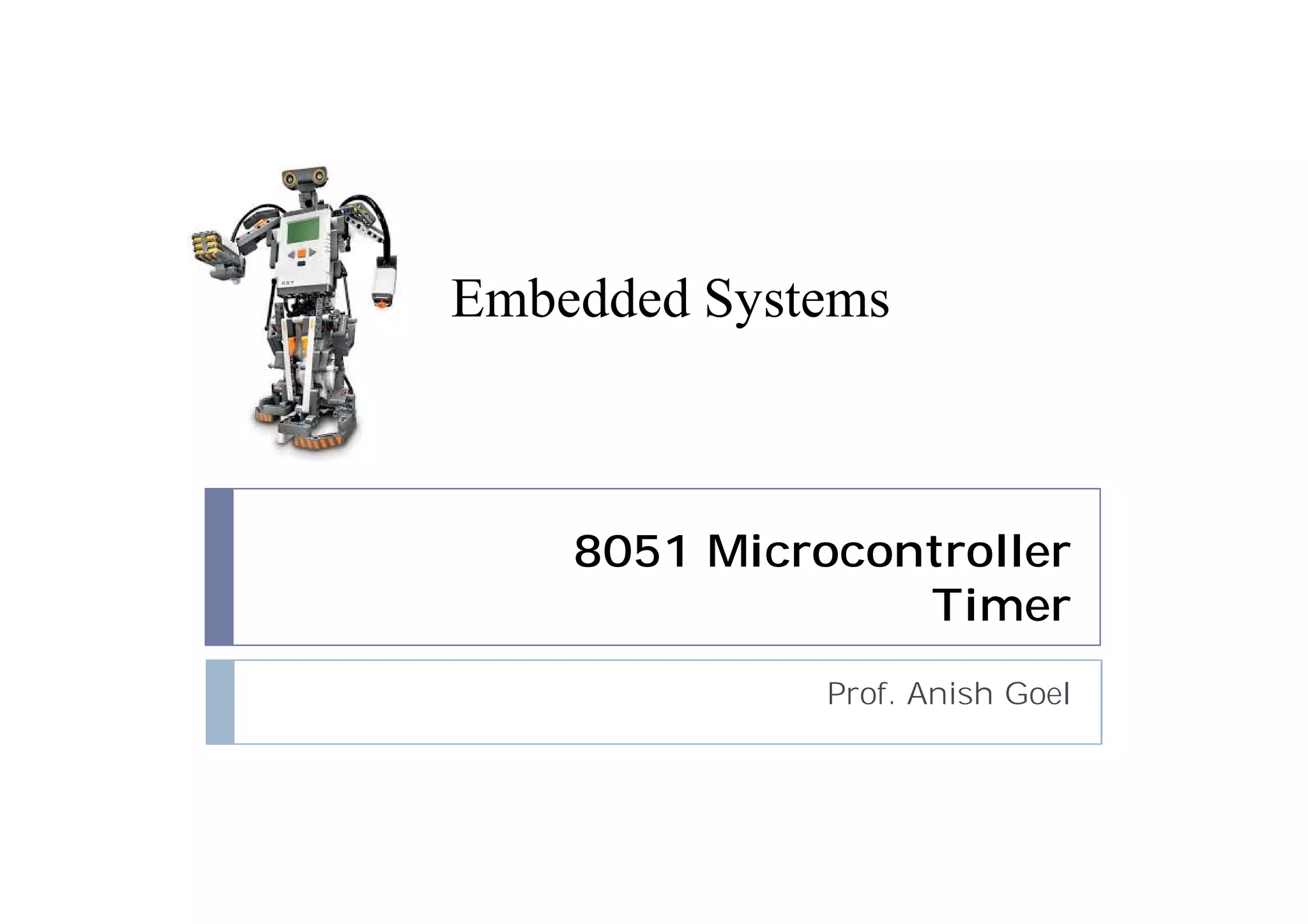
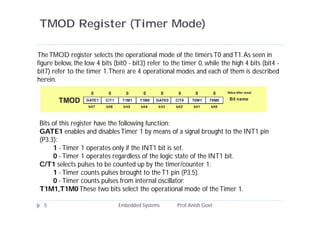
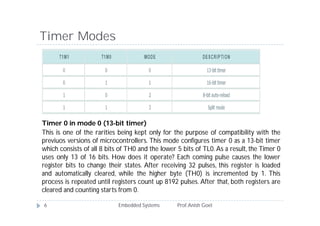
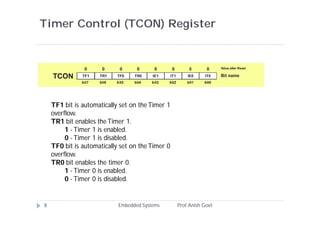
The document discusses timers and counters in 8051 microcontrollers. It describes the two timers, T0 and T1, which consist of register pairs that can count pulses from the microcontroller's oscillator or external sources. The TMOD register selects the operational mode for each timer, including modes that configure the timers as 8-bit, 13-bit, or 16-bit counters. The document explains how the timers count pulses and overflow values in each register. It also discusses the TCON register which controls enabling and disabling the timers.