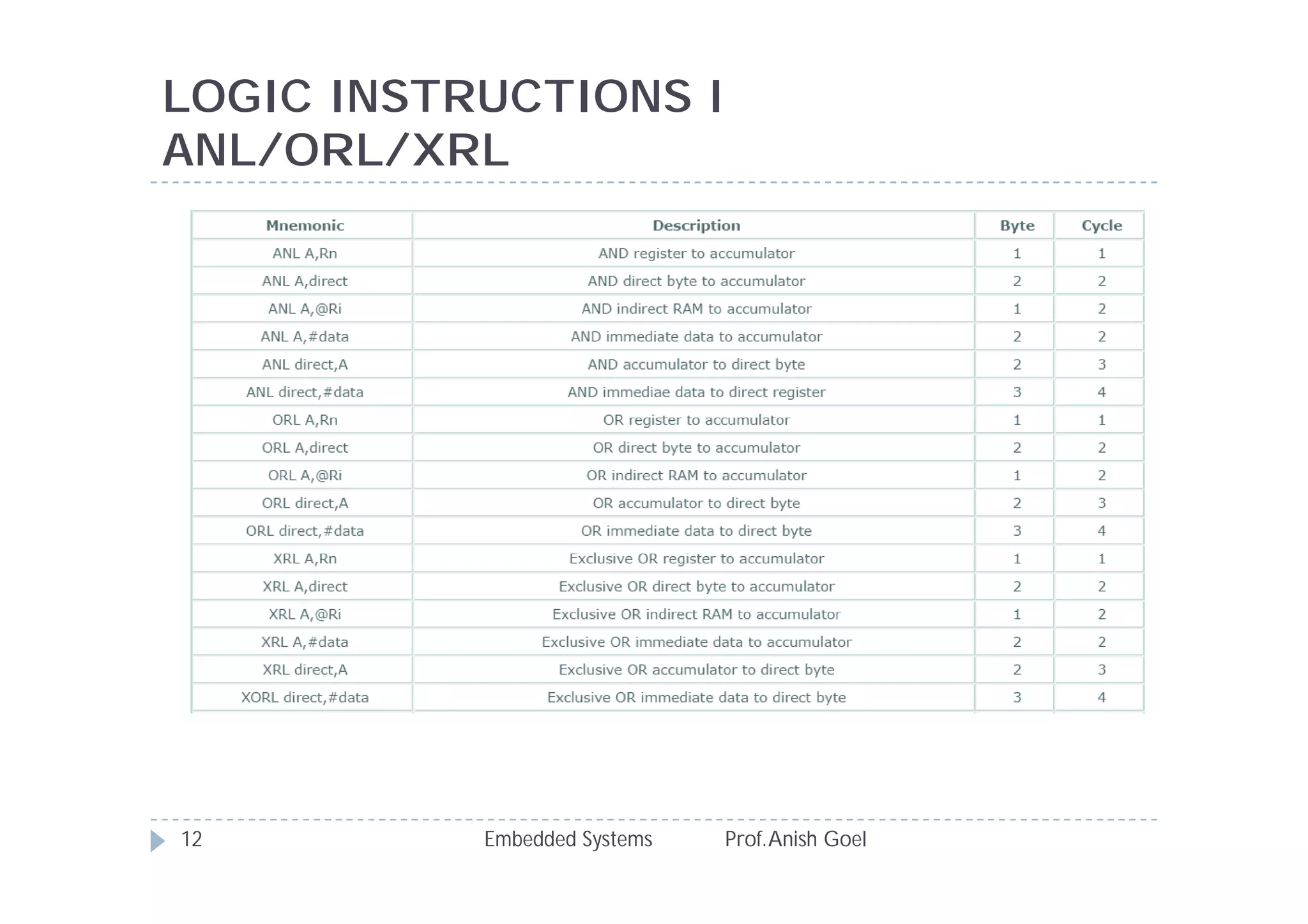
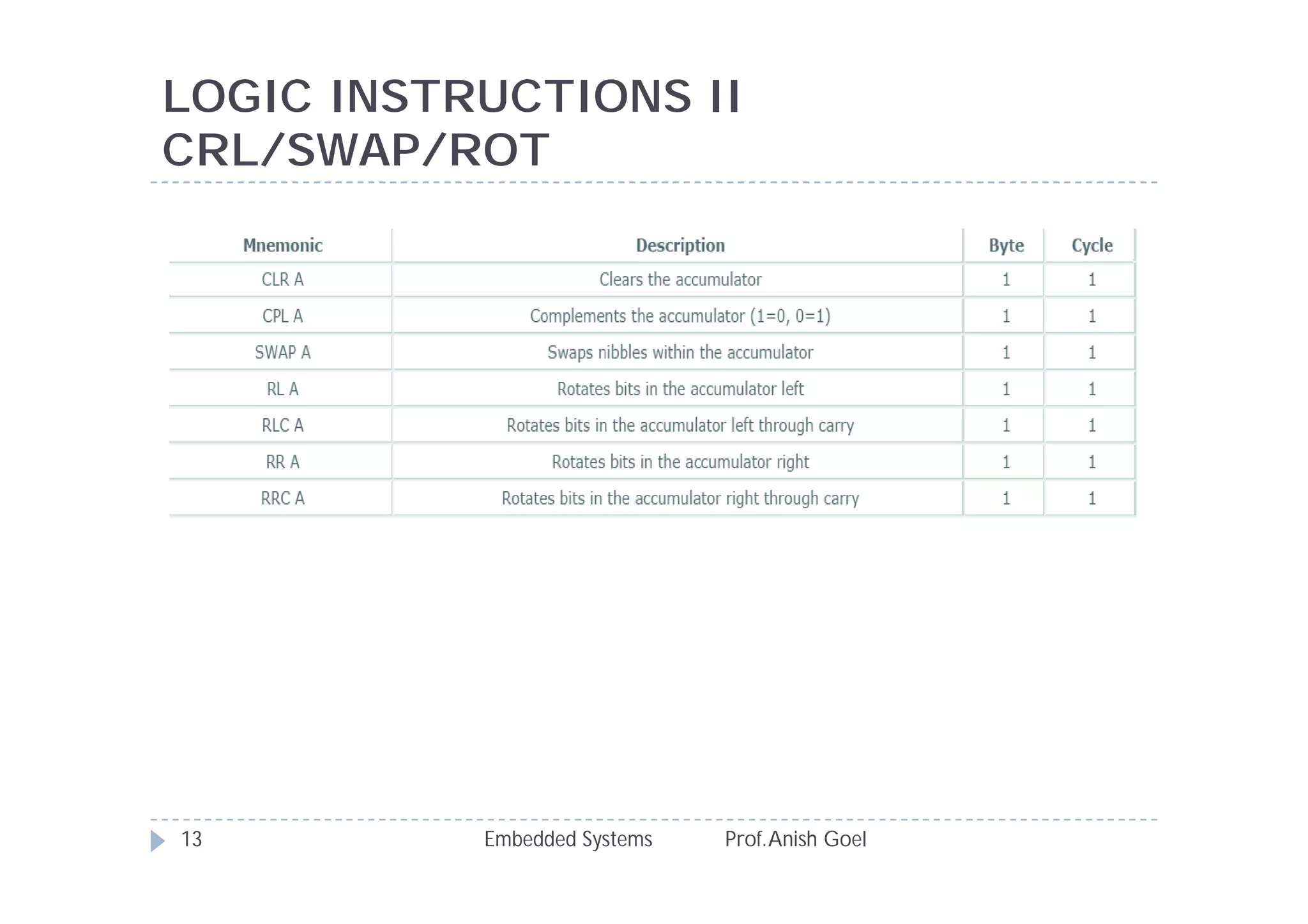
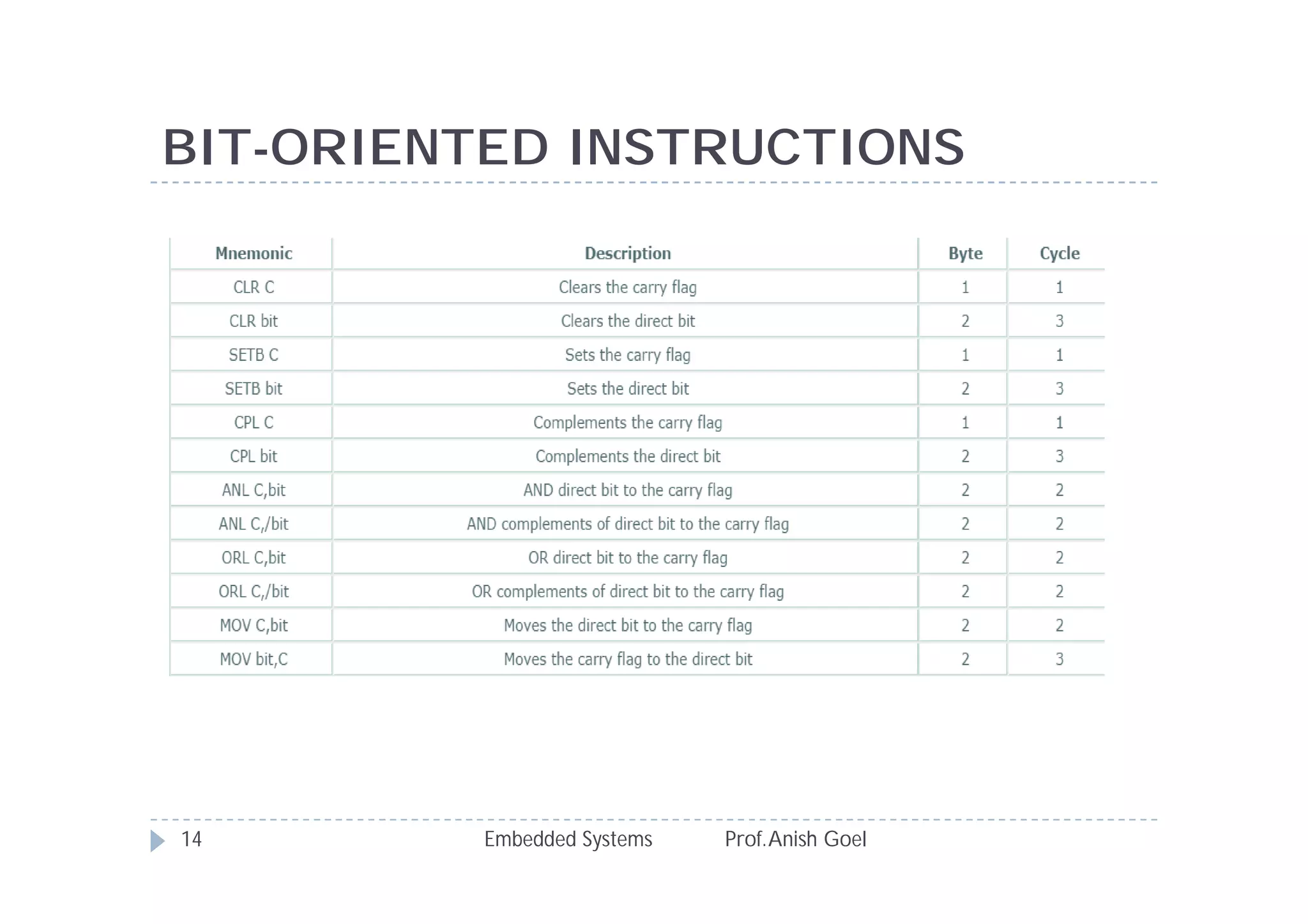
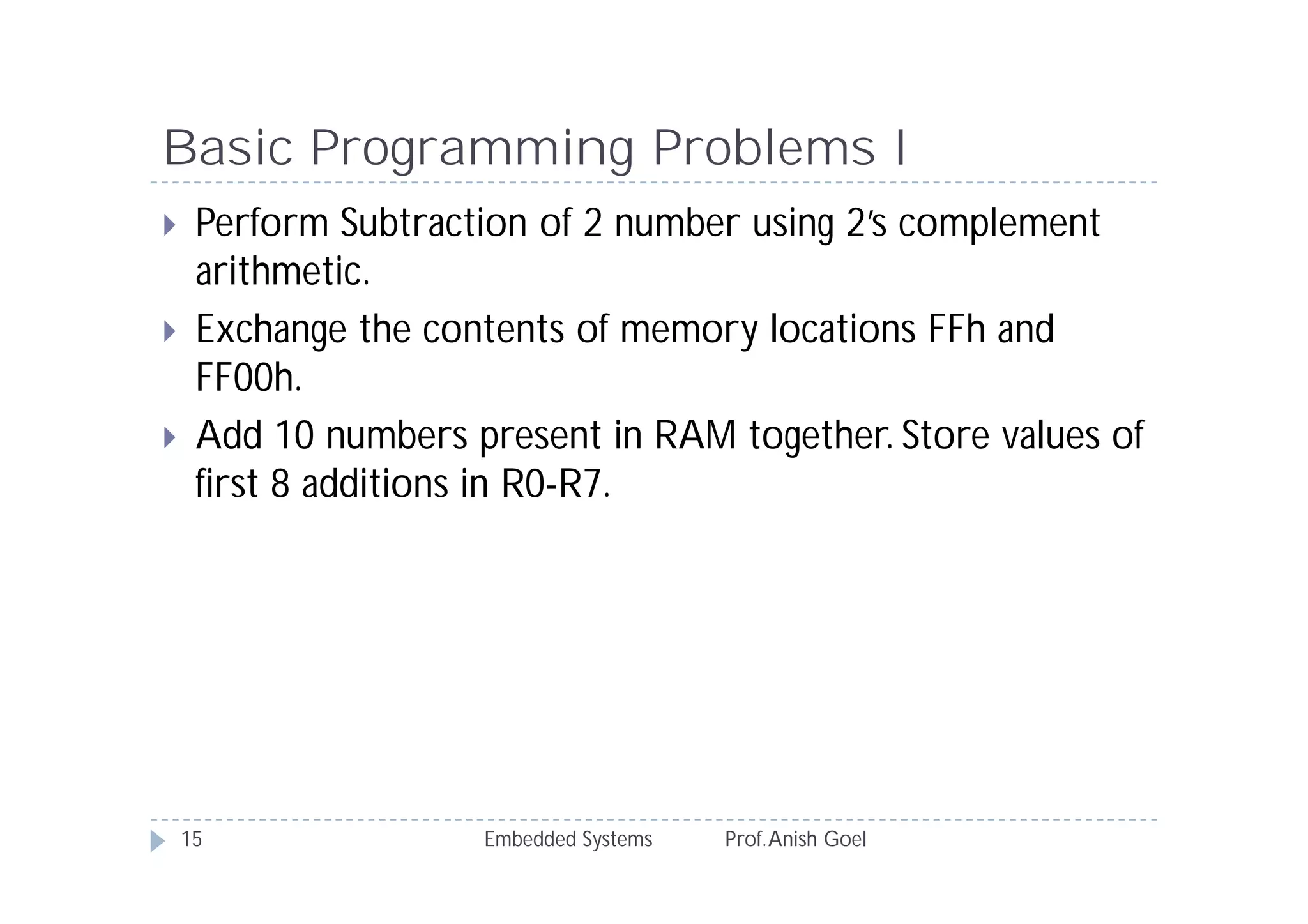
The document discusses the instruction set of the 8051 microcontroller. It describes that the 8051 has 255 total instructions divided into categories like arithmetic, branch, data transfer, logic, and bit-oriented instructions. It provides details on the operation and syntax of common instructions like ADD, SUB, MOV, JMP, CALL and others. It also gives some basic programming problems as examples to perform operations like subtraction, data exchange and addition using 8051 instructions.