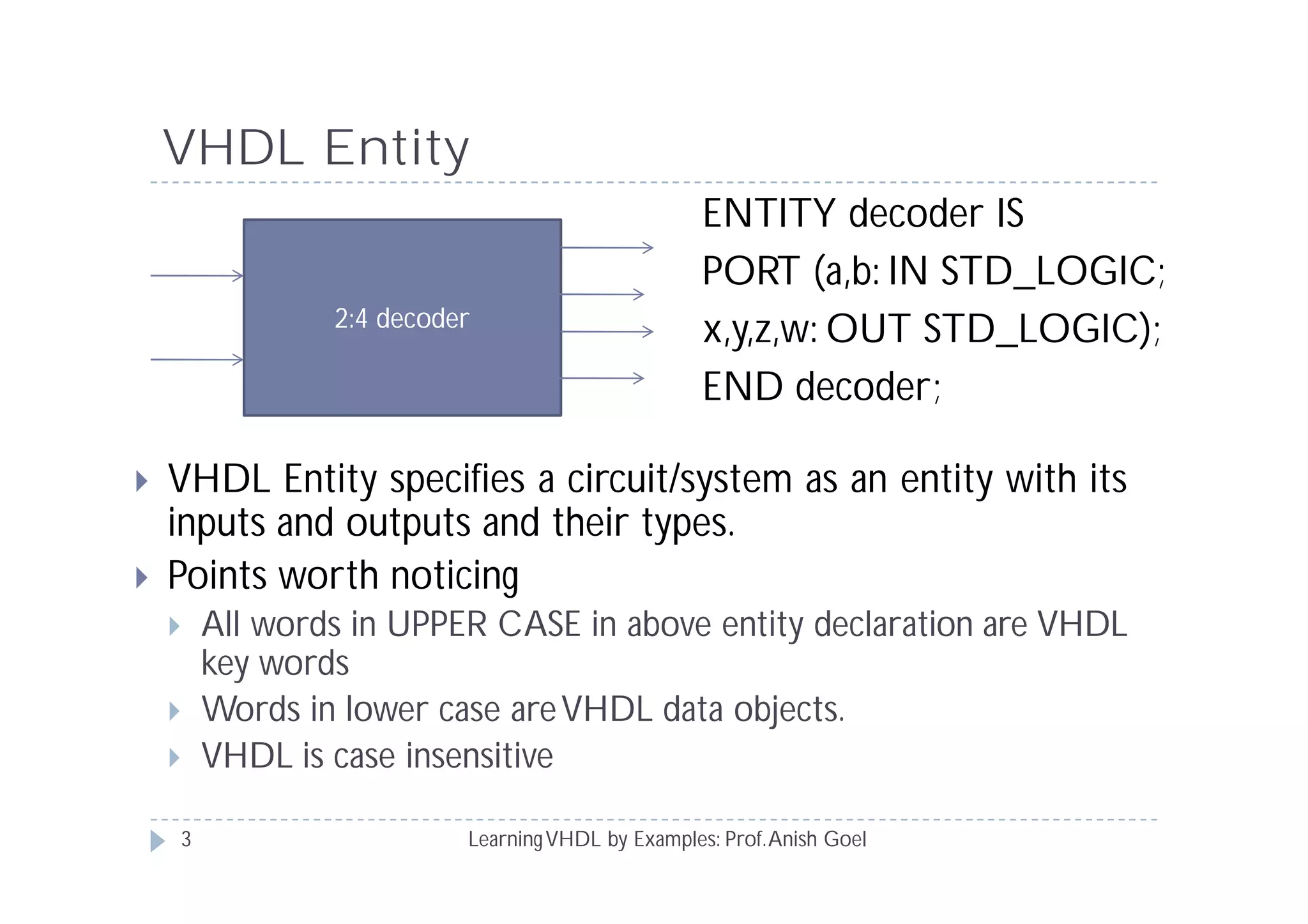
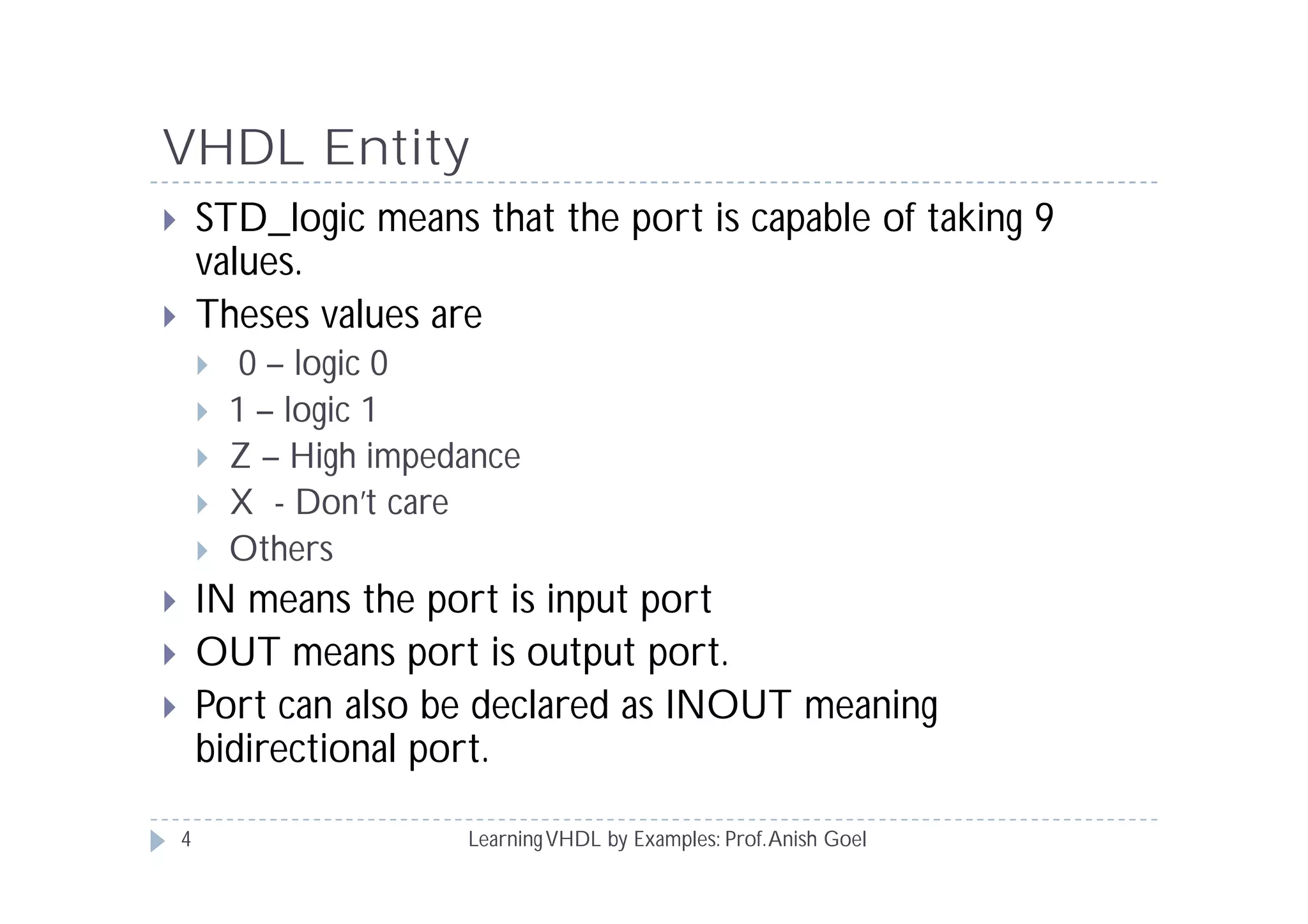
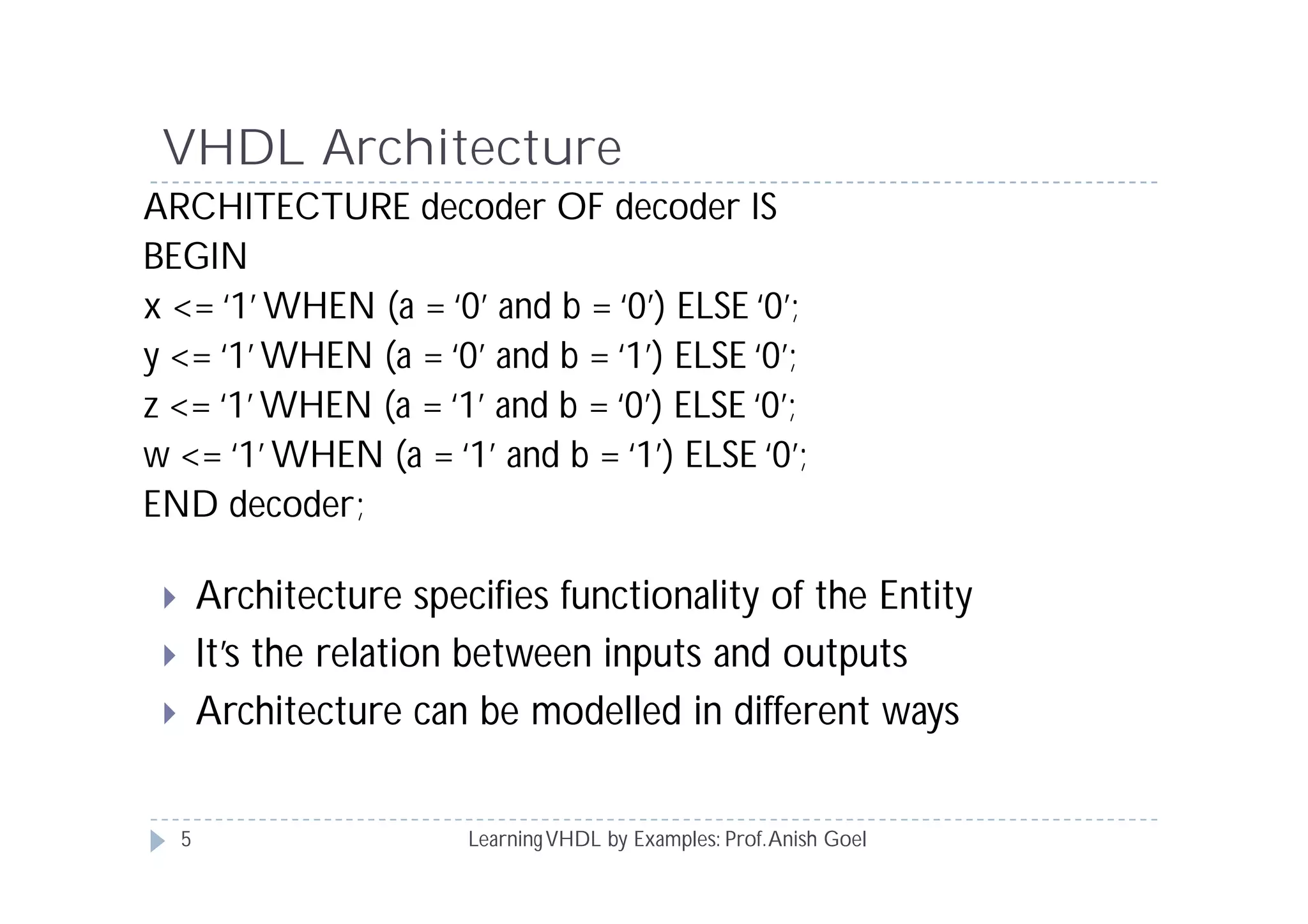
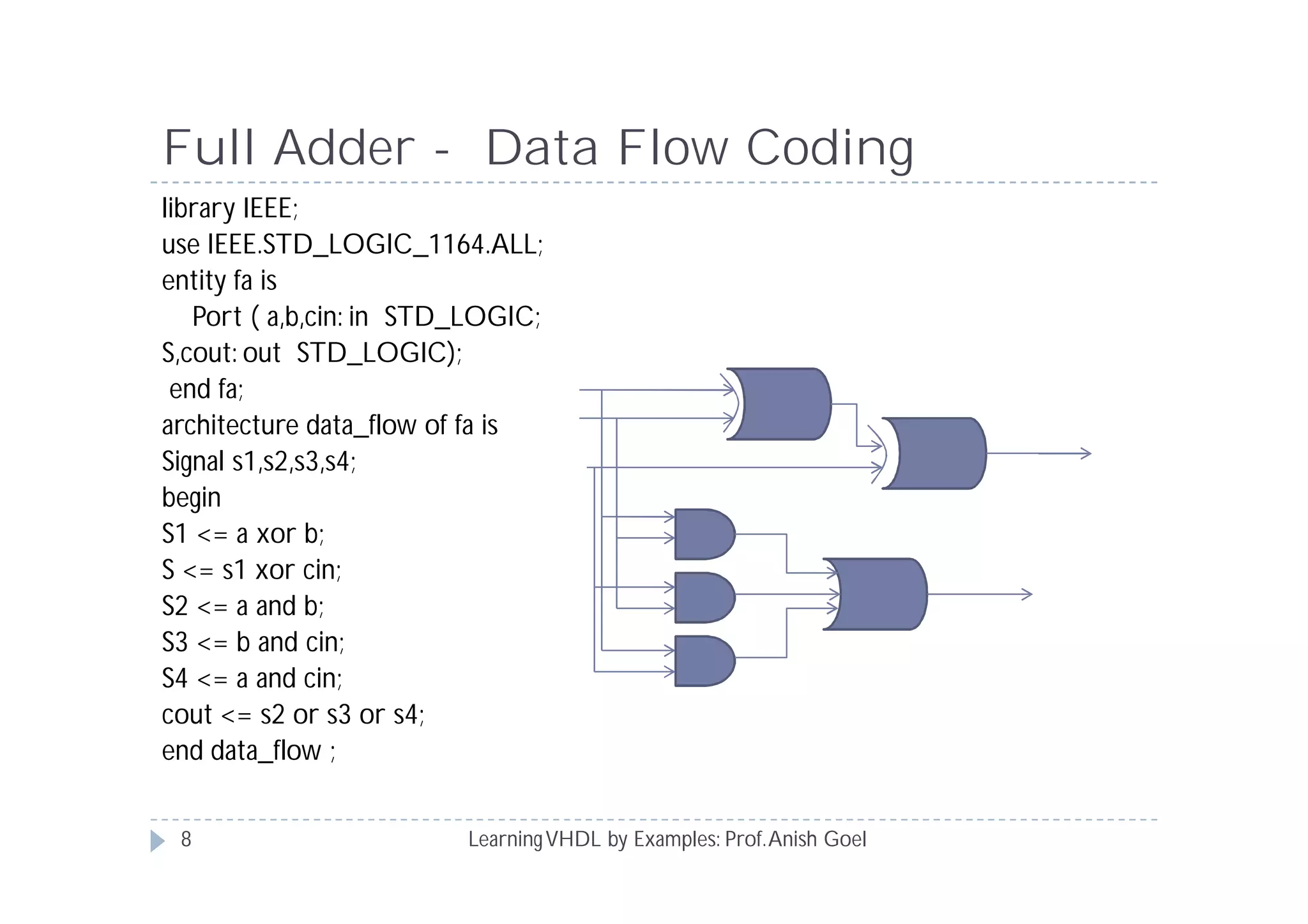
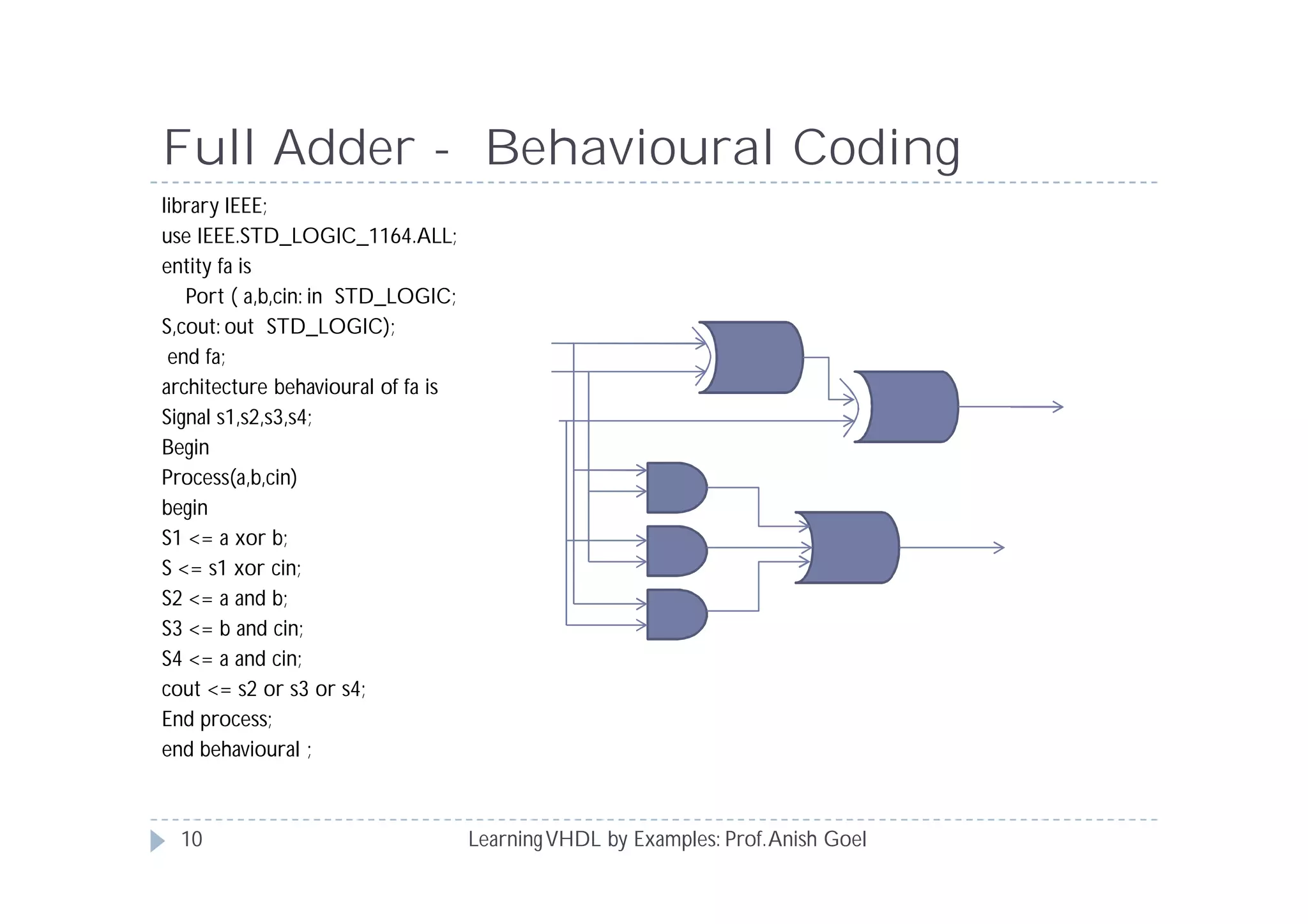
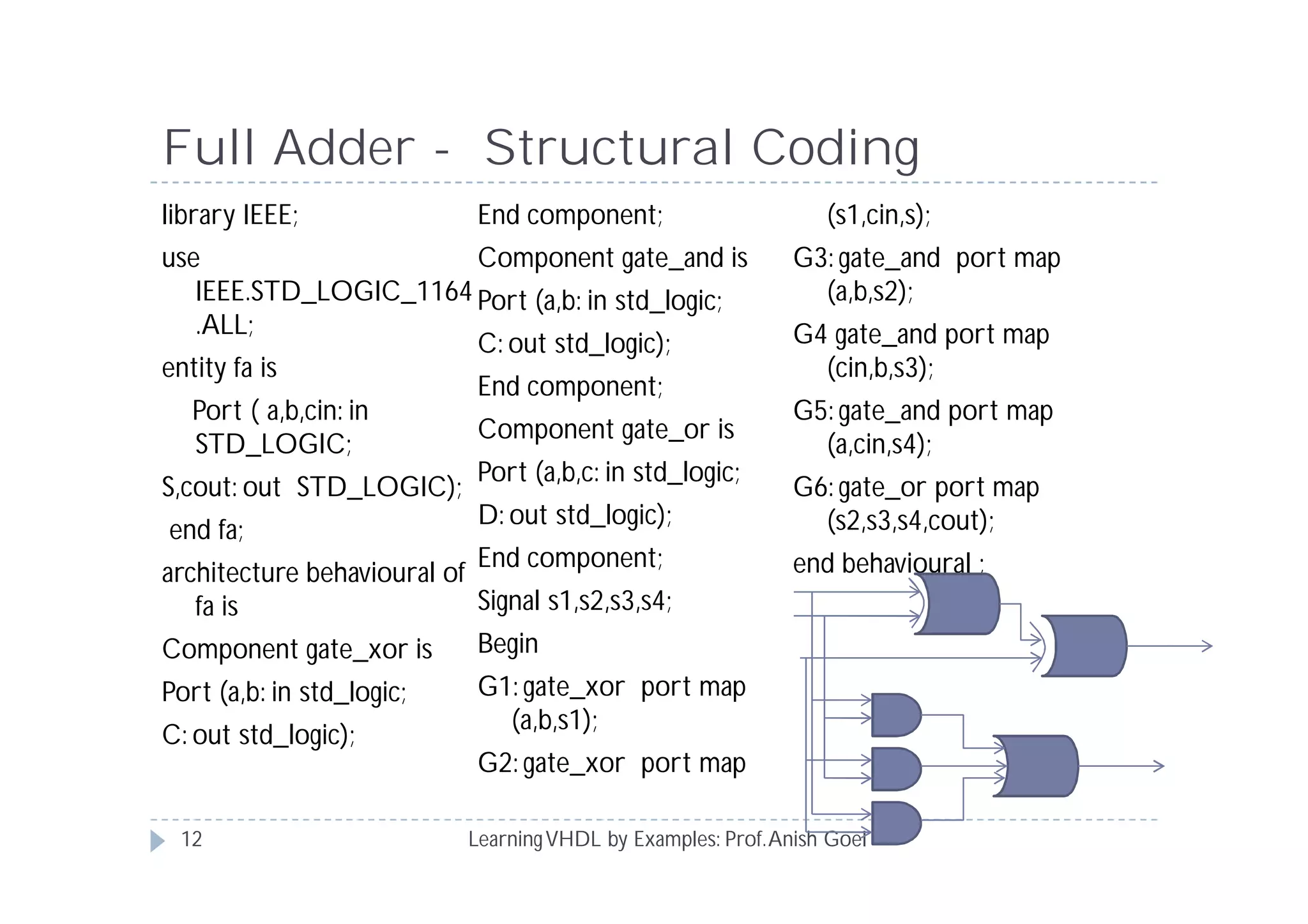
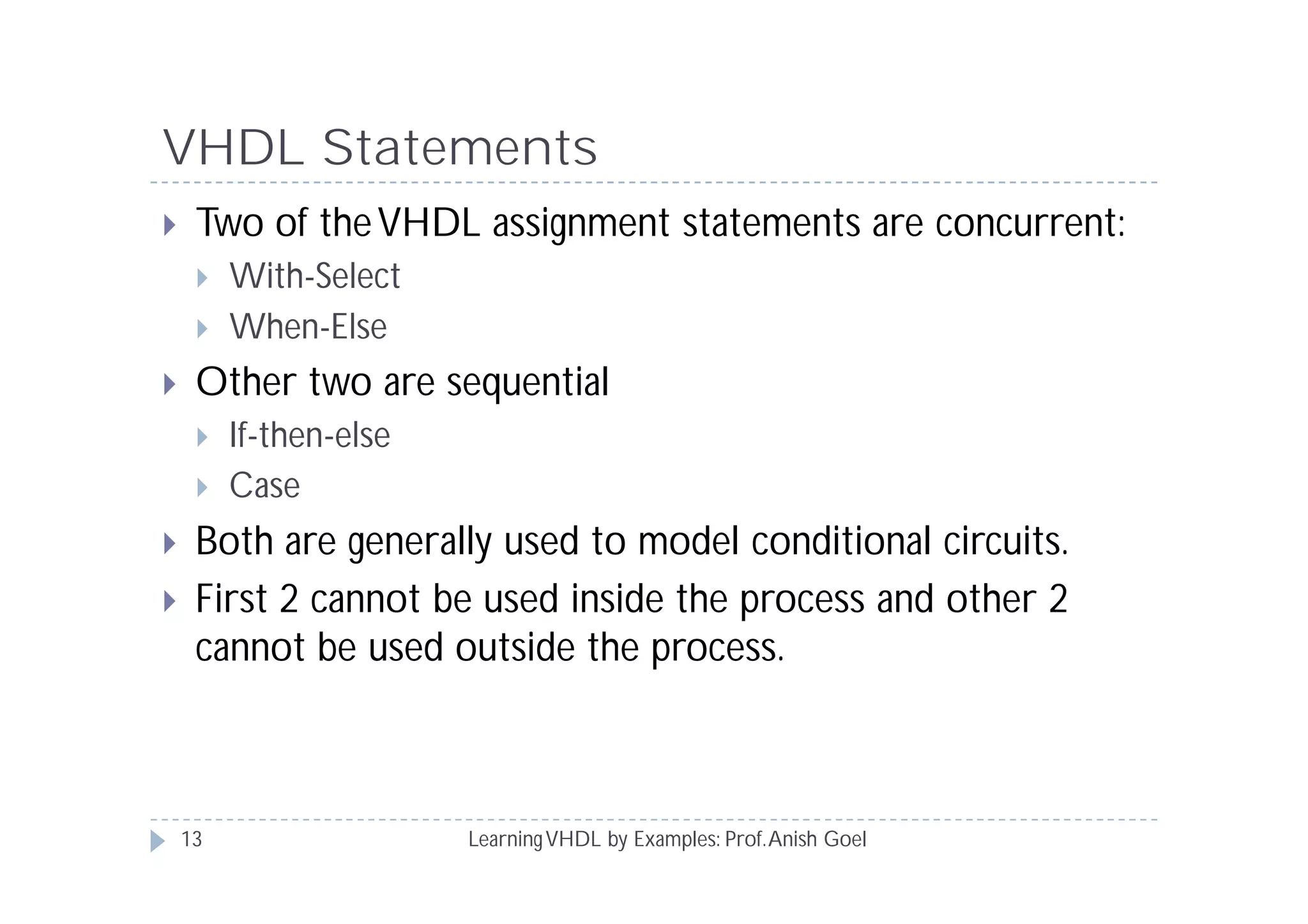
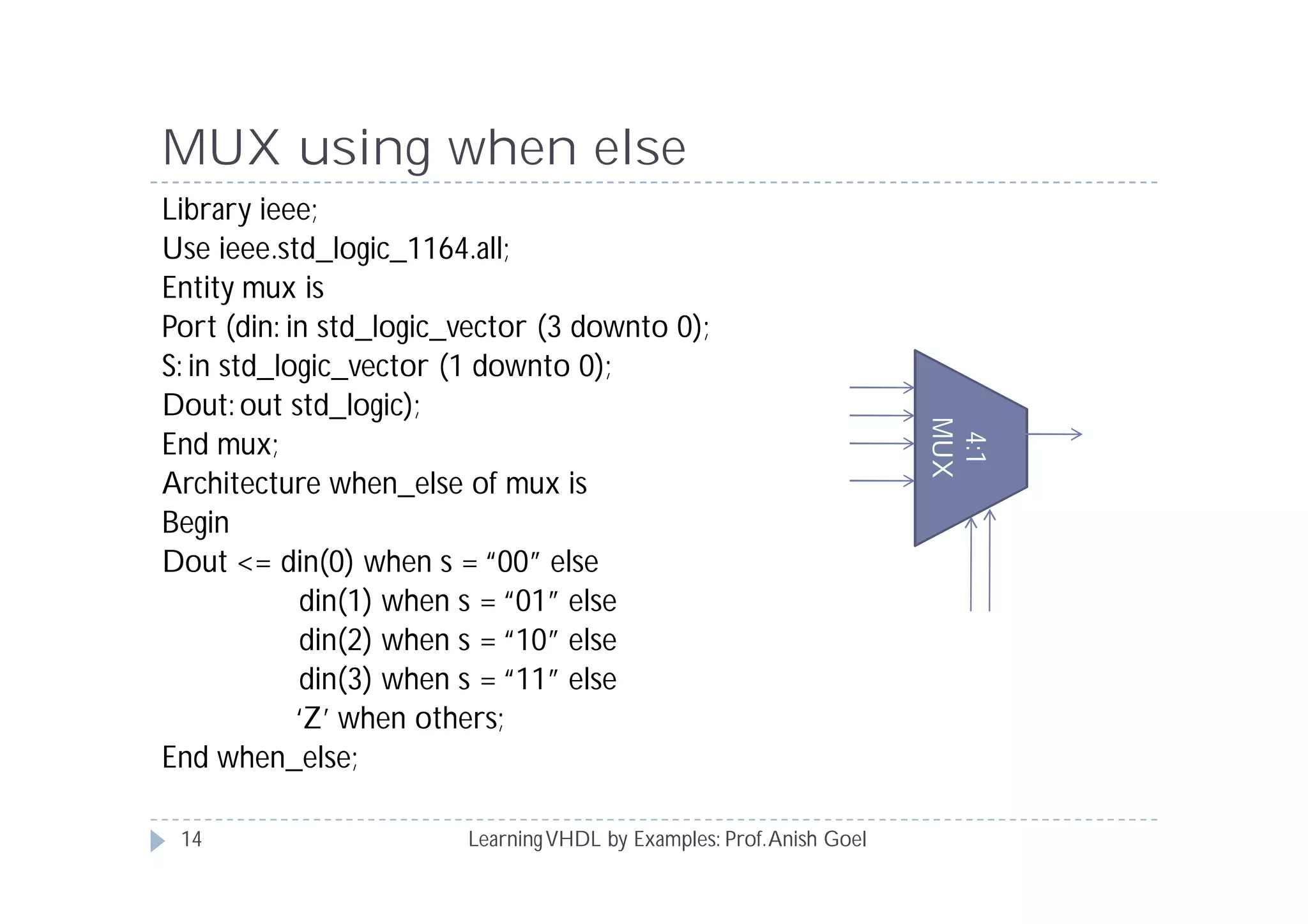
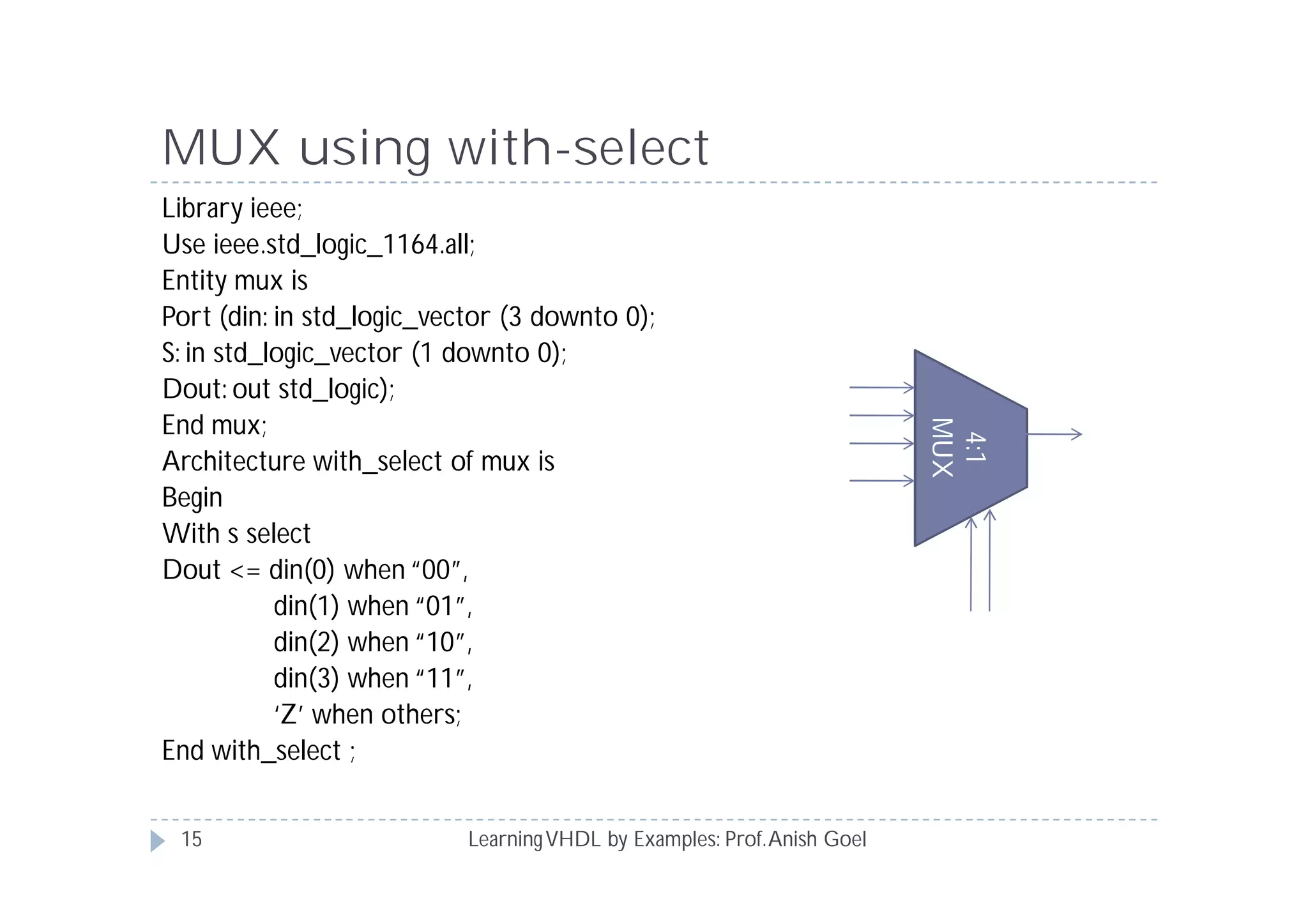
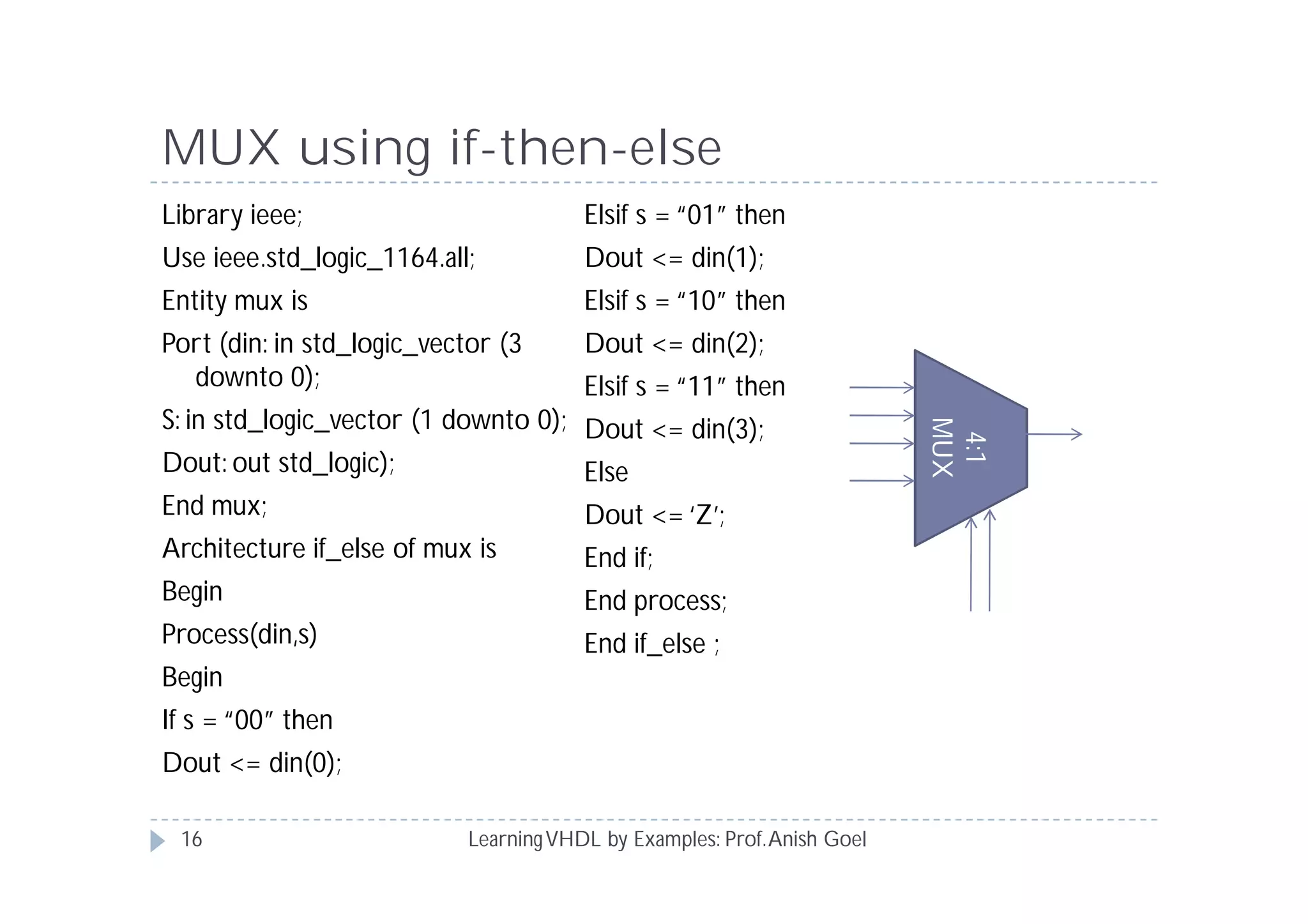
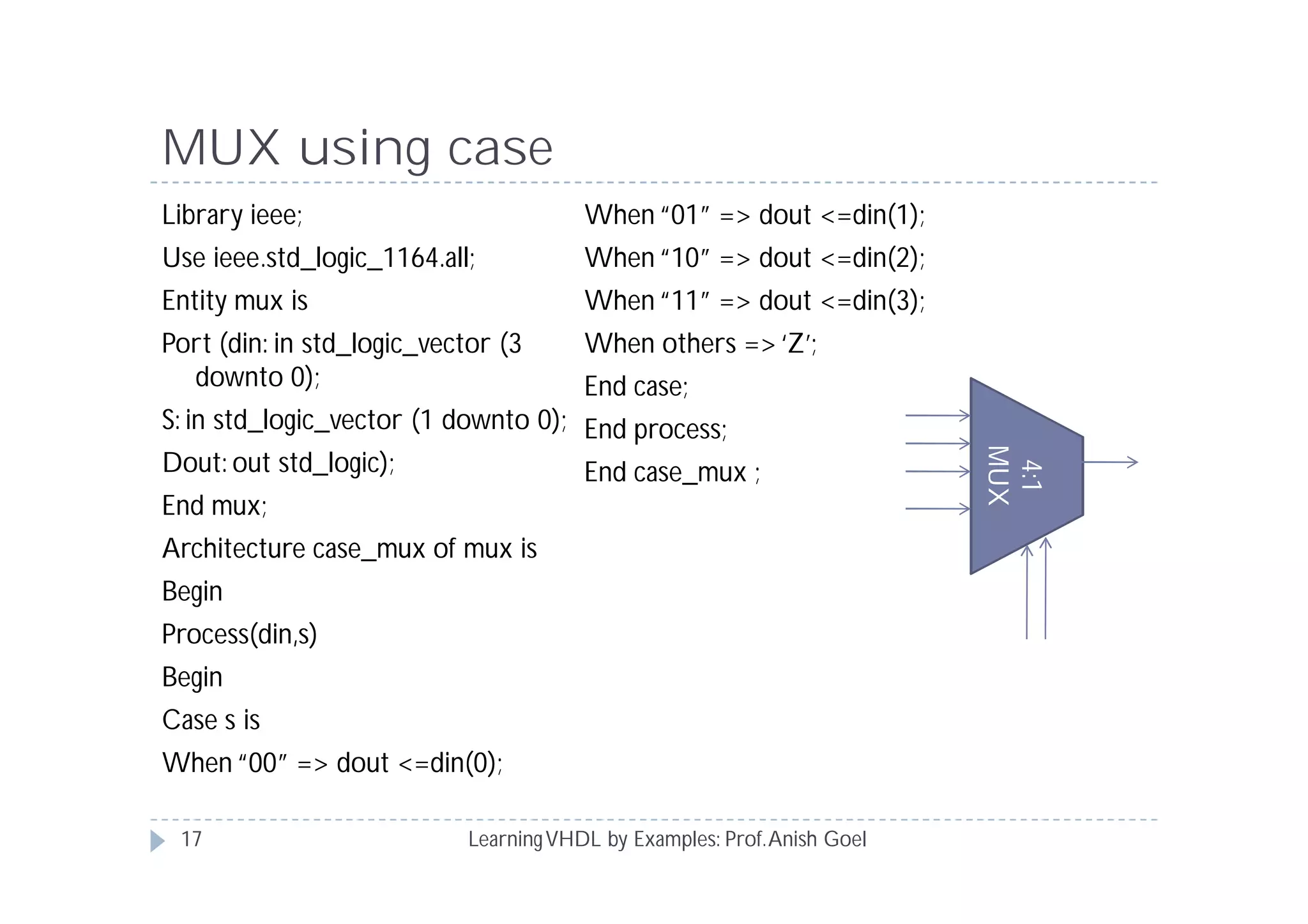
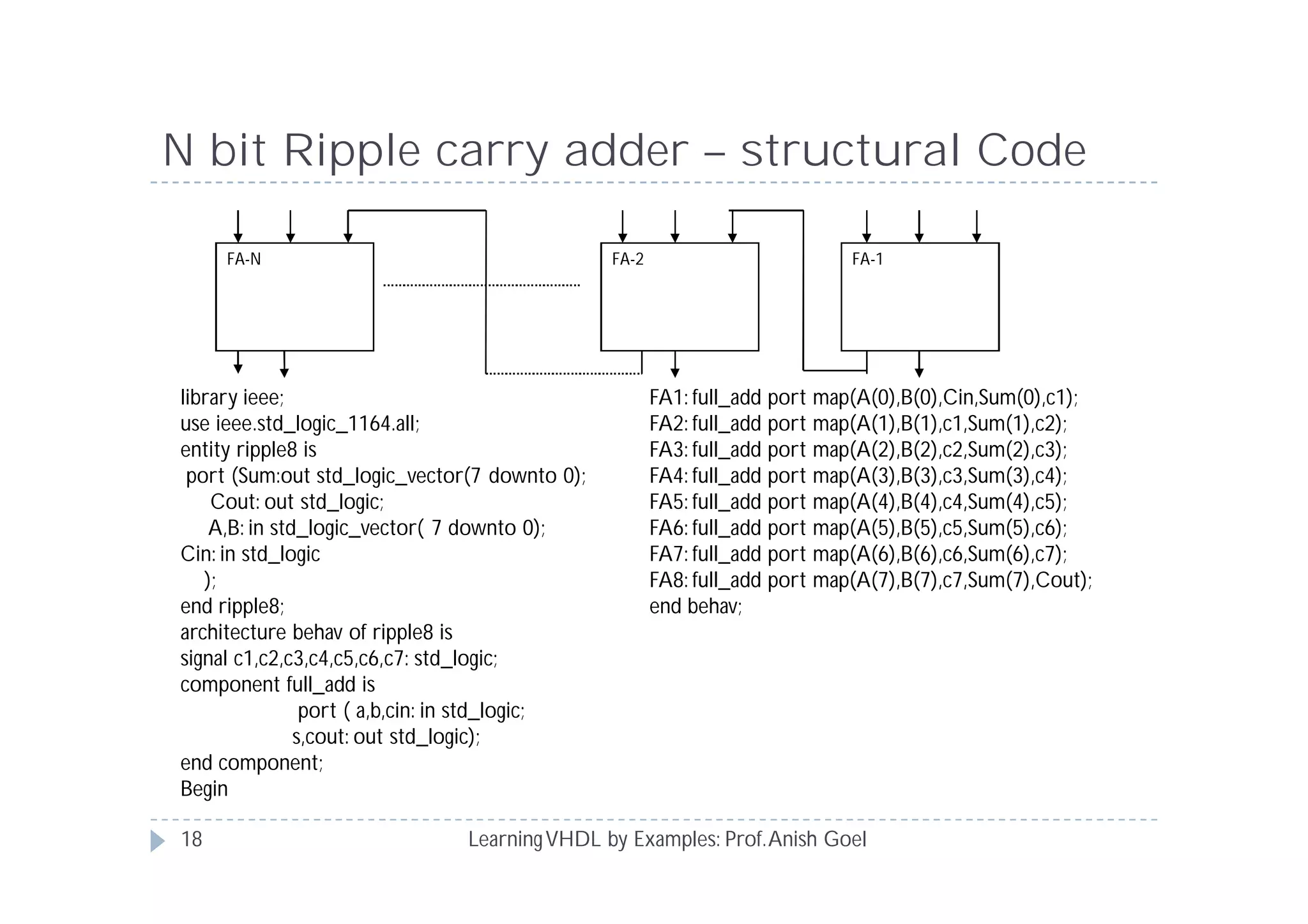
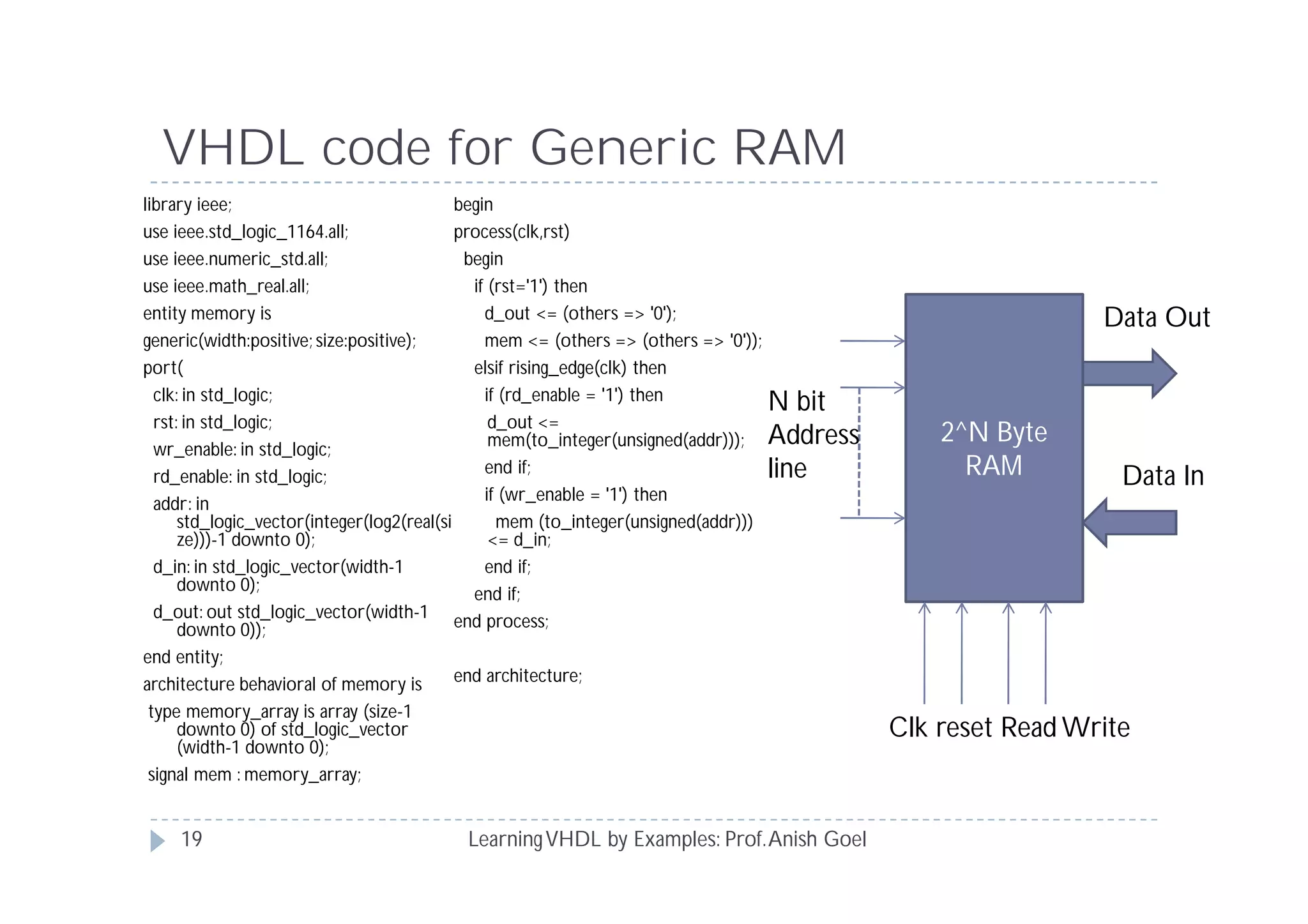
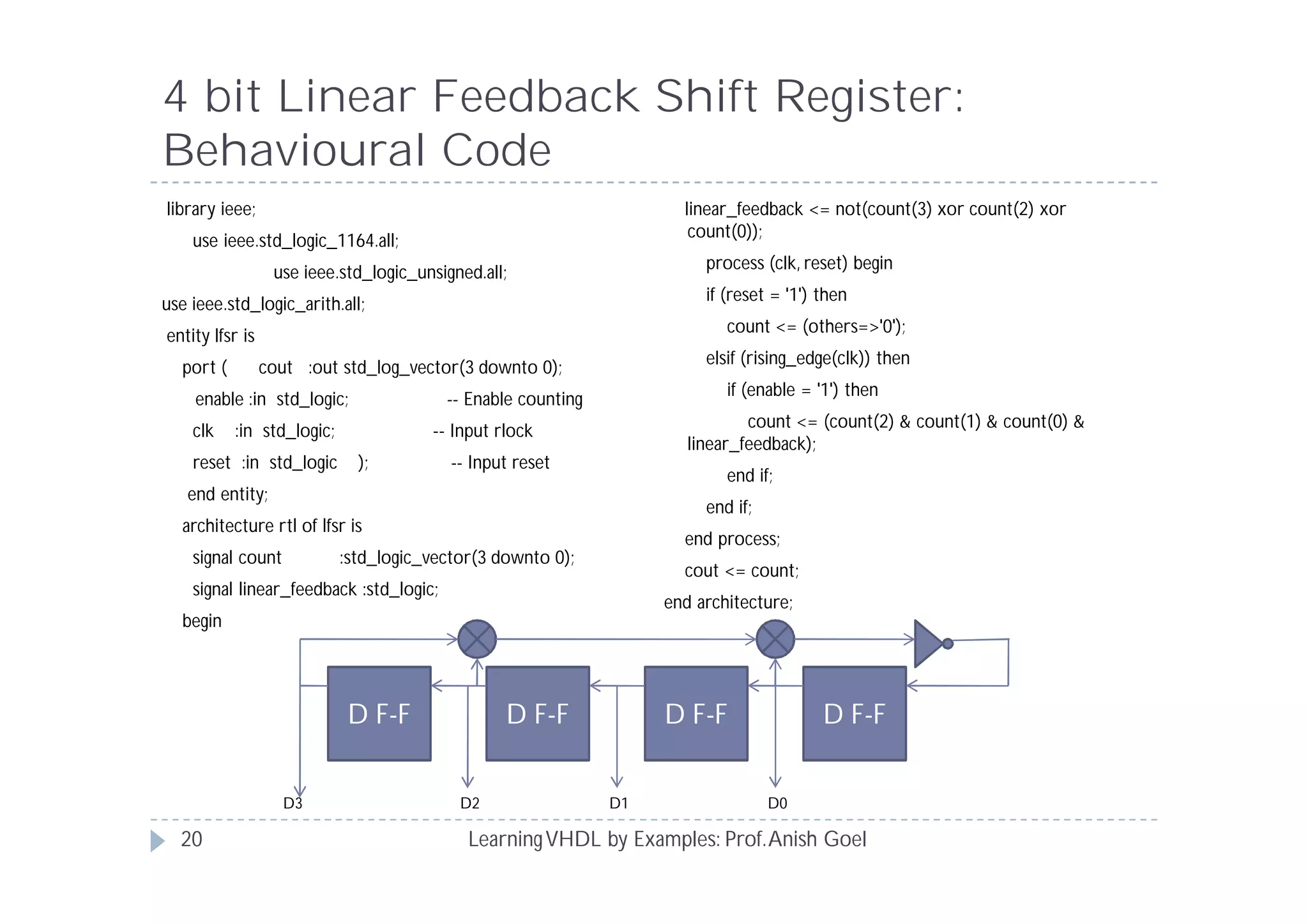
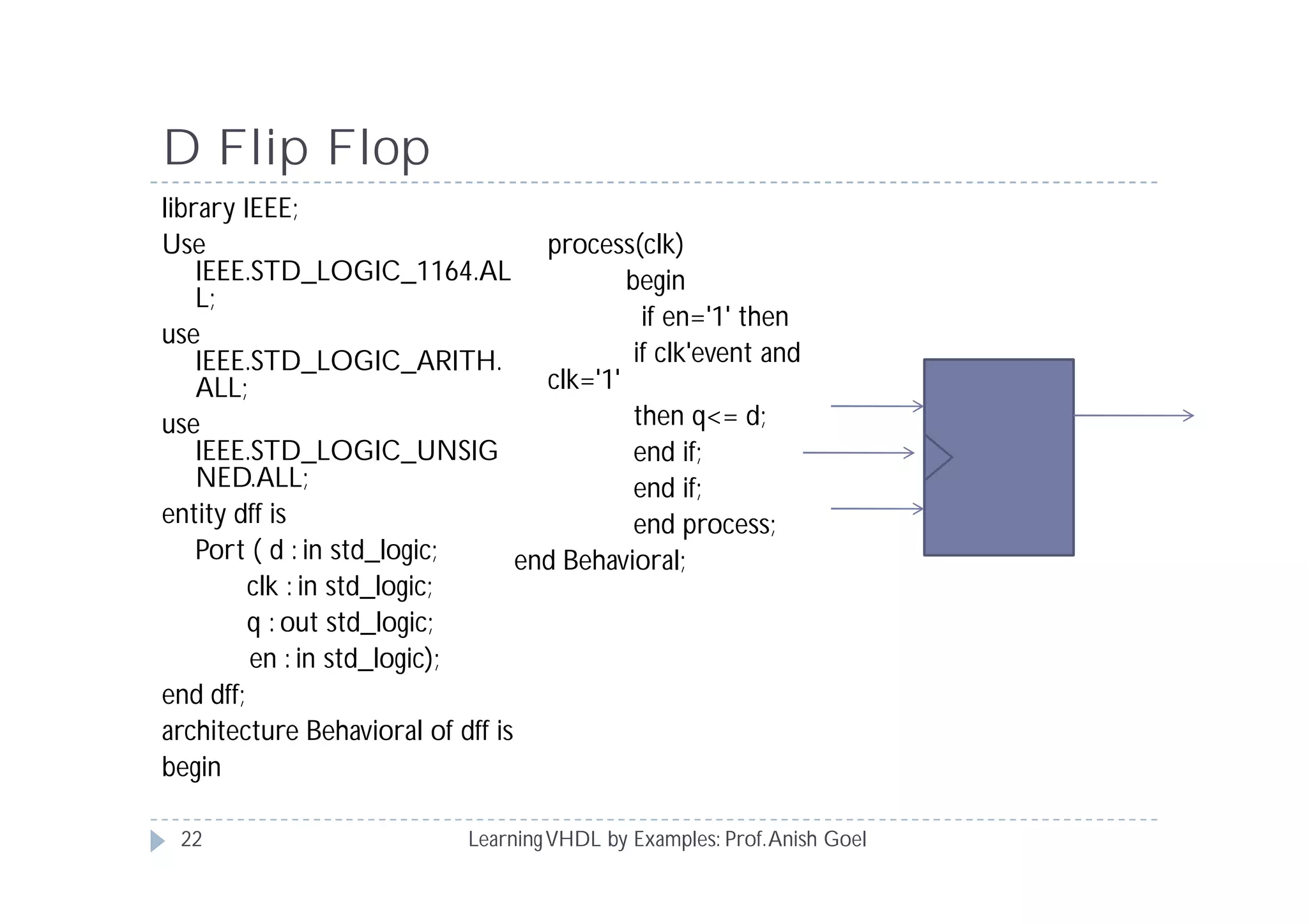
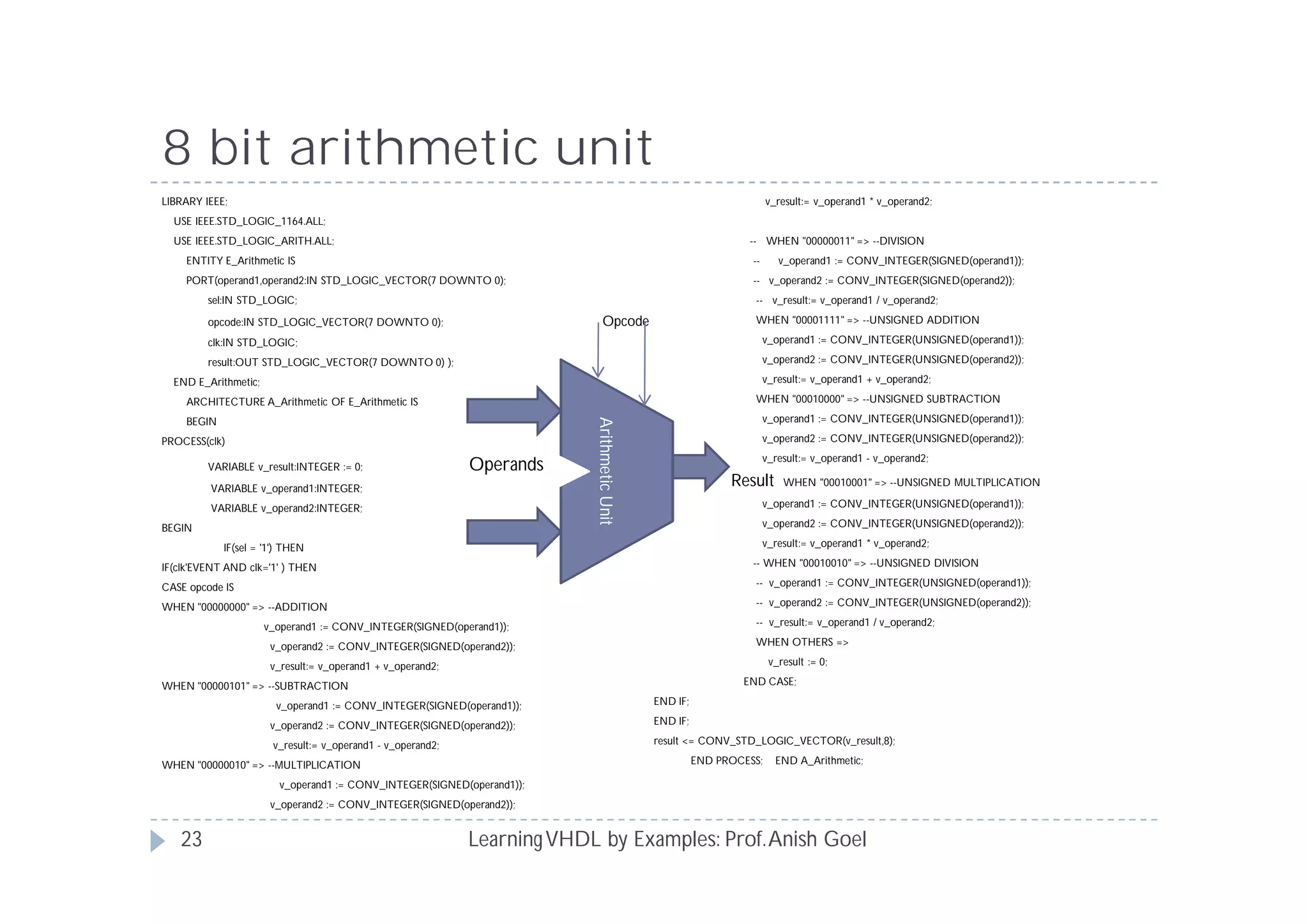
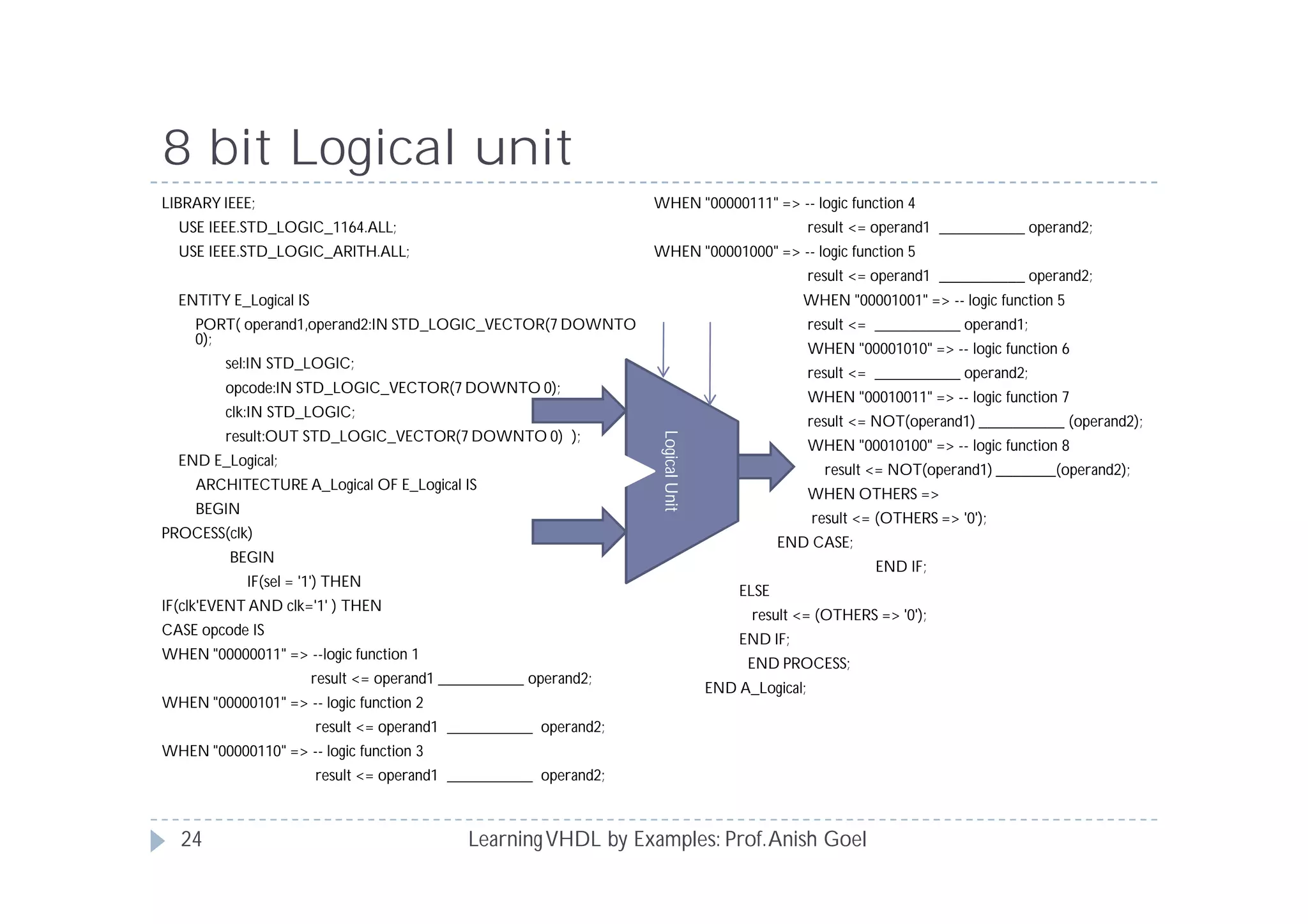
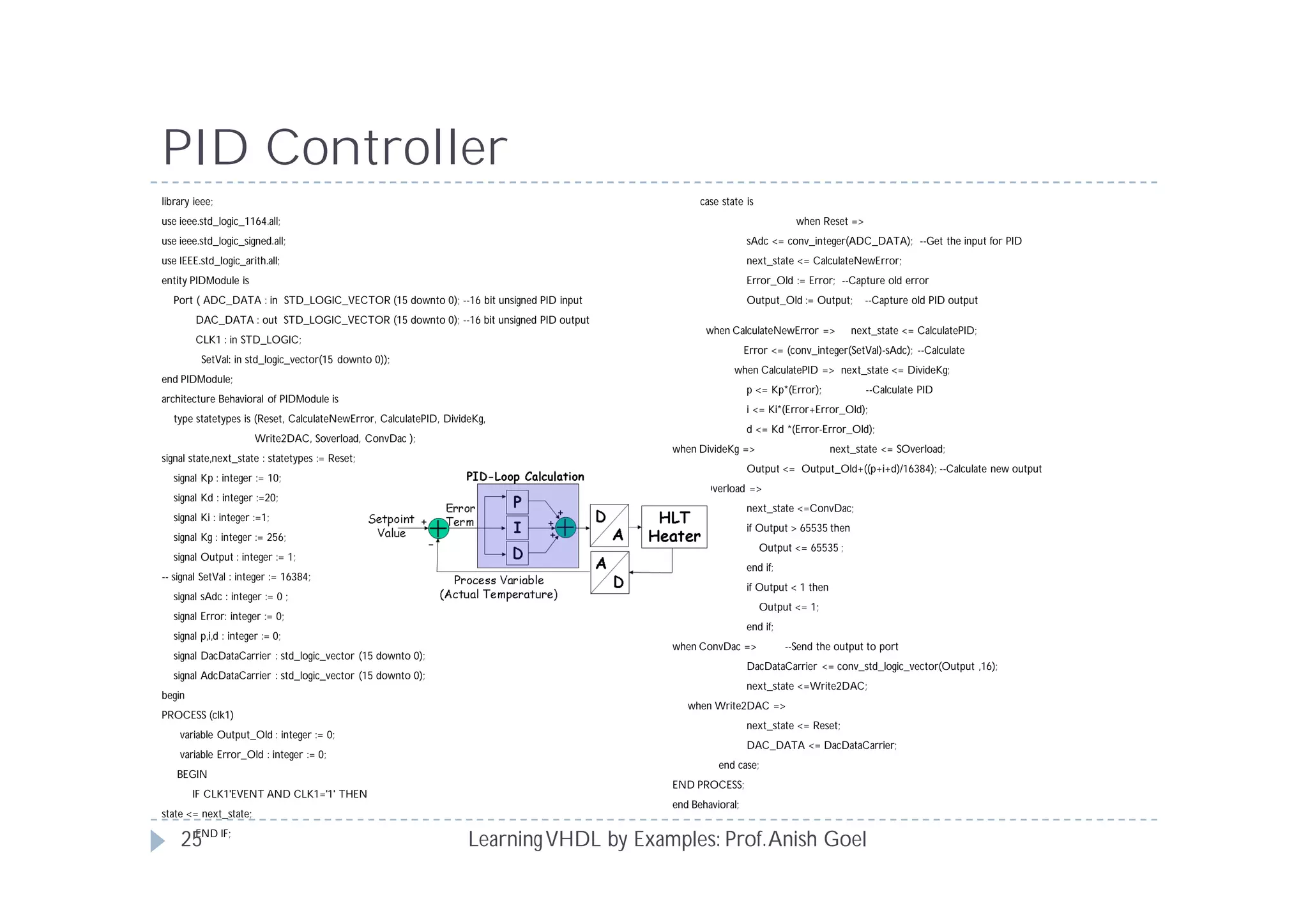
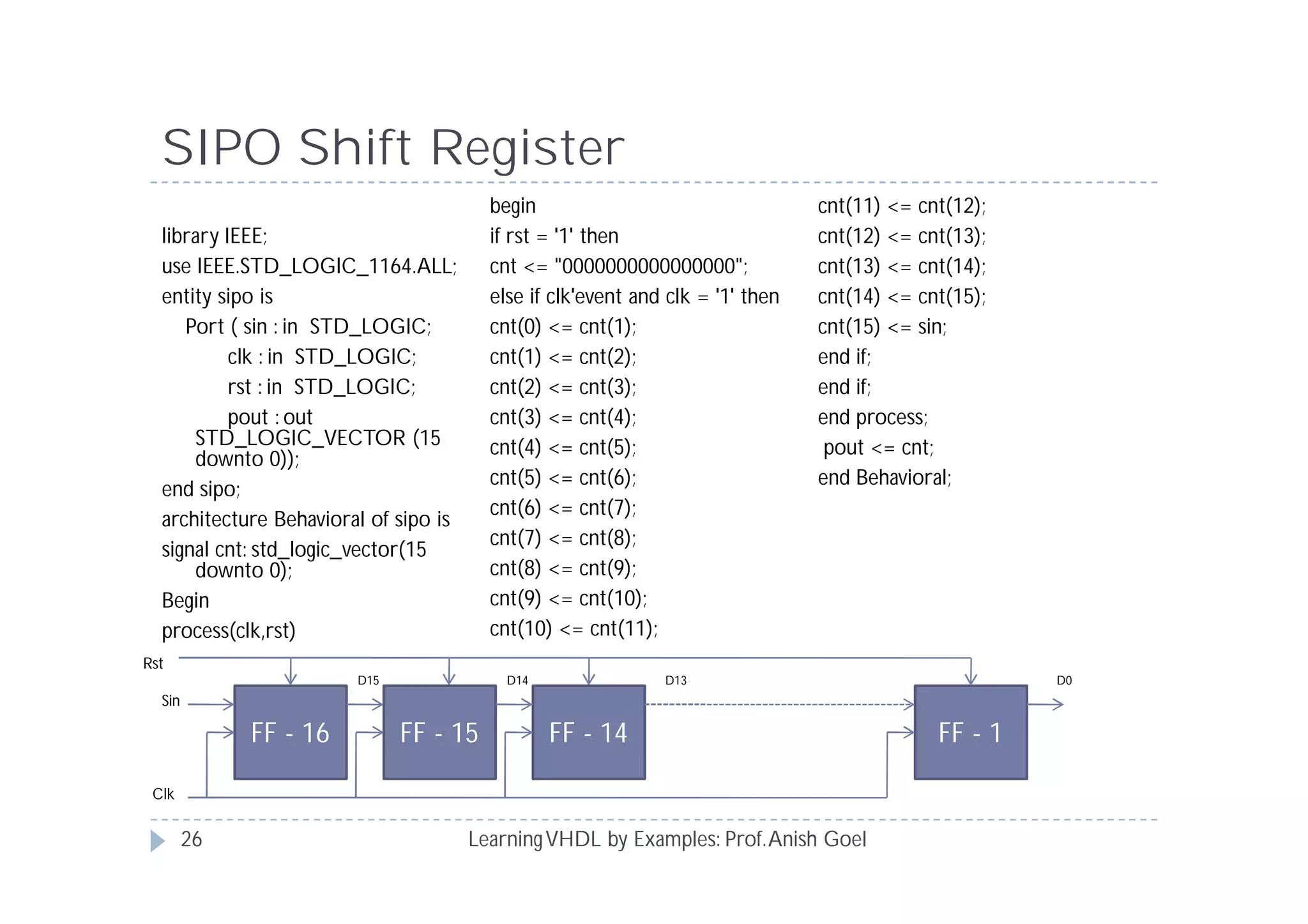
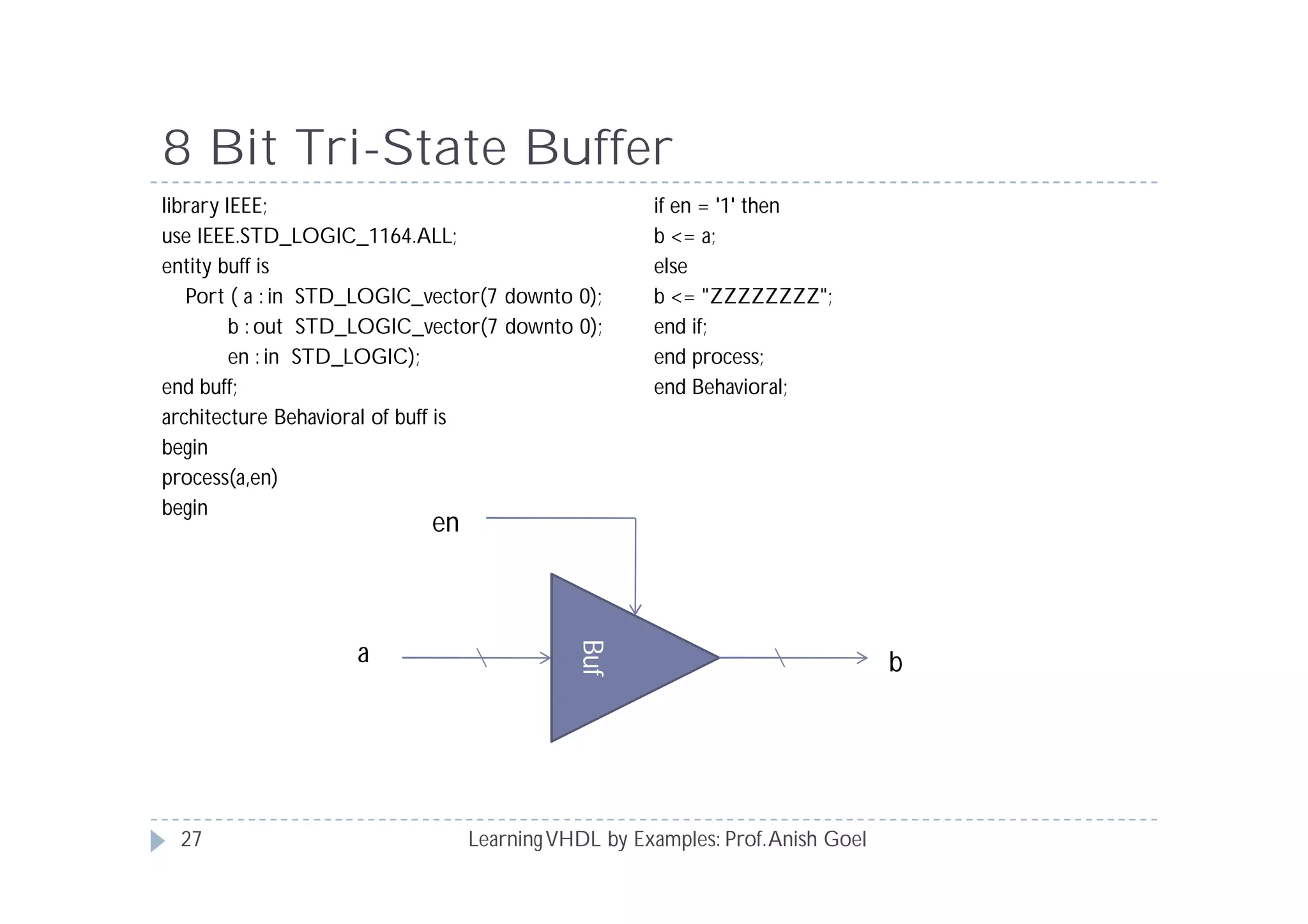
This document provides an overview of learning VHDL by examples. It discusses VHDL entity and architecture, styles of modeling including data flow, behavioral and structural, and conditional and concurrent assignment statements. Examples are provided to illustrate different modeling styles like a 2-4 decoder, full adder, 4-bit LFSR and 9-bit counter. Key concepts of VHDL like entity, ports, architecture, processes, concurrent statements and sequential statements are covered at a high level.